chapter2 2012 (no naming)
... 1. These isotopes decay over time 2. Emit other particles and are transformed into other elements • Particles emitted 1. Beta (β) particles: High speed electrons 2. Alpha (α) particles: helium nuclei 3. Gamma (γ) rays: high energy light ...
... 1. These isotopes decay over time 2. Emit other particles and are transformed into other elements • Particles emitted 1. Beta (β) particles: High speed electrons 2. Alpha (α) particles: helium nuclei 3. Gamma (γ) rays: high energy light ...
Properties of Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids
... Atomic Masses: What is the difference between the mass number for Carbon–14 and carbon’s atomic mass of 12.011 amu? ...
... Atomic Masses: What is the difference between the mass number for Carbon–14 and carbon’s atomic mass of 12.011 amu? ...
Biology – The Living Environment
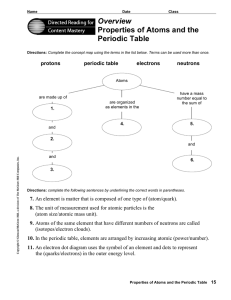
... Elements are arranged in the periodic table by increasing atomic number. The atomic number tells you the number of protons in an element. Because the charge on an atom must be neutral, the atomic number also tells you the number of electrons in an atom. Nearly the entire mass of an atom exists in t ...
... Elements are arranged in the periodic table by increasing atomic number. The atomic number tells you the number of protons in an element. Because the charge on an atom must be neutral, the atomic number also tells you the number of electrons in an atom. Nearly the entire mass of an atom exists in t ...
Electron
... • A subatomic particle of the nucleus of an atom without a charge that contributes to the mass of an atom. ...
... • A subatomic particle of the nucleus of an atom without a charge that contributes to the mass of an atom. ...
Matter
... electron is likely to be found. Each energy levels can hold only a limited number of electrons. The smallest, innermost energy level can hold only two electrons. The second energy level can hold up to eight electrons. The third energy level can hold up to 8 electrons. The 4th & 5th can hold up to 18 ...
... electron is likely to be found. Each energy levels can hold only a limited number of electrons. The smallest, innermost energy level can hold only two electrons. The second energy level can hold up to eight electrons. The third energy level can hold up to 8 electrons. The 4th & 5th can hold up to 18 ...
Reading Assignment Worksheet on Atoms - District 196 e
... 2. In this table, where are the metals located? 3. Where are the nonmetals located? 4. What are the elements in Groups 3 through 12 called? 5. What are the elements called that are next to the stairstep-shaped line on the right side of the table? 6. What do we call the letter or letters that represe ...
... 2. In this table, where are the metals located? 3. Where are the nonmetals located? 4. What are the elements in Groups 3 through 12 called? 5. What are the elements called that are next to the stairstep-shaped line on the right side of the table? 6. What do we call the letter or letters that represe ...
IPS Unit 2 Worksheet Packet
... ____ 11. An atom has a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by a large region in which scientists can predict where an electron is likely to be found. ____ 12. An atom is made of positively charged, pudding like material through which negatively charged particles are scattered. ____ 13. In a ...
... ____ 11. An atom has a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by a large region in which scientists can predict where an electron is likely to be found. ____ 12. An atom is made of positively charged, pudding like material through which negatively charged particles are scattered. ____ 13. In a ...
Atoms and their Structure
... • Organized by atomic number • Periodic Law: elements are grouped (in the same columns) according to similar physical and chemical properties • Period = horizontal row of periodic table; 7 periods • Group = vertical column, also called a family; 18 groups ...
... • Organized by atomic number • Periodic Law: elements are grouped (in the same columns) according to similar physical and chemical properties • Period = horizontal row of periodic table; 7 periods • Group = vertical column, also called a family; 18 groups ...
Democritus John Dalton Joseph John (J.J.) Thomson Dimitri
... Developed the first periodic table The periodic table was arranged according to increasing atomic weight, and left spaces for elements that were yet to be discovered. Later versions refined & expanded the table. ...
... Developed the first periodic table The periodic table was arranged according to increasing atomic weight, and left spaces for elements that were yet to be discovered. Later versions refined & expanded the table. ...
34.) Write out the set of four quantum numbers for the last electron
... 6.) What is the mass of 15 nickels? 7.) What is the density of 15 nickels? Unit 2 * Classify as element, compound, solution, or heterogeneous mixture. 8.) Flat soda 9.) Potassium iodide 10.) Iodine 11.) Potassium iodide completely dissolved in water 12.) Soil 13.) Chromium * Classify as chemical or ...
... 6.) What is the mass of 15 nickels? 7.) What is the density of 15 nickels? Unit 2 * Classify as element, compound, solution, or heterogeneous mixture. 8.) Flat soda 9.) Potassium iodide 10.) Iodine 11.) Potassium iodide completely dissolved in water 12.) Soil 13.) Chromium * Classify as chemical or ...
File
... 1913 Ad Neil bohr proposes a theory “ Bohr Model” of the atom in which the electrons are restricted to specific shells around the nucleus. The amount of energy an electron has is related to how far it is from the nucleus. 1920’S Further discoveries were made about the behaviour of electrons in atoms ...
