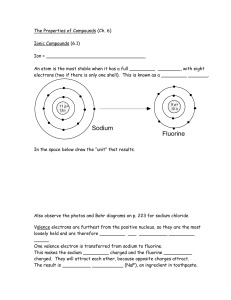
Review for Exam 1
... other that you think are bonded together. Place H and halogens on the periphery, since they can only form one bond. ...
... other that you think are bonded together. Place H and halogens on the periphery, since they can only form one bond. ...
Page 1 of 3 Chapter 2 Essential Chemistry CONTENT I. Basic
... 3. Using a table, compare and contrast 3 types of chemical bonds. 4. Using a sketch, compare and contrast non-polar and polar molecules, as well as dissociation of hydrophilic substances. 5. List and describe the properties of water and provide an example of their impact to life. 6. Using a pH scale ...
... 3. Using a table, compare and contrast 3 types of chemical bonds. 4. Using a sketch, compare and contrast non-polar and polar molecules, as well as dissociation of hydrophilic substances. 5. List and describe the properties of water and provide an example of their impact to life. 6. Using a pH scale ...
Bonding. A. Ionic bonds form when anions and cations arise
... Covalent bonds form when it is not possible for electrons to be transferred and so must be shared between atoms. 1. Generally this is the case when two nonmetals bond. The tendency of nonmetals is to gain electrons according to the octet rule, a very easy thing to accomplish when they bond with meta ...
... Covalent bonds form when it is not possible for electrons to be transferred and so must be shared between atoms. 1. Generally this is the case when two nonmetals bond. The tendency of nonmetals is to gain electrons according to the octet rule, a very easy thing to accomplish when they bond with meta ...
CHM134 General Chemistry I Semester Review – Dr. Steel This list
... 26. What bond angles are present between sp2 hybridized orbitals? 27. What geometry is associated with sp3d hybridization? 28. The ClF3 molecule will have what type of geometry? 29. The SF4 molecule will have what type of geometry? 30. What atomic orbital hybridization is used by Si in SiCl4? 31. In ...
... 26. What bond angles are present between sp2 hybridized orbitals? 27. What geometry is associated with sp3d hybridization? 28. The ClF3 molecule will have what type of geometry? 29. The SF4 molecule will have what type of geometry? 30. What atomic orbital hybridization is used by Si in SiCl4? 31. In ...
Unit 3 Practice Test
... A. Non-metals generally have the higher electronegativities and tend to attract electrons to themselves in a chemical bond. B. Elements with high ionization energies tend to have small atomic radii. C. Elements with high electronegativities generally form ions with small radii. D. The second ionizat ...
... A. Non-metals generally have the higher electronegativities and tend to attract electrons to themselves in a chemical bond. B. Elements with high ionization energies tend to have small atomic radii. C. Elements with high electronegativities generally form ions with small radii. D. The second ionizat ...
unit 2 - chemistry
... 2. element – basic unit of all matter (109 total) a. 92 natural elements b. 4 basic – H, C, O, N, -96% of human mass Ca, P -> 99% (3%) K, S, Cl, Mg, I, FE, (16 other)1% -> ...
... 2. element – basic unit of all matter (109 total) a. 92 natural elements b. 4 basic – H, C, O, N, -96% of human mass Ca, P -> 99% (3%) K, S, Cl, Mg, I, FE, (16 other)1% -> ...
MidTerm Review Questions
... Use the following molar masses: NH3 = 17.031 g/mol, O2 = 32.000 g/mol, ...
... Use the following molar masses: NH3 = 17.031 g/mol, O2 = 32.000 g/mol, ...
Basic Chemistry notes
... ______________________—two or more like atoms combined chemically ______________________—two or more different atoms combined chemically ...
... ______________________—two or more like atoms combined chemically ______________________—two or more different atoms combined chemically ...
Exam on Matter through Bonding
... atom, the orbitals are regions of the most probable location of (1) protons (3) electrons (2) neutrons (4) positrons 5. Which type of bond is formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another? (1) covalent (3) hydrogen (2) ionic (4) metallic 6. Which substance can not be decomposed by a ...
