5.1 Worksheet File
... Electron Configurations An electron configuration describes the arrangement of electrons in an atom. The aufbau principle says that electrons occupy the orbitals of lowest energy first. According to the Pauli exclusion principle, each orbital can contain at most two electrons. The two electrons must ...
... Electron Configurations An electron configuration describes the arrangement of electrons in an atom. The aufbau principle says that electrons occupy the orbitals of lowest energy first. According to the Pauli exclusion principle, each orbital can contain at most two electrons. The two electrons must ...
Chapter 6 Outline full
... • It cannot explain the spectra of atoms other than hydrogen. • Electrons do not move about the nucleus in circular orbits. ...
... • It cannot explain the spectra of atoms other than hydrogen. • Electrons do not move about the nucleus in circular orbits. ...
Class 27: The Bohr model for the atom
... At the time of Rydberg’s discovery, there was no physical explanation for his formula. ...
... At the time of Rydberg’s discovery, there was no physical explanation for his formula. ...
Spin Quantum Number - stpats-sch3u-sem1-2013
... Electrons are found in atomic orbitals, or atomic space, surrounding the nucleus of an atom. For a neutral atom, the number of electrons in the element is equal to the atomic number. For example, nitrogen’s atomic number is 7 and so, an atom of nitrogen has 7 electrons. However, these 7 electrons do ...
... Electrons are found in atomic orbitals, or atomic space, surrounding the nucleus of an atom. For a neutral atom, the number of electrons in the element is equal to the atomic number. For example, nitrogen’s atomic number is 7 and so, an atom of nitrogen has 7 electrons. However, these 7 electrons do ...
File - Ingolstadt Academy
... Dimensional analysis Instruments that measure mass, volume, pressure, etc. (lab stuff!) The Scientific Method Atomic Structure: ...
... Dimensional analysis Instruments that measure mass, volume, pressure, etc. (lab stuff!) The Scientific Method Atomic Structure: ...
Chapter 7 Lect. 2
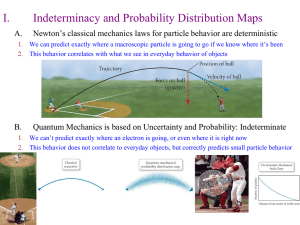
... 1. We can’t predict exactly where an electron is going, or even where it is right now 2. This behavior does not correlate to everyday objects, but correctly predicts small particle behavior ...
... 1. We can’t predict exactly where an electron is going, or even where it is right now 2. This behavior does not correlate to everyday objects, but correctly predicts small particle behavior ...
Chemistry-Chapter 2 Lecture Notes Page
... positive H and two other atoms (slightly negative O or N) - Easily broken by Temp or pH - Found in: H2O, Proteins, Nucleic Acids ...
... positive H and two other atoms (slightly negative O or N) - Easily broken by Temp or pH - Found in: H2O, Proteins, Nucleic Acids ...
Electron Configuration Notes
... • electrons move around nucleus in orbits similar to how planets orbit the sun • energy levels for electrons are quantized Major developments that put Bohr’s Model into question: Einstein: Light energy exhibits properties of matter. Matter and energy are different forms of the same thing. De Broglie ...
... • electrons move around nucleus in orbits similar to how planets orbit the sun • energy levels for electrons are quantized Major developments that put Bohr’s Model into question: Einstein: Light energy exhibits properties of matter. Matter and energy are different forms of the same thing. De Broglie ...
The Quantum mechanical model of the atom
... Therefore, there are 2 possible orbital shapes (sublevels), l=0 (s) and l=1 (p). The s-orbital only has electrons in 1 orientation so ml=0 but the p orbitals have electrons in 3 different orientations so ml=-1, 0, 1. Each electron can spin in either direction around its axis so the possible ms ...
... Therefore, there are 2 possible orbital shapes (sublevels), l=0 (s) and l=1 (p). The s-orbital only has electrons in 1 orientation so ml=0 but the p orbitals have electrons in 3 different orientations so ml=-1, 0, 1. Each electron can spin in either direction around its axis so the possible ms ...
Chapter 5 PPT/Notes B
... • If single objects approach a double slit, they pass through and slowly build up, one by one, the double slit pattern. Shut one slit off and they, one by one, create the single slit diffraction pattern. Question: How do single "objects" "know" of the existence of two slits? "Clearly" they only pass ...
... • If single objects approach a double slit, they pass through and slowly build up, one by one, the double slit pattern. Shut one slit off and they, one by one, create the single slit diffraction pattern. Question: How do single "objects" "know" of the existence of two slits? "Clearly" they only pass ...
Electron Configuration
... 1. In the 1900s scientists observed that certain elements emitted visible light when heated in a flame. The analysis of that flame revealed that the chemical behavior is related to the arrangement of the electrons in its atom. 2. Scientists also observed that light behave somehow like the electrons. ...
... 1. In the 1900s scientists observed that certain elements emitted visible light when heated in a flame. The analysis of that flame revealed that the chemical behavior is related to the arrangement of the electrons in its atom. 2. Scientists also observed that light behave somehow like the electrons. ...
electron cloud - Wickliffe City School
... If an electron is given enough energy to overcome the forces holding it in the cloud, it can leave the atom completely. The atom has been “ionized” or charged. The number of protons and electrons is no longer equal. The energy required to remove an electron from an atom is ionization energy. (measur ...
... If an electron is given enough energy to overcome the forces holding it in the cloud, it can leave the atom completely. The atom has been “ionized” or charged. The number of protons and electrons is no longer equal. The energy required to remove an electron from an atom is ionization energy. (measur ...
Atomic Physics - Moodle-Arquivo
... Positive charge is concentrated in the center of the atom, called the nucleus Electrons orbit the nucleus like planets orbit the sun ...
... Positive charge is concentrated in the center of the atom, called the nucleus Electrons orbit the nucleus like planets orbit the sun ...
Chemistry CPA Activity Sheet Week of November 18, 2013 Unit
... It is your responsibility to check the homework board and teacher’s website for changes to the activity sheet. NJCCCS Science: 5.1.12.A-D, 5.2.12.A.5, 5.2.12.D. ...
... It is your responsibility to check the homework board and teacher’s website for changes to the activity sheet. NJCCCS Science: 5.1.12.A-D, 5.2.12.A.5, 5.2.12.D. ...
Name - Net Start Class
... 29. If one variable increases while the other variable decreases, what type of relationship is it? Sketch a graph of this relationship. An inversely proportional relationship ...
... 29. If one variable increases while the other variable decreases, what type of relationship is it? Sketch a graph of this relationship. An inversely proportional relationship ...
Laboratory Exercise: The Electronic Structure of the Hydrogen Atom
... Electromagnetic Spectrum of photon wavelengths is represented below: ...
... Electromagnetic Spectrum of photon wavelengths is represented below: ...
Final “Intro Quantum Mechanics”
... (a) (T) One needs quantum mechanics to explain the spectrum of blackbody radiation, as classical physics gives the wrong answer. This was the effect that prompted Planck to introduce his constant. (b) (T) One needs quantum mechanics to explain the structure of atoms, as classical physics gives the w ...
... (a) (T) One needs quantum mechanics to explain the spectrum of blackbody radiation, as classical physics gives the wrong answer. This was the effect that prompted Planck to introduce his constant. (b) (T) One needs quantum mechanics to explain the structure of atoms, as classical physics gives the w ...