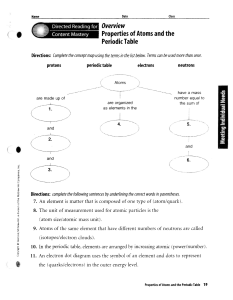
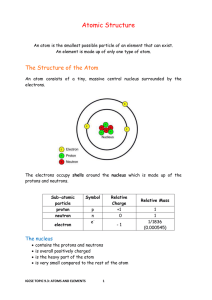
Atomic Theory & the Periodic Table
... valence e- absorb that packet of energy & become unstable. In order to return to stability (lower their energy) they “spit out” that energy in the form of a photon that has a frequency in the visible light part of the electromagnetic spectrum that we can ...
... valence e- absorb that packet of energy & become unstable. In order to return to stability (lower their energy) they “spit out” that energy in the form of a photon that has a frequency in the visible light part of the electromagnetic spectrum that we can ...
CHEMISTRY unit 2
... Elements are made of atoms. All atoms of element are identical. Atoms of a given element are different from those of ...
... Elements are made of atoms. All atoms of element are identical. Atoms of a given element are different from those of ...
Shiny, Happy Pretest - Alex LeMay – Science
... that Rutherford should let Marsden get some lab experience. __________________________ 15. Believed that the world was made of matter that could be divided infinitely. _____________ 16. Figured out that radiation can be divided into alpha particles, beta particles and gamma rays and that atoms were ...
... that Rutherford should let Marsden get some lab experience. __________________________ 15. Believed that the world was made of matter that could be divided infinitely. _____________ 16. Figured out that radiation can be divided into alpha particles, beta particles and gamma rays and that atoms were ...
form revision a
... There are two types of compound. Covalent compounds form when non-metal atoms form covalent bonds by sharing their outer electrons. Covalent compounds exist as molecules. Ionic compounds form when metal atoms join to non-metal atoms by transferring electron(s) from the metal to the non-metal. The re ...
... There are two types of compound. Covalent compounds form when non-metal atoms form covalent bonds by sharing their outer electrons. Covalent compounds exist as molecules. Ionic compounds form when metal atoms join to non-metal atoms by transferring electron(s) from the metal to the non-metal. The re ...
chapter02_part1_lecture - bloodhounds Incorporated
... before the next higher level contains any electrons. ...
... before the next higher level contains any electrons. ...
PowerPoint
... • He determined that most of the atom was made up of 'empty space'. • Before this, everyone figured atoms were solid mixes of all the different particles. • This is how we know the weight of an atom is all in a small nucleus in the center. ...
... • He determined that most of the atom was made up of 'empty space'. • Before this, everyone figured atoms were solid mixes of all the different particles. • This is how we know the weight of an atom is all in a small nucleus in the center. ...
Chap 1-3 Review
... In terms of electrons, what is the primary difference between ionic and covalently boned compounds? ...
... In terms of electrons, what is the primary difference between ionic and covalently boned compounds? ...
What is an atom?
... • Suggested all atoms of a given element were alike • Believed different atoms could join together to form compounds • His theories are considered the foundation for modern atomic theory ...
... • Suggested all atoms of a given element were alike • Believed different atoms could join together to form compounds • His theories are considered the foundation for modern atomic theory ...
Atomic Theory
... Discovered electron clouds (s, p, d, f) Explains that electrons move like waves and not in a ...
... Discovered electron clouds (s, p, d, f) Explains that electrons move like waves and not in a ...
Atomic Structure Notes
... □ Horizontal Rows (label these from top to bottom #’s 1 through 7. The row number ...
... □ Horizontal Rows (label these from top to bottom #’s 1 through 7. The row number ...
Getting to Know: Periodic Table
... them. Should he classify the elements by their state at a certain temperature? Should he group them by color? Which system would be most useful? Mendeleev decided to group the elements by specific chemical properties. After much research, he used the properties and atomic masses of the elements to a ...
... them. Should he classify the elements by their state at a certain temperature? Should he group them by color? Which system would be most useful? Mendeleev decided to group the elements by specific chemical properties. After much research, he used the properties and atomic masses of the elements to a ...
