Review for Bonding Test
... What is the difference between a molecule and a compound? A molecule is formed when two or more atoms join together chemically. A compound is a molecule that contains at least two different elements. All compounds are molecules but not all molecules are compounds. Which of these is a compound? He, ...
... What is the difference between a molecule and a compound? A molecule is formed when two or more atoms join together chemically. A compound is a molecule that contains at least two different elements. All compounds are molecules but not all molecules are compounds. Which of these is a compound? He, ...
CH 222 Problem Set #2
... What is the hybridization of the nitrogen atom? What orbitals on N and F overlap to form bonds between these elements? 2. Specify the electron pair and molecular geometry for each of the following. Describe the hybrid orbital set used by the central atom in each molecule or ion. a. CSe2 b. SO2 c. ...
... What is the hybridization of the nitrogen atom? What orbitals on N and F overlap to form bonds between these elements? 2. Specify the electron pair and molecular geometry for each of the following. Describe the hybrid orbital set used by the central atom in each molecule or ion. a. CSe2 b. SO2 c. ...
Exam 3 Review - Iowa State University
... 13. Which of the following are solids at room temperature, and which are gases? a. CO2 b. BaO c. CuO d. F2 e. NO 14. Which substances are ionic and which are covalent? a. Br2 b. KO2 c. AsH3 d. SO2 e. Ca(ClO4)2 15. Which substance should form an acidic solution in water? a. Na2O b. SO2 c. CO d. BaO 1 ...
... 13. Which of the following are solids at room temperature, and which are gases? a. CO2 b. BaO c. CuO d. F2 e. NO 14. Which substances are ionic and which are covalent? a. Br2 b. KO2 c. AsH3 d. SO2 e. Ca(ClO4)2 15. Which substance should form an acidic solution in water? a. Na2O b. SO2 c. CO d. BaO 1 ...
Bonding and Nomenclature
... atoms, or groups of atoms about a central atom in a covalent compound, or charged ion, is determined solely by the repulsions between electron pairs present in the valence shell of the central atom. • The number of electron pairs around the central atom can be determined by writing the Lewis structu ...
... atoms, or groups of atoms about a central atom in a covalent compound, or charged ion, is determined solely by the repulsions between electron pairs present in the valence shell of the central atom. • The number of electron pairs around the central atom can be determined by writing the Lewis structu ...
Answer on Question #48952 - Chemistry
... Explain the structure of the following molecules on the basis of USEPR theory: ClF 3 and PF3. predict the geometry of the following molecules using the VSEPR model. CO2, NH3 CH4, H2O, SO2, NO2, CLF3, SF6 Answer: Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory is a model used, in chemistry, to i ...
... Explain the structure of the following molecules on the basis of USEPR theory: ClF 3 and PF3. predict the geometry of the following molecules using the VSEPR model. CO2, NH3 CH4, H2O, SO2, NO2, CLF3, SF6 Answer: Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory is a model used, in chemistry, to i ...
Chapter 8 - TeacherWeb
... A single covalent bond occurs when two atoms share one pair of valence electrons A double covalent bond occurs when two atoms share two pairs of valence electrons A triple covalent bond occurs when two atoms share three pairs of covalent bonds ...
... A single covalent bond occurs when two atoms share one pair of valence electrons A double covalent bond occurs when two atoms share two pairs of valence electrons A triple covalent bond occurs when two atoms share three pairs of covalent bonds ...
Atom - Sites
... •All compounds are molecules but not all molecules are compounds. (ex. H2O vs. O2) •Molecules can also join together to form larger molecules. •Many, many repeating small molecules joined together form a polymer. http://pslc.ws/macrog/kidsmac/basics.htm ...
... •All compounds are molecules but not all molecules are compounds. (ex. H2O vs. O2) •Molecules can also join together to form larger molecules. •Many, many repeating small molecules joined together form a polymer. http://pslc.ws/macrog/kidsmac/basics.htm ...
Atomic Crossword Name: Period: ____
... 29. An atom that has too many or too few electrons 30. A positively charged atom 31. The "nonexistent" rings that hold electrons 32. C, Fe, Au are all examples of this ...
... 29. An atom that has too many or too few electrons 30. A positively charged atom 31. The "nonexistent" rings that hold electrons 32. C, Fe, Au are all examples of this ...
SCH4C Junior Chemistry Review - Molecular Compounds
... • Binary compounds consist of exactly TWO elements. • Naming binary molecular compounds that do NOT contain hydrogen atoms use GREEK prefixes to indicate how many atoms are present ...