... 1913 Ad Neil bohr proposes a theory “ Bohr Model” of the atom in which the electrons are restricted to specific shells around the nucleus. The amount of energy an electron has is related to how far it is from the nucleus. 1920’S Further discoveries were made about the behaviour of electrons in atoms ...
HISTORY OF THE ATOM AND ATOMIC THEORY
... through the foil, a few would be slightly deflected. – most went through, but some were deflected by a large amount – this indicated there was a positive charge in the center of the atom, and the center was small compared to the size of the atom ...
... through the foil, a few would be slightly deflected. – most went through, but some were deflected by a large amount – this indicated there was a positive charge in the center of the atom, and the center was small compared to the size of the atom ...
Pure Substances and Mixtures
... • Valence electrons is the name given to electrons in the last energy level of the atom. There will NEVER be more than 8 valence electrons • Elements in columns 1A through VIIIA: the number of valence electrons can be determined by the column number; 1A has 1 valence electron, IIA has 2 valence elec ...
... • Valence electrons is the name given to electrons in the last energy level of the atom. There will NEVER be more than 8 valence electrons • Elements in columns 1A through VIIIA: the number of valence electrons can be determined by the column number; 1A has 1 valence electron, IIA has 2 valence elec ...
Ch 18 - Atoms and Elements
... d. Electrons are found in orbitals within energy levels 1) s orbital a) sphere shaped b) closest to the nucleus c) holds 2 electrons 2) p orbital a) dumbbell-shaped b) 3 different orientations each holding 2 electrons – total 6 electrons ...
... d. Electrons are found in orbitals within energy levels 1) s orbital a) sphere shaped b) closest to the nucleus c) holds 2 electrons 2) p orbital a) dumbbell-shaped b) 3 different orientations each holding 2 electrons – total 6 electrons ...
Basic structure of atoms
... Electron cloud • Electrons move very rapidly in complicated paths called orbitals. • Because of this motion, they appear to form a cloud. – Negative charge -1 – Mass: 9.1 x10-28 grams – Symbols include e-, -1e0 ...
... Electron cloud • Electrons move very rapidly in complicated paths called orbitals. • Because of this motion, they appear to form a cloud. – Negative charge -1 – Mass: 9.1 x10-28 grams – Symbols include e-, -1e0 ...
Name Date Class Chapter 6 – The Periodic Table Guided Reading
... Which type of elements tend to be good conductors or heat and electrical current? ...
... Which type of elements tend to be good conductors or heat and electrical current? ...
Atoms pg. 102
... Ancient Greeks proposed the idea of atoms. The theory of atoms grew as more evidence was collected over time. ...
... Ancient Greeks proposed the idea of atoms. The theory of atoms grew as more evidence was collected over time. ...
Atoms, Elements, and the Periodic Table Part 1: The Atomic Model
... Rutherford discovered protons and the nucleus. He showed that atoms have (+) particles in the center, and are mostly empty space. ...
... Rutherford discovered protons and the nucleus. He showed that atoms have (+) particles in the center, and are mostly empty space. ...
Atoms - SWThornton
... Atoms may neither be divided nor destroyed. Atoms may be combined, separated, and rearranged to form new compounds. Atoms of different elements combine in whole-number ratios to form compounds. ...
... Atoms may neither be divided nor destroyed. Atoms may be combined, separated, and rearranged to form new compounds. Atoms of different elements combine in whole-number ratios to form compounds. ...
O 2 (g)
... Noble Gas Configurations • The inner-most electrons of an element comprise what is known as a noble gas core. – At the close of each shell, you have a noble gas configuration. Noble gases are chemically inactive because they have completely filled shells. • Lithium, for example, has a two electron ...
... Noble Gas Configurations • The inner-most electrons of an element comprise what is known as a noble gas core. – At the close of each shell, you have a noble gas configuration. Noble gases are chemically inactive because they have completely filled shells. • Lithium, for example, has a two electron ...
10-2 Intensive Chemistry Review for Chapters 3
... organized by increasing _________________. 24. Know the following terms and locations relating to the periodic table: group, family, period, transition metals, main group elements, metalloids, active metals, non-metals, rare earth metals, alkali metals, halogens, noble gases, alkaline earth metals, ...
... organized by increasing _________________. 24. Know the following terms and locations relating to the periodic table: group, family, period, transition metals, main group elements, metalloids, active metals, non-metals, rare earth metals, alkali metals, halogens, noble gases, alkaline earth metals, ...
A Thumbnail Review of Regents Chemistry
... Metal atoms LOSE ELECTRONS to form smaller, positive ions Non Metal atoms GAIN ELECTRONS to form larger, negative ions Down a Group, elements get larger (more shells) and more metallic = lower IE and EN Across a Period, elements get smaller and less metallic = higher IE and EN Most metallic element ...
... Metal atoms LOSE ELECTRONS to form smaller, positive ions Non Metal atoms GAIN ELECTRONS to form larger, negative ions Down a Group, elements get larger (more shells) and more metallic = lower IE and EN Across a Period, elements get smaller and less metallic = higher IE and EN Most metallic element ...