Midterm Review File
... 19. Answer the following questions about the periodic table. a. Explain why noble gases are inert and do not form ions. b. Identify the name of the group that contains the element fluorine _______________ c. Give the name of the element in the alkali group that has the greatest electron affinity ___ ...
... 19. Answer the following questions about the periodic table. a. Explain why noble gases are inert and do not form ions. b. Identify the name of the group that contains the element fluorine _______________ c. Give the name of the element in the alkali group that has the greatest electron affinity ___ ...
File - Mr. Gittermann
... • The number of protons in a nucleus; all atoms of any given element have the same atomic number; because an uncharged atom has the same number of protons and electrons, typically the number of electrons is the same as the atomic number ...
... • The number of protons in a nucleus; all atoms of any given element have the same atomic number; because an uncharged atom has the same number of protons and electrons, typically the number of electrons is the same as the atomic number ...
Review of the Atom
... Ground state: electrons in lowest possible energy levels Excited state: one or more electrons move up to a higher energy level ...
... Ground state: electrons in lowest possible energy levels Excited state: one or more electrons move up to a higher energy level ...
CHAPTER 4 ATOMIC STRUCTURE
... • Same atomic number but different mass #’s • Ex. Oxygen-16, 17, and 18 • All oxygen atoms have 8 protons, but some have 9 or 10 neutrons • Ques. 1-7 pg. 112 ...
... • Same atomic number but different mass #’s • Ex. Oxygen-16, 17, and 18 • All oxygen atoms have 8 protons, but some have 9 or 10 neutrons • Ques. 1-7 pg. 112 ...
Models of the Atom
... properties, and is a form of energy, maybe since electrons are particles with mass, maybe they can have energy properties • Since electrons cannot exist between energy levels, they only “jump” them, and get or give off energy. • We will get back to this in a few days! ...
... properties, and is a form of energy, maybe since electrons are particles with mass, maybe they can have energy properties • Since electrons cannot exist between energy levels, they only “jump” them, and get or give off energy. • We will get back to this in a few days! ...
Section 2.1
... • All atoms of a given element are identical to one another in mass and other properties, but atoms of an element are unique to that element only. • Atoms of an element are not changed into atoms of a different element by chemical reactions; they are neither created nor destroyed. • Compounds are fo ...
... • All atoms of a given element are identical to one another in mass and other properties, but atoms of an element are unique to that element only. • Atoms of an element are not changed into atoms of a different element by chemical reactions; they are neither created nor destroyed. • Compounds are fo ...
Chapter 2 - Speedway High School
... • Atoms of the various elements differ in number of subatomic particles – Atomic number – Mass number – Atomic mass ...
... • Atoms of the various elements differ in number of subatomic particles – Atomic number – Mass number – Atomic mass ...
9.3 Atoms and Elements notes
... number of electrons in an atom = number of protons Electrons are arranged in energy levels (also known as shells) around the nucleus. The lowest energy levels are always filled first. These are closer to the nucleus and hold the least numbers of electrons. The first energy level can only hold 2 el ...
... number of electrons in an atom = number of protons Electrons are arranged in energy levels (also known as shells) around the nucleus. The lowest energy levels are always filled first. These are closer to the nucleus and hold the least numbers of electrons. The first energy level can only hold 2 el ...
Atomic number
... How many protons does Calcium have? What element has 17 protons and 18 neutrons? What is its atomic number? What is its atomic mass? ...
... How many protons does Calcium have? What element has 17 protons and 18 neutrons? What is its atomic number? What is its atomic mass? ...
Periodic Table
... electrons are also called valence electrons. They are the ones involved in chemical bonds with other elements. Besides that, a row goes from left to right, it’s is called a period. Elements of the same period have the same number of electron shells. - Every element in the first column (group one) ha ...
... electrons are also called valence electrons. They are the ones involved in chemical bonds with other elements. Besides that, a row goes from left to right, it’s is called a period. Elements of the same period have the same number of electron shells. - Every element in the first column (group one) ha ...