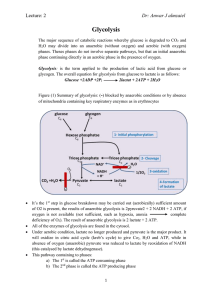
Glycolysis
... - Pyruvate: enters the mitochondria & is converted into acetyl CoA. Acetyl CoA enters citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to yield energy in the form of ATP - NADH: utilizes mitochondria & oxygen to yield energy 2- In cells with no mitochondria or adequate oxygen (or Both) (Anaerobic glycolysis) Lactate ...
... - Pyruvate: enters the mitochondria & is converted into acetyl CoA. Acetyl CoA enters citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to yield energy in the form of ATP - NADH: utilizes mitochondria & oxygen to yield energy 2- In cells with no mitochondria or adequate oxygen (or Both) (Anaerobic glycolysis) Lactate ...
Key enzymes in glycolysis
... - Pyruvate: enters the mitochondria & is converted into acetyl CoA. Acetyl CoA enters citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to yield energy in the form of ATP - NADH: utilizes mitochondria & oxygen to yield energy 2- In cells with no mitochondria or adequate oxygen (or Both) (Anaerobic glycolysis) Lactate ...
... - Pyruvate: enters the mitochondria & is converted into acetyl CoA. Acetyl CoA enters citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to yield energy in the form of ATP - NADH: utilizes mitochondria & oxygen to yield energy 2- In cells with no mitochondria or adequate oxygen (or Both) (Anaerobic glycolysis) Lactate ...
Photosynthesis II - christophersonbiology
... Wake-up 1. Write the summative equation for photosynthesis. 2. In examining the equation in #1, how does the light-dependent reaction contribute to ...
... Wake-up 1. Write the summative equation for photosynthesis. 2. In examining the equation in #1, how does the light-dependent reaction contribute to ...
METABOLISM IN HEALTH AND DISEASES I Lecture 2 Pentose
... ribose-5-P with NADPH by by-passing the oxidative steps. • This is achieved by the withdrawal of F-6P and G-3-P, but not glucose-6-P, from glycolysis. • The reaction of transketolase and transaldolase on F-6-P ...
... ribose-5-P with NADPH by by-passing the oxidative steps. • This is achieved by the withdrawal of F-6P and G-3-P, but not glucose-6-P, from glycolysis. • The reaction of transketolase and transaldolase on F-6-P ...
Cellular Respiration: Supplying Energy to Metabolic Reactions
... * The average vertebrate consumes its own body weight in ATP every day! ...
... * The average vertebrate consumes its own body weight in ATP every day! ...
EXERCISE 7 Cellular Respiration
... Name 2 molecules that are used as the final electron acceptor if oxygen is not available. State the products formed in each case. ...
... Name 2 molecules that are used as the final electron acceptor if oxygen is not available. State the products formed in each case. ...
video slide - Green River Community College
... by combining with oxaloacetate, forming citrate • The next seven steps decompose the citrate back to oxaloacetate, making the process a ...
... by combining with oxaloacetate, forming citrate • The next seven steps decompose the citrate back to oxaloacetate, making the process a ...
AP Biology Chapter 9.2016
... • Electrons from NADH and FADH2 pass along an ETC analogous to ETC chains in photophosphorylation. • These electrons pass from one protein carrier to another along the chain, losing energy along the way • Follow with pages 172-175 ...
... • Electrons from NADH and FADH2 pass along an ETC analogous to ETC chains in photophosphorylation. • These electrons pass from one protein carrier to another along the chain, losing energy along the way • Follow with pages 172-175 ...
Chapter 14 Glycolysis Glucose 2 Pyruvate → → → 2 Lactate (sent to
... the mitochondria using either the malate aspartate shuttle system or the α-glycerol phosphate shuttle system. The use of the shuttle systems result in NAD+ left in the cytosol and NADH (or FADH2 depending on shuttle) in the mitochondria which enters the electron transport system. → Under anaerobic c ...
