Basic Chemistry notes
... ______________________—two or more like atoms combined chemically ______________________—two or more different atoms combined chemically ...
... ______________________—two or more like atoms combined chemically ______________________—two or more different atoms combined chemically ...
PHY4604–Introduction to Quantum Mechanics Fall 2004 Practice
... for the proton motion. Changing mp → 2mp doesn’t change much, so to a good approximation the photon wavelength doesn’t change, λD ' λH . iii. positronium. In this case the positron is not heavier than the electron, but in fact has the same mass. The reduced mass of 2 identical particles of mass m is ...
... for the proton motion. Changing mp → 2mp doesn’t change much, so to a good approximation the photon wavelength doesn’t change, λD ' λH . iii. positronium. In this case the positron is not heavier than the electron, but in fact has the same mass. The reduced mass of 2 identical particles of mass m is ...
Exam and Study Notes
... o The Aufbau Principle (electrons start from the lowest energy) “The building up principle” The Aufbau Principle states that the to fill the 3d subshell, the 4s subshell must have 2 electrons in the subshell first o Pauli Exclusion Principle(Opposite spins) No two electron can have the same sp ...
... o The Aufbau Principle (electrons start from the lowest energy) “The building up principle” The Aufbau Principle states that the to fill the 3d subshell, the 4s subshell must have 2 electrons in the subshell first o Pauli Exclusion Principle(Opposite spins) No two electron can have the same sp ...
3.3 Why do atoms radiate light?
... • This explains too, why atoms can be stable, although they have a rotational momentum (in the classical description they would always radiate light and thus be destroyed). This classical explanation results from the wrong picture, that the electron is moving through the orbital, leading to a steady ...
... • This explains too, why atoms can be stable, although they have a rotational momentum (in the classical description they would always radiate light and thus be destroyed). This classical explanation results from the wrong picture, that the electron is moving through the orbital, leading to a steady ...
HW 8
... This print-out should have 5 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page – find all choices before answering. Mlib 02 0095 001 10.0 points Which of the following provided evidence that the electrons in atoms are arranged in distinct energy levels? 1. the results of t ...
... This print-out should have 5 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page – find all choices before answering. Mlib 02 0095 001 10.0 points Which of the following provided evidence that the electrons in atoms are arranged in distinct energy levels? 1. the results of t ...
WAVE MECHANICS AND QUANTUM NUMBERS
... 1. Louis de Broglie 1924- electrons are considered waves confined to the space around a nucleus. 2. supported by the facts that electrons undergo diffraction and interference 3. Werner Heisenberg 1927- Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle: it is impossible to simultaneously identify the position and vel ...
... 1. Louis de Broglie 1924- electrons are considered waves confined to the space around a nucleus. 2. supported by the facts that electrons undergo diffraction and interference 3. Werner Heisenberg 1927- Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle: it is impossible to simultaneously identify the position and vel ...
Atomic Emission Spectra and Quantum mechanical Model
... cars, baseball, marbles • In quantum mechanics, matter moves like waves and it ...
... cars, baseball, marbles • In quantum mechanics, matter moves like waves and it ...
Matter
... – Collection of the combination same type of atom elements and/or – Cannot be compounds or decomposed both. • Compound • USUALLY – 2 or more different heterogeneous atoms chemically bonded together. ...
... – Collection of the combination same type of atom elements and/or – Cannot be compounds or decomposed both. • Compound • USUALLY – 2 or more different heterogeneous atoms chemically bonded together. ...
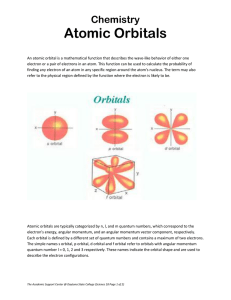
Atomic Orbitals - Daytona State College
... Atomic orbitals are typically categorized by n, l, and m quantum numbers, which correspond to the electron's energy, angular momentum, and an angular momentum vector component, respectively. Each orbital is defined by a different set of quantum numbers and contains a maximum of two electrons. The si ...
... Atomic orbitals are typically categorized by n, l, and m quantum numbers, which correspond to the electron's energy, angular momentum, and an angular momentum vector component, respectively. Each orbital is defined by a different set of quantum numbers and contains a maximum of two electrons. The si ...
vocab chap 6
... packed nucleus and that atoms are mostly empty space; also discovered the proton ...
... packed nucleus and that atoms are mostly empty space; also discovered the proton ...
e - Purdue Physics - Purdue University
... Atomic Structure The results of many experiments collectively suggest that all matter is made up of small, indivisible units which have a unique identity. Study of chemistry suggests a number of elementary substances (elements) that show unique chemical behavior. These elements are made up of ident ...
... Atomic Structure The results of many experiments collectively suggest that all matter is made up of small, indivisible units which have a unique identity. Study of chemistry suggests a number of elementary substances (elements) that show unique chemical behavior. These elements are made up of ident ...
Atomic structure ls on a periodic table.
... -metals, and noble gases are found on a periodic table. Specify how to predict the charge expected for the most stable ion of an atom. the line spectra of atomic species relate to the idea of quantized states of electrons in atoms. A Jablonksi diagram may be helpful in this discussion (so might unde ...
... -metals, and noble gases are found on a periodic table. Specify how to predict the charge expected for the most stable ion of an atom. the line spectra of atomic species relate to the idea of quantized states of electrons in atoms. A Jablonksi diagram may be helpful in this discussion (so might unde ...
1. Define each of the following terms: a.Alkaline earth metals
... m.Chemical property = a property that describes the behavior of a substance n.Physical property = a property that describes the appearance of a substance o.Electron = a negatively charged subatomic particle found in the orbits of an atom ...
... m.Chemical property = a property that describes the behavior of a substance n.Physical property = a property that describes the appearance of a substance o.Electron = a negatively charged subatomic particle found in the orbits of an atom ...
Problem Set 05
... c) An accelerating charge will lose energy due to radiation. Show that this will lead to a decrease in the electron orbital radius described by ...
... c) An accelerating charge will lose energy due to radiation. Show that this will lead to a decrease in the electron orbital radius described by ...