CHEM 1411 NAME: PRACTICE EXAM #3 (Chapters 6
... Sodium and potassium have similar chemical and physical properties. This is best explained by the fact that both elements A) are active metals. B) are in Period 1 of the periodic table. C) have the same ground-state valence-electron configuration. D) have low relative atomic masses. E) have relative ...
... Sodium and potassium have similar chemical and physical properties. This is best explained by the fact that both elements A) are active metals. B) are in Period 1 of the periodic table. C) have the same ground-state valence-electron configuration. D) have low relative atomic masses. E) have relative ...
No Slide Title - Rubin Gulaboski
... Orbitals and Quantum Numbers • Orbitals can be ranked in terms of energy to yield an Aufbau diagram. • As n increases, note that the spacing between energy levels becomes smaller. • Orbitals of the same energy are said to be degenerate. ...
... Orbitals and Quantum Numbers • Orbitals can be ranked in terms of energy to yield an Aufbau diagram. • As n increases, note that the spacing between energy levels becomes smaller. • Orbitals of the same energy are said to be degenerate. ...
chapters 1-4
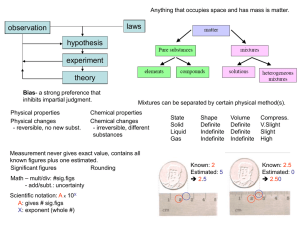
... ~100 elements, millions of compounds H and He most abundant in space, O and Si in earth crust, O and C in human bodies. Atom – smallest building block; molecule – combination of two or more atoms. Can be an element or compound. ...
... ~100 elements, millions of compounds H and He most abundant in space, O and Si in earth crust, O and C in human bodies. Atom – smallest building block; molecule – combination of two or more atoms. Can be an element or compound. ...
The Chemical Basis of Life
... Have a central nucleus Protons (+) Neutrons (0) Orbitals on the outside that hold Electrons (-) ...
... Have a central nucleus Protons (+) Neutrons (0) Orbitals on the outside that hold Electrons (-) ...
5. Quantum mechanics of chemical binding
... Why one decreases, the other increases? Look at an other representation of the orbitals (along the bond) ...
... Why one decreases, the other increases? Look at an other representation of the orbitals (along the bond) ...
test2 contoh(30sept 2010) Word document - e
... Answer all questions in the space provided. 1. What happen to the atomic radius as we go down the group from top to bottom and across the period from left to right. Give a brief explanation for the trend that you have described. ...
... Answer all questions in the space provided. 1. What happen to the atomic radius as we go down the group from top to bottom and across the period from left to right. Give a brief explanation for the trend that you have described. ...
cell molecules
... Matter consists of chemical elements in pure form and in combinations called compounds • Organisms are composed of matter. • Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions. • There are 92 naturall ...
... Matter consists of chemical elements in pure form and in combinations called compounds • Organisms are composed of matter. • Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions. • There are 92 naturall ...
Column A
... a. Calcium and Chlorine- CaCl2 b. Magnesium and oxygen- MgO c. Magnesium and phosphorus- Mg3P2 G) Write the formulas for the following compounds. ...
... a. Calcium and Chlorine- CaCl2 b. Magnesium and oxygen- MgO c. Magnesium and phosphorus- Mg3P2 G) Write the formulas for the following compounds. ...
CHEM 11 Practice Exam 2
... 8) Which of the following is a general trend from left to right in the periodic table of elements? A) atomic radius increases; ionization energy increases B) atomic radius increases; ionization energy decreases C) atomic radius decreases; ionization energy increases D) atomic radius decreases; ioni ...
... 8) Which of the following is a general trend from left to right in the periodic table of elements? A) atomic radius increases; ionization energy increases B) atomic radius increases; ionization energy decreases C) atomic radius decreases; ionization energy increases D) atomic radius decreases; ioni ...
Mid Term Examination 2 Text
... electron in the 2s wavefunction by analyzing the information in its quantum numbers only. b) (5 Points): Determine the number and the position of the radial nodes of the 2s wavefunction as deduced from Eq. 1.3. Then, sketch a 3-D plot of the wavefunction 2s Note: “Sketch” means a plot qualitativel ...
... electron in the 2s wavefunction by analyzing the information in its quantum numbers only. b) (5 Points): Determine the number and the position of the radial nodes of the 2s wavefunction as deduced from Eq. 1.3. Then, sketch a 3-D plot of the wavefunction 2s Note: “Sketch” means a plot qualitativel ...