... the mitochondria using either the malate aspartate shuttle system or the α-glycerol phosphate shuttle system. The use of the shuttle systems result in NAD+ left in the cytosol and NADH (or FADH2 depending on shuttle) in the mitochondria which enters the electron transport system. → Under anaerobic c ...
WEEK 11
... Galactose This aldose does not occur freely in nature. It is found in brain and nervous tissue as a component of compounds called cerebrosides. Galactose polymerizes to form agar-agar, which is found in seaweed and is used to solidify broth in microbiology. ...
... Galactose This aldose does not occur freely in nature. It is found in brain and nervous tissue as a component of compounds called cerebrosides. Galactose polymerizes to form agar-agar, which is found in seaweed and is used to solidify broth in microbiology. ...
Cell Respiration
... • only about 2% of the energy available from the oxidation of glucose is captured as ATP • energy originally contained in glucose is still held in pyruvic acid ...
... • only about 2% of the energy available from the oxidation of glucose is captured as ATP • energy originally contained in glucose is still held in pyruvic acid ...
Dr: Anwar J almzaiel Glycolysis
... H2O may divide into an anaerobic (without oxygen) and aerobic (with oxygen) phases. Theses phases do not involve separate pathways, but that an initial anaerobic phase continuing directly in an aerobic phase in the presence of oxygen. Glycolysis: is the term applied to the production of lactic acid ...
... H2O may divide into an anaerobic (without oxygen) and aerobic (with oxygen) phases. Theses phases do not involve separate pathways, but that an initial anaerobic phase continuing directly in an aerobic phase in the presence of oxygen. Glycolysis: is the term applied to the production of lactic acid ...
P3- Biochemical Processes
... The nature of biochemical processes within cells Catabolic and anabolic reactions – reactions releasing or requiring energy Role of enzymes as protein catalysts The role of ATP and ADP in energy ...
... The nature of biochemical processes within cells Catabolic and anabolic reactions – reactions releasing or requiring energy Role of enzymes as protein catalysts The role of ATP and ADP in energy ...
Energy and Metabolism
... Plants, algae, and certain kinds of bacteria capture a fraction of this energy through photosynthesis. In photosynthesis, energy garnered from sunlight is used to combine small molecules (water and carbon dioxide) into more complex molecules (sugars). The energy is stored as potential energy in the ...
... Plants, algae, and certain kinds of bacteria capture a fraction of this energy through photosynthesis. In photosynthesis, energy garnered from sunlight is used to combine small molecules (water and carbon dioxide) into more complex molecules (sugars). The energy is stored as potential energy in the ...
Bio 226: Cell and Molecular Biology
... • PSII sets Topt & upper limit for C4 plants • Topt for C3 also depends on photorespiration • Limiting factor varies at lower T depending on which enzymes fall behind -> rubisco usually limits C3 ...
... • PSII sets Topt & upper limit for C4 plants • Topt for C3 also depends on photorespiration • Limiting factor varies at lower T depending on which enzymes fall behind -> rubisco usually limits C3 ...
Figure 4.5 - Amazon S3
... quantified and expressed? How can the energy released from one reaction be compared to that of another reaction? A measurement of free energy is used to quantify these energy transfers. Recall that according to the second law of thermodynamics, all energy transfers involve the loss of some amount of ...
... quantified and expressed? How can the energy released from one reaction be compared to that of another reaction? A measurement of free energy is used to quantify these energy transfers. Recall that according to the second law of thermodynamics, all energy transfers involve the loss of some amount of ...
Concepts of Biology
... quantified and expressed? How can the energy released from one reaction be compared to that of another reaction? A measurement of free energy is used to quantify these energy transfers. Recall that according to the second law of thermodynamics, all energy transfers involve the loss of some amount of ...
... quantified and expressed? How can the energy released from one reaction be compared to that of another reaction? A measurement of free energy is used to quantify these energy transfers. Recall that according to the second law of thermodynamics, all energy transfers involve the loss of some amount of ...
