Learning Objectives
... b. atomic number and mass number c. atomic weight and mass number 5. Explain how the atomic number and mass number of an atom can be used to determine the number of neutrons. 6. Explain how two isotopes of an element are similar. Explain how they are different. 7. Describe two biological application ...
... b. atomic number and mass number c. atomic weight and mass number 5. Explain how the atomic number and mass number of an atom can be used to determine the number of neutrons. 6. Explain how two isotopes of an element are similar. Explain how they are different. 7. Describe two biological application ...
Lesson 1 Chemical introduction
... atom, ion, isotope, element, molecule 1. A substance composed of atoms with the same atomic number; it cannot be broken down in ordinary chemical reactions. 2.The smallest indivisible particle of matter that can have an independent existence. 3.Two or more atoms which are chemically combined to for ...
... atom, ion, isotope, element, molecule 1. A substance composed of atoms with the same atomic number; it cannot be broken down in ordinary chemical reactions. 2.The smallest indivisible particle of matter that can have an independent existence. 3.Two or more atoms which are chemically combined to for ...
build-a-balloon-molecule
... balloons and leave behind for all your classmates to see. After each group has completed their molecules, you will rotate through each group and complete the chart attached to this lab. Helpful Hints: All nonbonding pairs are represented by one color and all the non-bonding pair with another. No ...
... balloons and leave behind for all your classmates to see. After each group has completed their molecules, you will rotate through each group and complete the chart attached to this lab. Helpful Hints: All nonbonding pairs are represented by one color and all the non-bonding pair with another. No ...
No Slide Title
... with opposite charges results in an ionic bond. Some atoms share outer shell electrons with other atoms, forming covalent bonds. Ionic or covalent, atoms joined together by ionic or covalent bonds form molecules. ...
... with opposite charges results in an ionic bond. Some atoms share outer shell electrons with other atoms, forming covalent bonds. Ionic or covalent, atoms joined together by ionic or covalent bonds form molecules. ...
ionic bond. - cloudfront.net
... Metallic Bonding • Metallic Bonding - type of bonding found in metallic crystals. • 3-D lattice of positive ions. • remain fixed in a crystal lattice. • loosely-held valence e-’s move freely throughout the crystal. • The fluid-like movements of valence e-’s make metals good conductors of heat and e ...
... Metallic Bonding • Metallic Bonding - type of bonding found in metallic crystals. • 3-D lattice of positive ions. • remain fixed in a crystal lattice. • loosely-held valence e-’s move freely throughout the crystal. • The fluid-like movements of valence e-’s make metals good conductors of heat and e ...
Chemical Bonding
... • Proteins are complex, organic compounds made up of amino acids. • Lipids are organic compounds that contains fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. They are made of fatty acid chains. • Nucleic acids are large, complex molecules that contain the hereditary information for all living thing ...
... • Proteins are complex, organic compounds made up of amino acids. • Lipids are organic compounds that contains fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. They are made of fatty acid chains. • Nucleic acids are large, complex molecules that contain the hereditary information for all living thing ...
Draw atomic models showing the appropriate number of electrons
... Draw atomic models showing the appropriate number of electrons on each shell for the following elements: phosphorous #valence electrons ...
... Draw atomic models showing the appropriate number of electrons on each shell for the following elements: phosphorous #valence electrons ...
Odd Number of Electrons
... are not necessarily the lowest whole-number ratios. d. Can describe molecules consisting of one element. e. Does not tell you about the molecule’s structure 2. Using page 215 state the molecular formula for Ammonia and describe the types of diagrams and models used to represent Ammonia. ...
... are not necessarily the lowest whole-number ratios. d. Can describe molecules consisting of one element. e. Does not tell you about the molecule’s structure 2. Using page 215 state the molecular formula for Ammonia and describe the types of diagrams and models used to represent Ammonia. ...
Chapter 6: Chemistry in Biology
... When molecules come close together, the attractive forces between slightly positive and negative regions pull on the molecules and hold them together. ...
... When molecules come close together, the attractive forces between slightly positive and negative regions pull on the molecules and hold them together. ...
Basics of Chemistry
... atom depends on its electron arrangement depends on the number of electrons in its outermost shell, the ...
... atom depends on its electron arrangement depends on the number of electrons in its outermost shell, the ...
Note 1.1 Chemistry of Life
... Electronegativity - is the measure of an atom’s attraction to share electrons. Molecular diagrams use dashes or dots to represent covalent bonds between atoms. The number of covalent bonds formed between atoms depends on the number of valence electrons available to be shared. ...
... Electronegativity - is the measure of an atom’s attraction to share electrons. Molecular diagrams use dashes or dots to represent covalent bonds between atoms. The number of covalent bonds formed between atoms depends on the number of valence electrons available to be shared. ...
gr11chemreview
... The following questions highlight the main knowledge and skills from grade 11 chemistry. A good understanding of the concepts covered in grade 11 chemistry is essential for success in grade 12 chemistry and you may need to do some independent review of some material if you do not have a clear unders ...