... • Binary compounds consist of exactly TWO elements. • Naming binary molecular compounds that do NOT contain hydrogen atoms use GREEK prefixes to indicate how many atoms are present ...
cell molecules
... Matter consists of chemical elements in pure form and in combinations called compounds • Organisms are composed of matter. • Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions. • There are 92 naturall ...
... Matter consists of chemical elements in pure form and in combinations called compounds • Organisms are composed of matter. • Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions. • There are 92 naturall ...
CHEMISTRY IN LIVING SYSTEMS
... All life processes involve living things made of matter All matter is composed of elements The chemical foundation for the diversity of life is based on six elements: C, H, N, O, P, S Organic Molecules: a carbon-containing molecule in which carbon atoms are nearly always bonded to each other and to ...
... All life processes involve living things made of matter All matter is composed of elements The chemical foundation for the diversity of life is based on six elements: C, H, N, O, P, S Organic Molecules: a carbon-containing molecule in which carbon atoms are nearly always bonded to each other and to ...
AP Chapter 9 Molecular Shapes
... pairs exert greater repulsive forces on adjacent electron domains and tend to compress the bond angles. ...
... pairs exert greater repulsive forces on adjacent electron domains and tend to compress the bond angles. ...
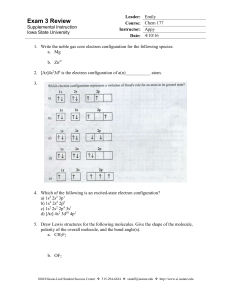
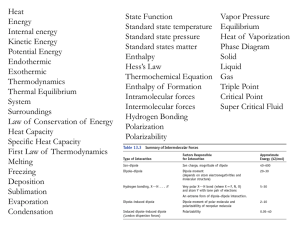
Exam 3 Review
... 1. list all the elements follow with an equal sign 2. follow with the number of atoms of that type in the molecule 1. follow with a multiplication sign 2. If the element is O follow with a -2 3. If the element is H follow with a +1 4. any other element enter a ? 5. follow with an = sign, do the math ...
... 1. list all the elements follow with an equal sign 2. follow with the number of atoms of that type in the molecule 1. follow with a multiplication sign 2. If the element is O follow with a -2 3. If the element is H follow with a +1 4. any other element enter a ? 5. follow with an = sign, do the math ...
Exam 3 2013 KEY
... Which of these molecules does not meet the octet rule? a. SO3 b. N2O (bonding = NNO) c. NO2 (odd electron) d. SF2 ...
... Which of these molecules does not meet the octet rule? a. SO3 b. N2O (bonding = NNO) c. NO2 (odd electron) d. SF2 ...
Physical Science 1
... • an unequal sharing of the e• Due to a difference of electro-negativity of the atoms – F is the most electronegative element on PT – A simulation of polar covalent bonding in the H2O molecule Only valence electrons are shown ...
... • an unequal sharing of the e• Due to a difference of electro-negativity of the atoms – F is the most electronegative element on PT – A simulation of polar covalent bonding in the H2O molecule Only valence electrons are shown ...
CHAPTER 9 : CHEMICAL BONDING I
... 9.74 The formulas for the fluorides of the third-period elements are NaF, MgF2, AlF3, SiF4, PF5, SF6, and CLF3. Classify these compounds as covalent or ionic. 9.76 Describe some characteristics of an ionic compound such as KF that would distinguish it from a covalent compound such as benzene (C6H6). ...
... 9.74 The formulas for the fluorides of the third-period elements are NaF, MgF2, AlF3, SiF4, PF5, SF6, and CLF3. Classify these compounds as covalent or ionic. 9.76 Describe some characteristics of an ionic compound such as KF that would distinguish it from a covalent compound such as benzene (C6H6). ...
Chemistry 11 Spring 2008 Exam 4. 60 points. Be sure to use as
... 10 points. Consider the following species: C2+, C2, and C2– A. Use molecular orbital energy diagrams to discuss the relative stability of these three species. B. Which species would be expected to be most stable? C. Which would have the strongest bond? D. Shortest bond? E. Which of these species are ...
... 10 points. Consider the following species: C2+, C2, and C2– A. Use molecular orbital energy diagrams to discuss the relative stability of these three species. B. Which species would be expected to be most stable? C. Which would have the strongest bond? D. Shortest bond? E. Which of these species are ...
2.1 The Nature of Matter - Sonoma Valley High School
... 24+ elements are found in living things (of 100+ elements) Some elements have isotopes, with different #s of neutrons and different mass. All isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties b/c their electrons are the same. ...
... 24+ elements are found in living things (of 100+ elements) Some elements have isotopes, with different #s of neutrons and different mass. All isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties b/c their electrons are the same. ...