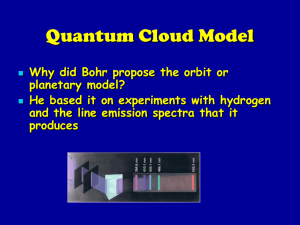
Quantum Cloud Model
... The original location of the electron is referred to as the Ground State The higher level is called the Excited State When the electron returns to the ground state it gives off energy equal to the difference between the two levels (excited and ground state) as electromagnetic radiation with its spec ...
... The original location of the electron is referred to as the Ground State The higher level is called the Excited State When the electron returns to the ground state it gives off energy equal to the difference between the two levels (excited and ground state) as electromagnetic radiation with its spec ...
1 The Photoelectric Effect 2 Line Spectra and Energy Levels
... Rutherford scattering : alpha particles projected onto atoms and the resulting deflection. scintillation: momentary flash caused by a particle being absorbed and re-emitted by certain materials. Geiger counter : a device commonly used to detect radiation. nucleus: positively charged, dense core of t ...
... Rutherford scattering : alpha particles projected onto atoms and the resulting deflection. scintillation: momentary flash caused by a particle being absorbed and re-emitted by certain materials. Geiger counter : a device commonly used to detect radiation. nucleus: positively charged, dense core of t ...
Chapter 28 notes
... Rutherford scattering : alpha particles projected onto atoms and the resulting deflection. scintillation: momentary flash caused by a particle being absorbed and re-emitted by certain materials. Geiger counter : a device commonly used to detect radiation. nucleus: positively charged, dense core of t ...
... Rutherford scattering : alpha particles projected onto atoms and the resulting deflection. scintillation: momentary flash caused by a particle being absorbed and re-emitted by certain materials. Geiger counter : a device commonly used to detect radiation. nucleus: positively charged, dense core of t ...
Chapter Summary
... referred to as “spin up” and “spin down.” The spin angular momentum is characterized by the spin quantum number, which can take on values of +1/2 or –1/2. Understanding the periodic table of elements One key to understanding the periodic table is the Pauli exclusion principle – no two electrons in a ...
... referred to as “spin up” and “spin down.” The spin angular momentum is characterized by the spin quantum number, which can take on values of +1/2 or –1/2. Understanding the periodic table of elements One key to understanding the periodic table is the Pauli exclusion principle – no two electrons in a ...
Lamb
... The very existence of atoms, (Bohr, 1913), requires the finiteness of Planck's constant to be taken into account for the behavior of the atomic electrons. However, once granted the existence of atoms, we shall see that all of the experimental photoelectric phenomena are described by a theory in whic ...
... The very existence of atoms, (Bohr, 1913), requires the finiteness of Planck's constant to be taken into account for the behavior of the atomic electrons. However, once granted the existence of atoms, we shall see that all of the experimental photoelectric phenomena are described by a theory in whic ...
Atomic and Molecular Physics for Physicists Ben-Gurion University of the Negev
... 1. Why do the helicities change upon reflection (this enables the atomchip setup)? 2. Until now we saw that all sigma (circular polatization) signs and/or helicities are the same for counter propagating beams in the MOT. Why is the above picture (also explaining a Mirror MOT) different? Hint: the en ...
... 1. Why do the helicities change upon reflection (this enables the atomchip setup)? 2. Until now we saw that all sigma (circular polatization) signs and/or helicities are the same for counter propagating beams in the MOT. Why is the above picture (also explaining a Mirror MOT) different? Hint: the en ...
visible Ultra violet Infra red Longer line ? Energy? Wavelength
... We cannot see individual molecules using visible radia2on Wavelength of visible light is much larger than the molecule Reduce wavelength and increase resolu2on Frequency increases ...
... We cannot see individual molecules using visible radia2on Wavelength of visible light is much larger than the molecule Reduce wavelength and increase resolu2on Frequency increases ...
Name
... Electron Configurations An electron configuration describes the arrangement of electrons in an atom. The aufbau principle says that electrons occupy the orbitals of lowest energy first. According to the Pauli exclusion principle, each orbital can contain at most two electrons. The two electrons must ...
... Electron Configurations An electron configuration describes the arrangement of electrons in an atom. The aufbau principle says that electrons occupy the orbitals of lowest energy first. According to the Pauli exclusion principle, each orbital can contain at most two electrons. The two electrons must ...