* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 06 Chapter 7 Notes
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Quantum teleportation wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Bell's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Copenhagen interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
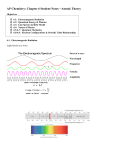
Unit 6 Chapter 7 Atomic Structure and Periodicity Section 1: Electromagnetic Radiation Define each of the following terms or answer each of the following questions prior to class. 1) Electromagnetic radiation2) Wavelength- 3) Frequency4) Why is electromagnetic radiation important? Equations: Identify each of the variables in the following equations. 1) λν = c c = speed of light 2.9979 x 108 m/s Homework: Section 2: The Nature of Matter 1) Particles2) Waves- 3) What did Max Planck discover? 4) Quantized – 5) What was Einstein’s proposal regarding electromagnetic radiation? 6) Does particulate matter exhibit wave properties? 7) Diffraction8) Diffraction pattern – Equations: Identify each of the variables in the following equations. 1) ∆E = nhν h = 6.626 x 10-34 J*s (n is an integer and v is frequency) 2 2) E = mc 3) m = h/( λυ) Homework: Section 3: The Atomic Spectrum of Hydrogen 1) What is the emission spectrum of hydrogen gas? 2) What is meant by excited atoms? 3) Is the hydrogen emission spectrum a continuous or line spectrum? Section 4: The Bohr Model 1) Describe the quantum model of the atom developed by Niels Bohr. 2) Ground State3) What is wrong with Bohr’s model? Equations: Identify each of the variables in the following equations. 1) E = -2.178 x 10-18 J (Z2/ n2) 2) ∆E = Efinal – Einitial a. When ∆E is negative, then energy is released. Homework: Section 5: The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom 1) Developed by: Heisenberg, de Broglie, and Schrodinger 2) Standing Wave: waves that are stationary, that do not gravel down the length of the string, similar to the electron’s motion around the nucleus a. There must be a of ½ wavelengths in any of the motions of the string 3) Orbital4) How does the electron moving around the nucleus? 5) Heisenberg uncertainty principle: 6) Probability distribution- 7) How do chemists define the size of an orbital? Section 6: Quantum Numbers 1) Principal Quantum Number- n – 2) Angular momentum quantum number – a. l = 0 is referred to as s b. l = 1 is referred to as p c. l = 2 is referred to as d d. l = 3 is referred to as f 3) Magnetic Quantum Number – ml – Homework: Section 7: Orbital Shapes and Energies 1) Nodes- a 2) Describe the shape of each of the following orbitals: 3) Energy levels of orbitals are determined by what? Study: Summary of hydrogen atom – pg Section 8: Electron Spin and the Pauli Principle 1) Why is it thought that electrons spin? 2) Electron spin quantum number- ms- 3) Pauli Exclusion PrincipleSection 9 Polyelectronic Atoms 1) Polyelectronic atom2) What are the 3 energy contributions that need to be considered in atoms? 3) Electron correlation problem: 4) How do we correct for the electron correlation problem? 5) Electron shielding or screening6) How do the orbitals for polyelectronic atoms compare to the orbitals of hydrogen? 7) Indicate how you can determine the energy of orbitals for polyelectronic atoms.