... atom, the orbitals are regions of the most probable location of (1) protons (3) electrons (2) neutrons (4) positrons 5. Which type of bond is formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another? (1) covalent (3) hydrogen (2) ionic (4) metallic 6. Which substance can not be decomposed by a ...
Test 4
... 3. Below are several ions and atoms. Rank these ions and atoms in order of increasing size Na+, Ca2+, Al3+, N-3, Se2-, Cl-, He, Ar Smallest ___________________________________ Largest ...
... 3. Below are several ions and atoms. Rank these ions and atoms in order of increasing size Na+, Ca2+, Al3+, N-3, Se2-, Cl-, He, Ar Smallest ___________________________________ Largest ...
Understanding the Properties of Elements – Chapter 5
... 5. Compare the electrical conductivity of pure water, tap water, and salt water. ...
... 5. Compare the electrical conductivity of pure water, tap water, and salt water. ...
BONDING
... Electronegativity, symbol χ, is a chemical property that describes the ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself in a covalent bond. First proposed by Linus Pauling in 1932 as a development of valence bond theory, it has been shown to correlate with a number of other chemical properties ...
... Electronegativity, symbol χ, is a chemical property that describes the ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself in a covalent bond. First proposed by Linus Pauling in 1932 as a development of valence bond theory, it has been shown to correlate with a number of other chemical properties ...
6.2 Covalent Bonds
... Nonmetels share electrons with other nonmetals to achieve a stable electron configuration When the electrons are shared a covalent bond forms between the two atoms Each nonmetal must have 8 valence electrons to reach stability ...
... Nonmetels share electrons with other nonmetals to achieve a stable electron configuration When the electrons are shared a covalent bond forms between the two atoms Each nonmetal must have 8 valence electrons to reach stability ...
2A Final Exam Review Worksheet
... A. If there is 10.0 g of P4O10, find the mass of phosphoric acid formed. B. If there is also 10.0 g of perchloric acid, find the mass of phosphoric acid formed. C. Considering A & B, how much of the excess reactant remains after the reaction is complete. D. Find the number of phosphorus atoms in 10. ...
... A. If there is 10.0 g of P4O10, find the mass of phosphoric acid formed. B. If there is also 10.0 g of perchloric acid, find the mass of phosphoric acid formed. C. Considering A & B, how much of the excess reactant remains after the reaction is complete. D. Find the number of phosphorus atoms in 10. ...
Chemistry of Life - juan-roldan
... reactions in an organism: ◦ Described by chemical equations ◦ Reactants are written on the left & products are written on the right ◦ Reactions can proceed simultaneously in both directions ◦ At dynamic equilibrium, forward and reverse rates of reaction are equal ...
... reactions in an organism: ◦ Described by chemical equations ◦ Reactants are written on the left & products are written on the right ◦ Reactions can proceed simultaneously in both directions ◦ At dynamic equilibrium, forward and reverse rates of reaction are equal ...
Part A - Chemical Bonding Review PowerPoint Presentation
... – Atoms attain an OCTET: a stable Noble Gas configuration. – the resulting system is at the lowest possible potential energy level. – The process of bonding is, therefore, exothermic: energy is being released. If the energy released is Large we get a strong bond; small ΔE bond is weak ...
... – Atoms attain an OCTET: a stable Noble Gas configuration. – the resulting system is at the lowest possible potential energy level. – The process of bonding is, therefore, exothermic: energy is being released. If the energy released is Large we get a strong bond; small ΔE bond is weak ...
BASIC CHEMISTRY
... The atomic number for O is 8. How many protons in O? How many electrons in O? The atomic mass of O is 16. How many neutrons in O? Draw an Oxygen atom. Show the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and the electrons in the energy ...
... The atomic number for O is 8. How many protons in O? How many electrons in O? The atomic mass of O is 16. How many neutrons in O? Draw an Oxygen atom. Show the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and the electrons in the energy ...