* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Molecular Geometry
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
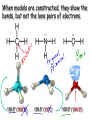
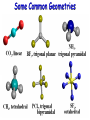
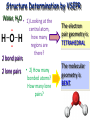
Molecular Geometry MOLECULAR GEOMETRY VSEPR stands for: Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory. • Most important factor in determining the shape of the molecule is the repulsion between electron pairs. Molecules form their shapes to minimize the repulsions of the electrons. *They get as far away from each other as possible! VSEPR Charts • Use the Lewis Structure to determine the geometry of the molecule. • Focus only on the CENTRAL atom for all molecules! Count the number of electron regions. • Look for REGIONS WHERE ELECTRONS ARE FOUND rather than number of bonds. (Ex: Double and Triple bonds count as 1 region) Lets look at Methane (CH4). The molecule is really three dimensional, not planar and flat. H C H H H When models are constructed, they show the bonds, but not the lone pairs of electrons. .. 109.5° (109.5°) 109.5° (107°) .. .. 109.5° (104.5°) Some Common Geometries Structure Determination by VSEPR Water, H2O • 1) Looking at the central atom, •• how many regions are •• there? H O H The electron pair geometry is TETRAHEDRAL 2 bond pairs 2 lone pairs • 2) How many bonded atoms? How many lone pairs? The molecular geometry is BENT. Structure Determination by VSEPR Ammonia, NH3 The electron pair geometry is Tetrahedral , and the Geometry name is TRIGONAL PYRAMID.