... The following questions highlight the main knowledge and skills from grade 11 chemistry. A good understanding of the concepts covered in grade 11 chemistry is essential for success in grade 12 chemistry and you may need to do some independent review of some material if you do not have a clear unders ...
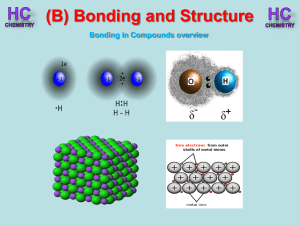
Lesson 1 - Bonding in compounds overview
... Silicon and oxygen make up nearly 75% of the Earth’s crust. They are therefore the most common elements in the Earth’s crust. They combine together to make a covalent network compound called silicon dioxide. This is usually found in the form of sand or quartz. Each Si atom is bonded to 4 O atoms, an ...
... Silicon and oxygen make up nearly 75% of the Earth’s crust. They are therefore the most common elements in the Earth’s crust. They combine together to make a covalent network compound called silicon dioxide. This is usually found in the form of sand or quartz. Each Si atom is bonded to 4 O atoms, an ...
File - Chemistry
... • You could be told an unknown substance has a specific heat of 0.129 J/g˚C … what is it? home ...
... • You could be told an unknown substance has a specific heat of 0.129 J/g˚C … what is it? home ...
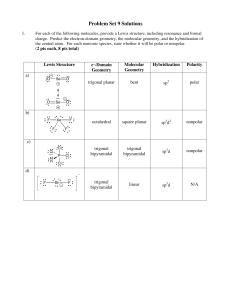
Problem Set 9 Solutions
... Describe the bonding in this molecule in terms of sigma (σ) and/or pi (π) bonds and the orbitals involved in bond formation. (4 pts) There are three σ bonds made between left C sp3 hybrid orbitals and H s-orbitals. There is one σ bond made between left C sp3 hybrid orbital and right C sp hybrid orbi ...
... Describe the bonding in this molecule in terms of sigma (σ) and/or pi (π) bonds and the orbitals involved in bond formation. (4 pts) There are three σ bonds made between left C sp3 hybrid orbitals and H s-orbitals. There is one σ bond made between left C sp3 hybrid orbital and right C sp hybrid orbi ...
The Chemical Basis of Life
... Isotopes are atoms of an element that all have the same number of protons, but have different numbers of neutrons. Radioisotopes – radioactive decay The time it takes for half of a radioactive substance to decay is called its half-life. ...
... Isotopes are atoms of an element that all have the same number of protons, but have different numbers of neutrons. Radioisotopes – radioactive decay The time it takes for half of a radioactive substance to decay is called its half-life. ...
CHAPTER 10 - NUCLEAR PHYSICS
... In covalently bonded compounds, two or three pairs of electrons can be shared by two atoms. When two pairs are shared the chemical bond is called a double bond. When three pairs are shared it is called a triple bond. Characteristics of Ionic Compounds 1. Crystalline solids made of ions 2. High melti ...
... In covalently bonded compounds, two or three pairs of electrons can be shared by two atoms. When two pairs are shared the chemical bond is called a double bond. When three pairs are shared it is called a triple bond. Characteristics of Ionic Compounds 1. Crystalline solids made of ions 2. High melti ...
Chemical bonding
... negative ions, or anions. Therefore, bond time depends on electronegativity. ...
... negative ions, or anions. Therefore, bond time depends on electronegativity. ...
The Nature of Molecules
... ***Inner energy shells (those closest to the nucleus) contain electrons with lower energy than the outer energy shells ***important concept as it will be discussed in the Light Dependent reaction of Photosynthesis ...
... ***Inner energy shells (those closest to the nucleus) contain electrons with lower energy than the outer energy shells ***important concept as it will be discussed in the Light Dependent reaction of Photosynthesis ...
Microsoft Word
... Covalent Bonding Elements which are neither highly electropositive nor highly electronegative are less likely to form ionic compounds. Consider CH4, methane; carbon and hydrogen have similar electronegativities. It would be inappropriate to describe the bonds between carbon and hydrogen in methane a ...
... Covalent Bonding Elements which are neither highly electropositive nor highly electronegative are less likely to form ionic compounds. Consider CH4, methane; carbon and hydrogen have similar electronegativities. It would be inappropriate to describe the bonds between carbon and hydrogen in methane a ...
1B Practice Final Ch 12, 13
... 13. For the following, draw two Lewis structures, one which satisfies the octet rule and one which minimizes formal charge: a. SO42b. ClO314. Order the following species with respect to the carbon-oxygen bond length (shortest to longest): CO, CO2, CO32-, CH3OH What is the order from weakest to stron ...
... 13. For the following, draw two Lewis structures, one which satisfies the octet rule and one which minimizes formal charge: a. SO42b. ClO314. Order the following species with respect to the carbon-oxygen bond length (shortest to longest): CO, CO2, CO32-, CH3OH What is the order from weakest to stron ...