effective nuclear charge
... ◦ in general, the increase in mass is greater than the increase in volume ...
... ◦ in general, the increase in mass is greater than the increase in volume ...
lecture30
... We need accelerators because: •As the momentum of a particle increases, its wavelength decreases (λ = h/p), providing details of smaller and smaller structures •If an incoming particle in a nuclear reaction has enough energy, new particles ...
... We need accelerators because: •As the momentum of a particle increases, its wavelength decreases (λ = h/p), providing details of smaller and smaller structures •If an incoming particle in a nuclear reaction has enough energy, new particles ...
General Chemistry First Semester Review General
... What should you expect to be on the chemistry final? The chemistry final is a cumulative exam testing you on topics from each of the units given during 1st semester. It will be somewhat longer than a regular unit exam. However, each student should have more than enough time to finish it during the a ...
... What should you expect to be on the chemistry final? The chemistry final is a cumulative exam testing you on topics from each of the units given during 1st semester. It will be somewhat longer than a regular unit exam. However, each student should have more than enough time to finish it during the a ...
ELECTROMAGNETIC EMISSION OF ATOMIC ELECTRONS
... INTERNAL bremsstrahlung in {3 decay and K capture was first considered by Knipp and Uhlenbeck[1J. Later Glauber and Martin developed a more consistent theory of radiative capture of orbital electrons [ 2• 3]; Lewis and Ford [ 4] took account of the contribution from the ''virtual intermediate state" ...
... INTERNAL bremsstrahlung in {3 decay and K capture was first considered by Knipp and Uhlenbeck[1J. Later Glauber and Martin developed a more consistent theory of radiative capture of orbital electrons [ 2• 3]; Lewis and Ford [ 4] took account of the contribution from the ''virtual intermediate state" ...
Two valence electrons.
... elements by increasing atomic mass, leaving blank spaces where he was sure elements Dmitri yet to be discovered Mendeleev would fit. ...
... elements by increasing atomic mass, leaving blank spaces where he was sure elements Dmitri yet to be discovered Mendeleev would fit. ...
powerpoint on Bohr/Quantum File
... Werner Heisenberg (Uncertainty Principle) Louis de Broglie (electron has wave properties) Erwin Schrodinger (mathematical equations using probability, quantum numbers) ...
... Werner Heisenberg (Uncertainty Principle) Louis de Broglie (electron has wave properties) Erwin Schrodinger (mathematical equations using probability, quantum numbers) ...
ATOMIC PHYSICS: Things You Should Remember Here are the
... • By analogy with spin-orbit interaction, the energy level of the entire atom is now described using by I, J, F and MF where F = I + J is the total angular momentum of the entire atom. The energy levels of given I and J are split according to the different values of F . (Vector addition gives |I − J ...
... • By analogy with spin-orbit interaction, the energy level of the entire atom is now described using by I, J, F and MF where F = I + J is the total angular momentum of the entire atom. The energy levels of given I and J are split according to the different values of F . (Vector addition gives |I − J ...
Nov 18
... occupied in an atom, and how many electrons they contain Ground state: lowest energy, most stable state for an atom - has all electrons in the lowest energy possible orbitals The energy of an electron in an H atom depends only on the principal quantum number, n, so in its ground state, the electron ...
... occupied in an atom, and how many electrons they contain Ground state: lowest energy, most stable state for an atom - has all electrons in the lowest energy possible orbitals The energy of an electron in an H atom depends only on the principal quantum number, n, so in its ground state, the electron ...
Rutherford Model 1911 - University of St Andrews
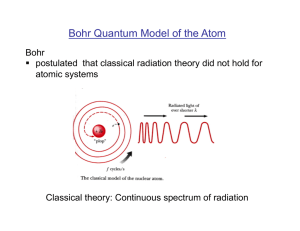
... (I) If electrons are stationary, there is nothing to prevent them from responding to the Coulomb force of attraction and being sucked into the nucleus. But the atomic diameter would then be ~ nuclear diameter. ...