4|HOW CELLS OBTAIN ENERGY
... quantified and expressed? How can the energy released from one reaction be compared to that of another reaction? A measurement of free energy is used to quantify these energy transfers. Recall that according to the second law of thermodynamics, all energy transfers involve the loss of some amount of ...
... quantified and expressed? How can the energy released from one reaction be compared to that of another reaction? A measurement of free energy is used to quantify these energy transfers. Recall that according to the second law of thermodynamics, all energy transfers involve the loss of some amount of ...
Citric Acid Cycle
... • One acetyl enters in a form of Acetyl-CoA • Carbon is oxidized to CO2 • Electrons from oxidation are captured on 3 NADH and 1 FADH2 • Production of one GTP (ATP) • One molecule of oxaloacetate reacts to one citrate ...
... • One acetyl enters in a form of Acetyl-CoA • Carbon is oxidized to CO2 • Electrons from oxidation are captured on 3 NADH and 1 FADH2 • Production of one GTP (ATP) • One molecule of oxaloacetate reacts to one citrate ...
PowerPoint Show - Science Prof Online
... • The SPO Virtual Classrooms offer many educational resources, including practice test questions, review questions, lecture PowerPoints, video tutorials, sample assignments and course syllabi. New materials are continually being developed, so check back frequently, or follow us on Facebook (Science ...
... • The SPO Virtual Classrooms offer many educational resources, including practice test questions, review questions, lecture PowerPoints, video tutorials, sample assignments and course syllabi. New materials are continually being developed, so check back frequently, or follow us on Facebook (Science ...
File
... B) cyanide is an electron transport blocker, while dinitrophenol makes the membrane of the mitochondrion leaky to H+ ions. C) cyanide makes the membrane of mitochondria leaky to H+ ions and prevents a concentration gradient from building up, while dinitrophenol blocks the passage of electrons throug ...
... B) cyanide is an electron transport blocker, while dinitrophenol makes the membrane of the mitochondrion leaky to H+ ions. C) cyanide makes the membrane of mitochondria leaky to H+ ions and prevents a concentration gradient from building up, while dinitrophenol blocks the passage of electrons throug ...
Bell work
... and Krebs to create ATP • Electron Transport - NAPH and FADH pass from carrier to carrier to power hydrogen pumps and create a hydrogen gradient in inter-membrane space! • ATP Production ATP synthase allows H to flow through like turbine (into matix) and produce ATP ...
... and Krebs to create ATP • Electron Transport - NAPH and FADH pass from carrier to carrier to power hydrogen pumps and create a hydrogen gradient in inter-membrane space! • ATP Production ATP synthase allows H to flow through like turbine (into matix) and produce ATP ...
File
... B) cyanide is an electron transport blocker, while dinitrophenol makes the membrane of the mitochondrion leaky to H+ ions. C) cyanide makes the membrane of mitochondria leaky to H+ ions and prevents a concentration gradient from building up, while dinitrophenol blocks the passage of electrons throug ...
... B) cyanide is an electron transport blocker, while dinitrophenol makes the membrane of the mitochondrion leaky to H+ ions. C) cyanide makes the membrane of mitochondria leaky to H+ ions and prevents a concentration gradient from building up, while dinitrophenol blocks the passage of electrons throug ...
Final Exam (5/15/14)
... 9. In some bacteria, the citric acid cycle runs backwards from oxaloacetate to citrate to reduce CO2. We feed bacteria with oxaloacetate labeled with14-C on the methyl carbon (-CH2-). a. Draw the citrate molecule indicating where the label is. If only a fraction of molecules contain that label, indi ...
... 9. In some bacteria, the citric acid cycle runs backwards from oxaloacetate to citrate to reduce CO2. We feed bacteria with oxaloacetate labeled with14-C on the methyl carbon (-CH2-). a. Draw the citrate molecule indicating where the label is. If only a fraction of molecules contain that label, indi ...