chapter 6 sec 2 resonance structure
... But H2O is also a chemical formula because we use atomic symbols and subscripts to describe it. ...
... But H2O is also a chemical formula because we use atomic symbols and subscripts to describe it. ...
AP LAb 8
... A single covalent bond is formed when two atoms share a pair of electrons. Each atom can provide one of the electrons of the pair (though there are exceptions). A group of atoms held together by covalent bonds is called a molecule. Molecules can be either polar or nonpolar. If the bonds are nonpolar ...
... A single covalent bond is formed when two atoms share a pair of electrons. Each atom can provide one of the electrons of the pair (though there are exceptions). A group of atoms held together by covalent bonds is called a molecule. Molecules can be either polar or nonpolar. If the bonds are nonpolar ...
Advanced Chemistry Midterm
... 57. What are the three main subatomic particles? Give their charges, mass, and their location in the atom. ...
... 57. What are the three main subatomic particles? Give their charges, mass, and their location in the atom. ...
Name : Version B Student I.D For the following two molecules give
... b) electron group geometry (draw it) c) molecular geometry d) hybridization on the central atom e) and indicate whether the molecule is polar or not. Take the Pauling electronegativity value for Xe to be 2.6 and a lone pair = 3.7. ...
... b) electron group geometry (draw it) c) molecular geometry d) hybridization on the central atom e) and indicate whether the molecule is polar or not. Take the Pauling electronegativity value for Xe to be 2.6 and a lone pair = 3.7. ...
Chapter 6: Chemical Bonding
... • A neutral group of atoms that are held together by covalent bonds. • Molecular Compound – A chemical compound whose simplest units are molecules. • Chemical Formula – It indicates the number of atoms by using atomic symbols and subscripts. • Molecular Formula – Shows the types and numbers of atoms ...
... • A neutral group of atoms that are held together by covalent bonds. • Molecular Compound – A chemical compound whose simplest units are molecules. • Chemical Formula – It indicates the number of atoms by using atomic symbols and subscripts. • Molecular Formula – Shows the types and numbers of atoms ...
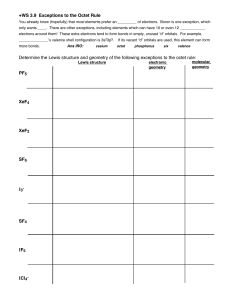
WS 3.9 - Exceptions to Octet Rule
... You already know (hopefully) that most elements prefer an _________ of electrons. Boron is one exception, which only wants ____. There are other exceptions, including elements which can have 10 or even 12 ____________ electrons around them! These extra electrons tend to form bonds in empty, unused “ ...
... You already know (hopefully) that most elements prefer an _________ of electrons. Boron is one exception, which only wants ____. There are other exceptions, including elements which can have 10 or even 12 ____________ electrons around them! These extra electrons tend to form bonds in empty, unused “ ...
Learning Standards vocab chemical basis and molecules of life 09
... formed (e.g., sodium atoms lose an electron and chlorine atoms gain an electron, then the charged ions are attracted to each other and form bonds). Explain the meaning of a chemical formula for an ionic array (e.g., NaCl). Give examples to illustrate that molecules are groups of two or more atom ...
... formed (e.g., sodium atoms lose an electron and chlorine atoms gain an electron, then the charged ions are attracted to each other and form bonds). Explain the meaning of a chemical formula for an ionic array (e.g., NaCl). Give examples to illustrate that molecules are groups of two or more atom ...
First Semester Final - Review Questions
... 37. Describe the different amounts and kinds of damage in matter produced by the different penetrations of each type of radioactive decay. 38. How does the energy release in a nuclear reaction compare to the energy release in a chemical reaction. Investigation and Experimentation 39. What is the pur ...
... 37. Describe the different amounts and kinds of damage in matter produced by the different penetrations of each type of radioactive decay. 38. How does the energy release in a nuclear reaction compare to the energy release in a chemical reaction. Investigation and Experimentation 39. What is the pur ...
3.1 Classifying Chemical Compounds
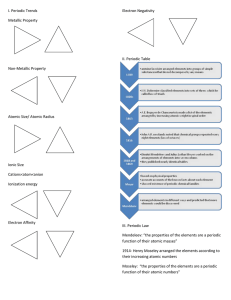
... to decide whether the bond between two atoms is ionic or covalent. The symbol Δ EN stands for the difference between two electronegativity values. When calculating the Δ EN, the smaller EN is always subtracted from the larger EN, so that the Δ EN is always positive. ...