... (I) If electrons are stationary, there is nothing to prevent them from responding to the Coulomb force of attraction and being sucked into the nucleus. But the atomic diameter would then be ~ nuclear diameter. ...
final exam practice test - Clayton State University
... 14. After interpreting the results of his oil drop experiment in 1909, Mullikan was able to determine____________________. a.) b.) c.) d.) e.) ...
... 14. After interpreting the results of his oil drop experiment in 1909, Mullikan was able to determine____________________. a.) b.) c.) d.) e.) ...
Exercises - Galena Park ISD
... 33. Explain why an electron in a low-energy orbit does not spiral into the nucleus. The possible energy levels for the electron are quantized. To spiral into the nucleus, the electron would have to pass through energy states that are less than that of its lowest energy orbit. Such orbits cannot exis ...
... 33. Explain why an electron in a low-energy orbit does not spiral into the nucleus. The possible energy levels for the electron are quantized. To spiral into the nucleus, the electron would have to pass through energy states that are less than that of its lowest energy orbit. Such orbits cannot exis ...
What is Light?
... • Electrons in atoms cannot lose/gain energy continuously (Planck/Einstein) but do so in “jumps” • Light emitted when e- jumps from higher to lower state • Eu – El = hf • Problem: Orbiting electrons do not emit EM waves (energy) • Normally charged particles do when accelerated (changing E field) ...
... • Electrons in atoms cannot lose/gain energy continuously (Planck/Einstein) but do so in “jumps” • Light emitted when e- jumps from higher to lower state • Eu – El = hf • Problem: Orbiting electrons do not emit EM waves (energy) • Normally charged particles do when accelerated (changing E field) ...
Quantum Lecture _08
... the nucleus of an atom exhibited wave behavior, acting at certain frequencies around the nucleus Further experiments proved more wavelike behavior such as a stream of electrons can be bent (diffracted), or that two electron beams can interfere with each other, just like water waves. ...
... the nucleus of an atom exhibited wave behavior, acting at certain frequencies around the nucleus Further experiments proved more wavelike behavior such as a stream of electrons can be bent (diffracted), or that two electron beams can interfere with each other, just like water waves. ...
Atomic Theory electron charge: -1.6 X 10-19C
... Still, scientists did not have a clear idea of what the atom looked like. The English researcher, Ernest Rutherford, provided clearer focus when he bombarded a thin sheet of gold foil with alpha rays (beams of helium nuclei). If atoms were uniformly dense, as he expected, all of the rays would have ...
... Still, scientists did not have a clear idea of what the atom looked like. The English researcher, Ernest Rutherford, provided clearer focus when he bombarded a thin sheet of gold foil with alpha rays (beams of helium nuclei). If atoms were uniformly dense, as he expected, all of the rays would have ...
Chapter 5 reveiw
... 14. Any orbital, no matter what sublevel (s, p, d, f) it is in, can hold up to 2 electrons. 15. The maximum no. of electrons in a sublevel is (s=2, p = 6, d = 10, f= 14) 16. The number of orbitals in each sublevel is s = 1, p = 3, d = 5, f = 7 a. The maximum number of electrons in the each principal ...
... 14. Any orbital, no matter what sublevel (s, p, d, f) it is in, can hold up to 2 electrons. 15. The maximum no. of electrons in a sublevel is (s=2, p = 6, d = 10, f= 14) 16. The number of orbitals in each sublevel is s = 1, p = 3, d = 5, f = 7 a. The maximum number of electrons in the each principal ...
Packet
... 102. What is the minimum amount of uranium called? 103. What is the spontaneous emission of nuclear radiation? 104. Where are protons located? 105. What is the charge of a beta particle? 106. What is a positively charged electron? 107. The measure of which a radioactive substance loses half of its r ...
... 102. What is the minimum amount of uranium called? 103. What is the spontaneous emission of nuclear radiation? 104. Where are protons located? 105. What is the charge of a beta particle? 106. What is a positively charged electron? 107. The measure of which a radioactive substance loses half of its r ...