Chem 400 Chem 150 REVIEW SHEET Amanda R
... o Protons, electrons and neutrons make up an atom o Atoms make up molecules, all matter is made of atoms o Protons and neutrons are in the nucleus, and electrons are buzzing outside the nucleus around the nucleus in orbitals o # of protons defines an element, # of protons = atomic # o # of neutrons ...
... o Protons, electrons and neutrons make up an atom o Atoms make up molecules, all matter is made of atoms o Protons and neutrons are in the nucleus, and electrons are buzzing outside the nucleus around the nucleus in orbitals o # of protons defines an element, # of protons = atomic # o # of neutrons ...
Name - TeacherWeb
... 5. Complete the electron dot structure for each molecule. Each molecule contains only single covalent bonds. ...
... 5. Complete the electron dot structure for each molecule. Each molecule contains only single covalent bonds. ...
Chem 101A Exam 4 Concepts Chapter 7 – Modern Atomic Theory
... Ionic radius trends (atom vs ion, and compare isoelectronic series) Bond energies to calculate Hrxn (Ebonds broken – Ebonds formed) Lewis structures predict which atoms bond to which and nonbonding electrons (lone pair) 2 valence electrons max: H, He 8 valence electrons max: 2nd row eleme ...
... Ionic radius trends (atom vs ion, and compare isoelectronic series) Bond energies to calculate Hrxn (Ebonds broken – Ebonds formed) Lewis structures predict which atoms bond to which and nonbonding electrons (lone pair) 2 valence electrons max: H, He 8 valence electrons max: 2nd row eleme ...
Exam 1 Key
... a. Why are the second ionization energies of the group two atoms (Li-Ne) larger than those of the group three atoms (Na-Ar)? In general, period two elements have a larger effective nuclear charge than the elements below them in period three. This is due, in part, to the fact that there are fewer ele ...
... a. Why are the second ionization energies of the group two atoms (Li-Ne) larger than those of the group three atoms (Na-Ar)? In general, period two elements have a larger effective nuclear charge than the elements below them in period three. This is due, in part, to the fact that there are fewer ele ...
•What makes up an atom? Draw an atom
... • Compound behave differently than individual elements • EX. Na vs NaCl ...
... • Compound behave differently than individual elements • EX. Na vs NaCl ...
Ch 8 AP Practice
... (B) H2O (C) CH4 (D) C2H4 (E) PH3 3. The molecule with only one double bond 4. The molecule with the largest dipole moment 5. The molecule that has trigonal pyramidal geometry 53. According to the VSEPR model, the progressive decrease in the bond angles in the series of molecules CH4, NH3, and H2O is ...
... (B) H2O (C) CH4 (D) C2H4 (E) PH3 3. The molecule with only one double bond 4. The molecule with the largest dipole moment 5. The molecule that has trigonal pyramidal geometry 53. According to the VSEPR model, the progressive decrease in the bond angles in the series of molecules CH4, NH3, and H2O is ...
Bonding Challenge
... 1) (a) Draw the Lewis electron-dot structures for CO32-, CO2, and CO, including resonance structures where appropriate. (b) Put the three species in order of increasing C-O bond length? Explain the reason for your answer. (c) Predict the molecular shapes for the three species. ...
... 1) (a) Draw the Lewis electron-dot structures for CO32-, CO2, and CO, including resonance structures where appropriate. (b) Put the three species in order of increasing C-O bond length? Explain the reason for your answer. (c) Predict the molecular shapes for the three species. ...
Chem 310 - Chemistry Courses
... quantitative nature in order to more fully account for all observations Fully explain what we are able to observe predictions of new “stuff” Historical development of understanding and describing bonding in molecules – from more simple explanations to more sophisticated ones Many of these concepts ...
... quantitative nature in order to more fully account for all observations Fully explain what we are able to observe predictions of new “stuff” Historical development of understanding and describing bonding in molecules – from more simple explanations to more sophisticated ones Many of these concepts ...
Name # ______ Honors Chemistry Carpenito/Dinota Reading Guide
... Although the valence electron pairs in ammonia, NH3, have a tetrahedral arrangement, the overall geometric structure of the ammonia molecule is not described as being tetrahedral. Explain. ...
... Although the valence electron pairs in ammonia, NH3, have a tetrahedral arrangement, the overall geometric structure of the ammonia molecule is not described as being tetrahedral. Explain. ...
SB Vocab list Word document
... A negatively charged particle found in the shells of an atom. Its mass is approximately 1/2000 that of a proton or neutron. Group A vertical column in the Periodic Table. Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties since they all have the same number of electrons in their outer (or v ...
... A negatively charged particle found in the shells of an atom. Its mass is approximately 1/2000 that of a proton or neutron. Group A vertical column in the Periodic Table. Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties since they all have the same number of electrons in their outer (or v ...
