* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Quantum Notes
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Bremsstrahlung wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
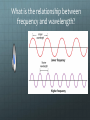
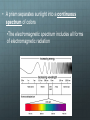
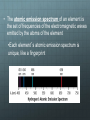
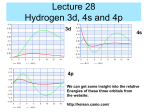
Quantum Theory Corresponds with your chapter 5 Limitations of the Early Models Early models don’t explain How the electrons were arranged around the nucleus Why negatively charged electrons are not pulled into the positively charged nucleus Why atoms of elements behave the way they do Light can act as waves or as particles. Wave Nature of Light The speed of light (c = 3.00 108 m/s) is the product of it’s wavelength (λ) and frequency (ν) c = λν What is the relationship between frequency and wavelength? • A prism separates sunlight into a continuous spectrum of colors •The electromagnetic spectrum includes all forms of electromagnetic radiation Particle Nature of Light • The wave model of light cannot explain all of light’s characteristics; Albert Einstein proposed in 1905 that light has a dual nature (wave-like and particle-like) • Matter can gain or lose energy only in small, specific amounts called quanta •A quantum is the minimum amount of energy that can be gained or lost by an atom • The atomic emission spectrum of an element is the set of frequencies of the electromagnetic waves emitted by the atoms of the element •Each element’s atomic emission spectrum is unique, like a fingerprint Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle • It is impossible to know the position and velocity/momentum of an electron at any time. • Because whatever you use to view it (light or radiation) would change the position or momentum Review Identify the parts of a wave: A A B C A D Review Compare the wave and particle models of light. Review Explain the difference between the continuous spectrum and the emission spectrum of an element. Finish spec 20 lab – make color observations! Physicists tend to view electrons as particles, hence the quantum theory which describes the behavior of subatomic particles. Does it take more energy for the painter to climb to the middle or to the top rung/stair? Suppose the painter climbed to the middle rung/stair and dropped the paintbrush. Then, she climbed to the top rung/stair and dropped the paintbrush. From which level did the paintbrush hit the ground with more energy? Ground vs. Excited Ground state is when the electrons are in the lowest energy levels. Electrons that have absorbed energy jump to higher levels and become excited. The ground represents the area of the nucleus and energy increases as you go up. Which seats in the arena are in more demand and more expensive? How does the seating arrangement represent energy levels? n = venue l = section ml = row ms = seat No two people can have the exact same ticket for the exact same seat! Take notes on the four quantum numbers: Principle Angular Magnetic Spin https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/electronic-structure-of-atoms/orbitalsand-electrons/v/quantum-numbers Make a table: n orbitals # e- in orbital #e- in shell https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/electronic-structure-ofatoms/orbitals-and-electrons/v/quantum-numbers-for-the-first-four-shells Review What does the principal quantum number indicate? What is the maximum number of p orbitals in a principal energy level? Another analogy In addition to the spectra, compounds can be identified when they are heated in a flame.