* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atomic Physics - Moodle-Arquivo
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
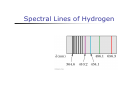
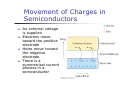
Atomic Physics Maria Luisa de Carvalho Departamento Física Universidade de Lisboa Importance of Hydrogen Atom Hydrogen is the simplest atom Nº Atómico e Nº de Massa This enables us to understand the periodic table Importance of Hydrogen Atom Hydrogen is the simplest atom Modelo do Átomo Rutherford, 1911 Modelo do Sistema planetário Positive charge is concentrated in the center of the atom, called the nucleus Electrons orbit the nucleus like planets orbit the sun Bohr’s Assumptions, cont Only certain electron orbits are stable Radiation is emitted by the atom when the electron “jumps” from a more energetic initial state to a lower state Bohr’s Assumptions, final Na transição do electrão: A energia é dada por Ei – Ef = h ƒ Specific Energy Levels, cont The ionization energy is the energy needed to completely remove the electron from the atom Atomic Transitions – Energy Levels An atom may have many possible energy levels At ordinary temperatures, most of the atoms in a sample are in the ground state Só fotões com energia igual à diferença de energia entre dois níveis podem ser absorvidos Energy Level Diagram Espectros de Emissão A gas at low pressure has a voltage applied to it A gas emits light characteristic of the gas When the emitted light is analyzed with a spectrometer, a series of discrete bright lines is observed Each line has a different wavelength and color This series of lines is called an emission spectrum Examples of Emission Spectra Spectral Lines of Hydrogen More Reasons the Hydrogen Atom is so Important The hydrogen atom Comportamento de metal alcalino e de gás (halogéneo) 1 1H; 2 1H; 3 1H He+ and Li2+ Absorption Spectra An element can also absorb light at specific wavelengths An absorption spectrum can be obtained by passing a continuous radiation spectrum through a vapor of the gas Energy Bands in Solids In solids, the discrete energy levels of isolated atoms broaden into allowed energy bands separated by forbidden gaps The separation and the electron population of the highest bands determine whether the solid is a conductor, an insulator, or a semiconductor Energy Bands, Detail Sodium example Blue represents energy bands occupied by the sodium electrons when the atoms are in their ground states Gold represents energy bands that are empty White represents energy gaps Electrons can have any energy within the allowed bands Electrons cannot have energies in the gaps Energy Level Definitions The valence band is the highest filled band The conduction band is the next higher empty band The energy gap has an energy, Eg, equal to the difference in energy between the top of the valence band and the bottom of the conduction band Conductors When a voltage is applied to a conductor, the electrons accelerate and gain energy In quantum terms, electron energies increase if there are a high number of unoccupied energy levels for the electron to jump to For example, it takes very little energy for electrons to jump from the partially filled to one of the nearby empty states Insulators The valence band is completely full of electrons A large band gap separates the valence and conduction bands A large amount of energy is needed for an electron to be able to jump from the valence to the conduction band The minimum required energy is Eg Semiconductors A semiconductor has a small energy gap Thermally excited electrons have enough energy to cross the band gap The resistivity of semiconductors decreases with increases in temperature The white area in the valence band represents holes Movement of Charges in Semiconductors An external voltage is supplied Electrons move toward the positive electrode Holes move toward the negative electrode There is a symmetrical current process in a semiconductor Interacção da radiação com a matéria Absorção da Radiação Se uma radiação de intensidade inicial I0 atravessa um material de espessura x a radiação é absorvida e a intensidade final será I I = Io e-µx Io x I Um dos processos principais de absorção da radiação é o efeito Fotoeléctrico. A intensidade inicial e final da radição são dadas pela relação 1, em que: µ é o coeficiente linear de absorção característico de uma dada substância