Slide 1
... • Orbitals overlap to form a bond between two atoms • Two electrons, of opposite spins can be accommodated in the overlapping orbitals. • Bonding electrons have higher probability of being found between two nuclei. Electrons are simultaneously attracted to both nuclei. ...
... • Orbitals overlap to form a bond between two atoms • Two electrons, of opposite spins can be accommodated in the overlapping orbitals. • Bonding electrons have higher probability of being found between two nuclei. Electrons are simultaneously attracted to both nuclei. ...
Biol 1441
... Nonpolar covalent bond: the electrons of the bond are shared equally. Ex: N2 Polar covalent bond: the electrons of the bond are not shared equally. Ex: HCl Ionic Bonds: Two atoms are so unequal in their attraction for valence electrons that the more electronegative atom strips an electron completely ...
... Nonpolar covalent bond: the electrons of the bond are shared equally. Ex: N2 Polar covalent bond: the electrons of the bond are not shared equally. Ex: HCl Ionic Bonds: Two atoms are so unequal in their attraction for valence electrons that the more electronegative atom strips an electron completely ...
The Theories: Molecular Geometry
... by the relative positions of the atomic nuclei. Theories Describing the structure and bonding of molecules are: – VSEPR = considers mostly electrostatics in determining the geometry of the molecule. – Valence Bond Theory = considers quantum mechanics and hybridization of atomic orbitals. ...
... by the relative positions of the atomic nuclei. Theories Describing the structure and bonding of molecules are: – VSEPR = considers mostly electrostatics in determining the geometry of the molecule. – Valence Bond Theory = considers quantum mechanics and hybridization of atomic orbitals. ...
How are Molecules Depicted? - Belle Vernon Area School District
... Used when single bonds don’t satisfy octets for each atom Resonance structure – a possible Lewis structure of a molecule when more than 1 L.S. is possible Delocalized – e- shared b/t more than 2 atoms ...
... Used when single bonds don’t satisfy octets for each atom Resonance structure – a possible Lewis structure of a molecule when more than 1 L.S. is possible Delocalized – e- shared b/t more than 2 atoms ...
chemical bond
... Diatomic molecule – can form a molecule when bonded with itself. It must contain 2 atoms. H, N, O, F, Cl, Br, I can form diatomic molecules. (They form a 7 and there are 7 of them) ...
... Diatomic molecule – can form a molecule when bonded with itself. It must contain 2 atoms. H, N, O, F, Cl, Br, I can form diatomic molecules. (They form a 7 and there are 7 of them) ...
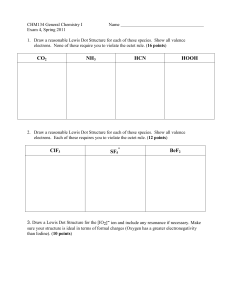
CO2 NH3 HCN HOOH ClF3 SF5 BeF2
... 2. Draw a reasonable Lewis Dot Structure for each of these species. Show all valence electrons. Each of these requires you to violate the octet rule. (12 points) ...
... 2. Draw a reasonable Lewis Dot Structure for each of these species. Show all valence electrons. Each of these requires you to violate the octet rule. (12 points) ...
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW Electron Configurations Explain the
... Explain the relationship between energy levels and sublevels and atomic orbitals. Describe the shapes of the s & p orbitals. Recall the reason for the x, y, z, axes. Apply the Pauli exclusion principle, the aufbau principle, and Hund’s rule to write electron configurations using orbital diag ...
... Explain the relationship between energy levels and sublevels and atomic orbitals. Describe the shapes of the s & p orbitals. Recall the reason for the x, y, z, axes. Apply the Pauli exclusion principle, the aufbau principle, and Hund’s rule to write electron configurations using orbital diag ...
Section 6.5 – Molecular Geometry The properties of molecules
... Two Theories – based on evidence VSEPR Theory: Accounts for molecular bond angles. Hybridization: Describes the orbitals that contain the valence electrons of a molecule’s atoms. VSEPR Theory = Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion -Repulsion between the valence-shell electrons surrounding an atom c ...
... Two Theories – based on evidence VSEPR Theory: Accounts for molecular bond angles. Hybridization: Describes the orbitals that contain the valence electrons of a molecule’s atoms. VSEPR Theory = Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion -Repulsion between the valence-shell electrons surrounding an atom c ...
Chapter 8: Chemical Reactions and Physical Changes
... • Mass number: total protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus • Atomic mass: the average mass of a sample of atoms of that element found in nature • Periodic table: chart that arranges elements by atomic number into rows and columns according to similarities in their properties ...
... • Mass number: total protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus • Atomic mass: the average mass of a sample of atoms of that element found in nature • Periodic table: chart that arranges elements by atomic number into rows and columns according to similarities in their properties ...