* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Theories: Molecular Geometry
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
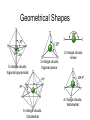
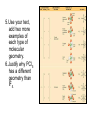
The Theories: Molecular Geometry • • • Atoms oriented in very well defined relative positions in the molecule. Molecular Geometry = general shape of the molecule as determined by the relative positions of the atomic nuclei. Theories Describing the structure and bonding of molecules are: – VSEPR = considers mostly electrostatics in determining the geometry of the molecule. – Valence Bond Theory = considers quantum mechanics and hybridization of atomic orbitals. – Molecular Orbital Theory = claims that upon bond formation new orbitals that are linear combinations of the atomic orbitals are formed. 1. What does VSEPR stand for? 2. What does hybridization mean? Geometrical Shapes 5 charge clouds, trigonal bipyramidal 3 charge clouds, trigonal planar 2 charge clouds, linear 4 charge clouds, tetrahedral 6 charge clouds, Octahedral 3.What is the difference between bonding and lone electron pairs? 4. How do you find out how many electrons are in a molecule? 5.Use your text, add two more examples of each type of molecular geometry. 6.Justify why PCl5 has a different geometry than IF5. How to predict? • Lewis dot structure determines the total # of electrons around the central atom. Multiple bonds (double and triple) count as one. • The number of bonding and nonbonding electron pairs determines the geometry of electron pairs and the molecular geometry. • Lone e Pairs affect geometry more than bonding pairs. 7. WHY? • Multiple bonds have larger affect on geometry than single bonds. 8. WHY? Polarity of Molecules • Bond dipole a positive charge next to a negative charge. • Dipole moment, the magnitude of the net bond dipole of a molecule = Qxr Q = the net charge separation; r = the separation distance. Units: debyes (D) where 1 D = 33.36x1030 Cm. • A polar bond forms when two atoms of between two atoms involved in a bond have significantly different electronegativities. – Most electronegative substance will have a slight negative charge (represented as ) – The positive (electron poor) side of the bond is represented as + or – points in direction of the negative charge. • Net polarity (dipole moment) of a molecule is obtained using the vector sum of polarities of individual bonds. 9.Determine if NH3, H2O, CO2 have dipole moments.