... to decide whether the bond between two atoms is ionic or covalent. The symbol Δ EN stands for the difference between two electronegativity values. When calculating the Δ EN, the smaller EN is always subtracted from the larger EN, so that the Δ EN is always positive. ...
Chem 102A
... d) An N-H bond is more polar than a P-H bond. e) None of the above statements (a-d) are false. 3. Two different compounds have the formula SF4Cl2 (where S is the central atom). Which of the following statements concerning the two SF4Cl2 compounds is false? a) The central atom in both compounds of SF ...
... d) An N-H bond is more polar than a P-H bond. e) None of the above statements (a-d) are false. 3. Two different compounds have the formula SF4Cl2 (where S is the central atom). Which of the following statements concerning the two SF4Cl2 compounds is false? a) The central atom in both compounds of SF ...
CHEMISTRY
... Held together by bonds Covalent bonds (strong): 2 or more atoms share electrons Ionic Bonds (weak): attractions between + and ions ...
... Held together by bonds Covalent bonds (strong): 2 or more atoms share electrons Ionic Bonds (weak): attractions between + and ions ...
Chem 222 Exam #1 Outline
... Lewis dot symbols Lewis structures for ionic compounds Lattice energies, Coulomb's Law, and Born-Haber cycles Lewis structures for covalent compounds, single, double, and triple bonds Bond lengths properties of covalent vs. ionic compounds polar covalent compounds trends in electronegativity predict ...
... Lewis dot symbols Lewis structures for ionic compounds Lattice energies, Coulomb's Law, and Born-Haber cycles Lewis structures for covalent compounds, single, double, and triple bonds Bond lengths properties of covalent vs. ionic compounds polar covalent compounds trends in electronegativity predict ...
ionic and covalent bonds
... Octet Rule: atoms want 8 electrons in the valence (outer) energy level Ionic Bond: bond in which one or more electrons from one atom are removed and attached to another atom. This creates positive and negative ions which attract each other. (Acids, bases, salts do this): ...
... Octet Rule: atoms want 8 electrons in the valence (outer) energy level Ionic Bond: bond in which one or more electrons from one atom are removed and attached to another atom. This creates positive and negative ions which attract each other. (Acids, bases, salts do this): ...
CHEM1101 2010-J-5 June 2010 • Describe the nature of an ionic
... • Describe the nature of an ionic bond in terms of atomic and molecular orbitals. When a covalent bond is formed between two elements of identical electronegativity, bonding and antibonding orbitals are formed which have equal contributions from both atoms. The covalent bonding arises from the incre ...
... • Describe the nature of an ionic bond in terms of atomic and molecular orbitals. When a covalent bond is formed between two elements of identical electronegativity, bonding and antibonding orbitals are formed which have equal contributions from both atoms. The covalent bonding arises from the incre ...
Exercise 7
... IBr2SbCl64) Give the hybridization of the central atom of the following molecules. Which bonding angles are expected? (2 points) BeF2 BeF3BeF42IF6+ 5) Which of the following molecules will (in total) be polar? Draw the Lewis structure and indicate the total dipole moment (or the polarity in each bon ...
... IBr2SbCl64) Give the hybridization of the central atom of the following molecules. Which bonding angles are expected? (2 points) BeF2 BeF3BeF42IF6+ 5) Which of the following molecules will (in total) be polar? Draw the Lewis structure and indicate the total dipole moment (or the polarity in each bon ...
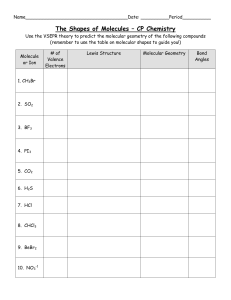
3.3 Test Review
... Write the number of valence shell electrons for each element in the compound and calculate the total number of valence electrons for the given molecule. Draw the skeleton structure for the molecule with each atom in the correct position. Show all bonding and nonbonding electrons with the appropriate ...
... Write the number of valence shell electrons for each element in the compound and calculate the total number of valence electrons for the given molecule. Draw the skeleton structure for the molecule with each atom in the correct position. Show all bonding and nonbonding electrons with the appropriate ...