Click here to the handout.
... Atoms are made up of smaller particles called protons, neutrons and electrons. Electrons (which have a negative charge) travel in orbits called shells around the nucleus. ...
... Atoms are made up of smaller particles called protons, neutrons and electrons. Electrons (which have a negative charge) travel in orbits called shells around the nucleus. ...
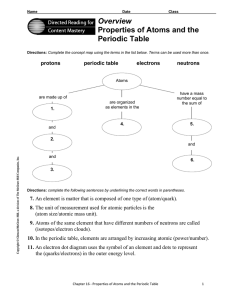
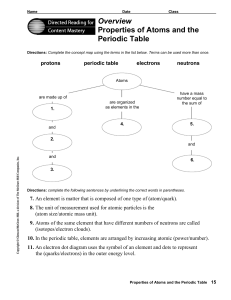
Overview Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... 7. An element is matter that is composed of one type of (atom/quark). 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit). 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called (isotopes/electron clouds). 10. In the periodic table, eleme ...
... 7. An element is matter that is composed of one type of (atom/quark). 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit). 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called (isotopes/electron clouds). 10. In the periodic table, eleme ...
atomic structure (see second part of ppt)
... 1913Bohr said electrons located outside the nucleus could only be located in specific paths called orbitals. This was supported by the line spectra of atoms His model is called the planetary model ...
... 1913Bohr said electrons located outside the nucleus could only be located in specific paths called orbitals. This was supported by the line spectra of atoms His model is called the planetary model ...
Atomic Structure
... Early Atomic Theory “Cosmic substance is made up of an infinite number of elements or particles ...
... Early Atomic Theory “Cosmic substance is made up of an infinite number of elements or particles ...
Chapter 5: The periodic table is a tool for organizing
... 10. Examine the following table of properties of two unknown compounds, X and Y. Which is most likely an ionic compound and which is most likely a molecular compound? Explain your reasoning. ...
... 10. Examine the following table of properties of two unknown compounds, X and Y. Which is most likely an ionic compound and which is most likely a molecular compound? Explain your reasoning. ...
Final Exam Class Review - Mrs. Kittrell`s Science Classes
... of the most likely locations for electrons in an atom. ...
... of the most likely locations for electrons in an atom. ...
Semester Exam Review Guide
... Chemisty Practice Multiple Choice 16. The atomic radius increases when going down a family because a. valence electrons are increasing b. the total number of protons, electrons, and neutrons is increasing c. electrons are repelling from each other in the valence shell d. elements are becoming very ...
... Chemisty Practice Multiple Choice 16. The atomic radius increases when going down a family because a. valence electrons are increasing b. the total number of protons, electrons, and neutrons is increasing c. electrons are repelling from each other in the valence shell d. elements are becoming very ...
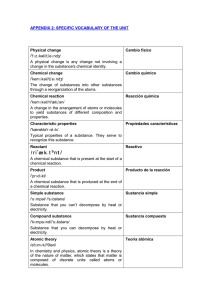
specific vocabulary of the unit
... Any of the elements of Group 18 (VIII, VIIIA), which includes helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, radon, and element 118. These elements are referred to as "inert" or "noble" because they do not easily form compounds with other elements. Transition elements /træn'zɪʃən//'eləmənts / A class of eleme ...
... Any of the elements of Group 18 (VIII, VIIIA), which includes helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, radon, and element 118. These elements are referred to as "inert" or "noble" because they do not easily form compounds with other elements. Transition elements /træn'zɪʃən//'eləmənts / A class of eleme ...
Atoms
... Atoms are the absolute smallest units that make up matter. Atoms are so small that we cannot see them with our bare eyes, they are so small that we can’t even see them with a light microscope. An element is a substance made from only one type of atom. ...
... Atoms are the absolute smallest units that make up matter. Atoms are so small that we cannot see them with our bare eyes, they are so small that we can’t even see them with a light microscope. An element is a substance made from only one type of atom. ...
Test 4
... electromagnetic radiation, emr, wavelength, frequency, photon, Bohr model, H atom emit light, principal energy levels, s, p, d, & f orbitals, probability map or density, Pauli Exclusion Principle, deBroglie matter wavelength, electron configuration, periodic properties, ionization energy, atomic siz ...
... electromagnetic radiation, emr, wavelength, frequency, photon, Bohr model, H atom emit light, principal energy levels, s, p, d, & f orbitals, probability map or density, Pauli Exclusion Principle, deBroglie matter wavelength, electron configuration, periodic properties, ionization energy, atomic siz ...
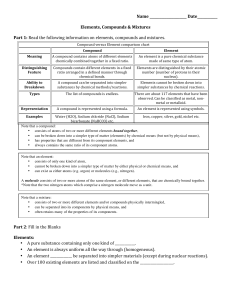
elements and compounds
... Table as we see it today. It is organized in order of an increasing atomic mass. He also grouped elements that bonded alike and had similar properties – he even predicted a few. ...
... Table as we see it today. It is organized in order of an increasing atomic mass. He also grouped elements that bonded alike and had similar properties – he even predicted a few. ...
Science - Atomic Structure
... atoms and nothing else (“atom” in Greek means that which can’t be cut or divided); atoms of the same kind form a pure “element” Alchemy in middle ages • Start of modern chemistry Lavoisier and oxygen: the idea that matter is not gained or lost in chemical reactions John Dalton revives the theory of ...
... atoms and nothing else (“atom” in Greek means that which can’t be cut or divided); atoms of the same kind form a pure “element” Alchemy in middle ages • Start of modern chemistry Lavoisier and oxygen: the idea that matter is not gained or lost in chemical reactions John Dalton revives the theory of ...
Chapter 2choutline - Madison County Schools
... The electron cloud model states that energy levels are ____________________regions of space around the nucleus in which _______________ are most likely found. The spherical regions where electrons travel may be depicted as ________________ around the nucleus. The space around the _________________of ...
... The electron cloud model states that energy levels are ____________________regions of space around the nucleus in which _______________ are most likely found. The spherical regions where electrons travel may be depicted as ________________ around the nucleus. The space around the _________________of ...
Intro. To Matter Jeopardy Review for Unit Test # Question Answer
... metals, nonmetals, or metalloids? ...
... metals, nonmetals, or metalloids? ...
Word format
... For example, each and every H atom has exactly ____ proton (atomic # = 1). Can atoms of the same element have different mass numbers? ...
... For example, each and every H atom has exactly ____ proton (atomic # = 1). Can atoms of the same element have different mass numbers? ...