4.2 Overview of Photosynthesis
... (1) Chlorophyll is a molecule that absorbs light energy. (2) Two types of Chlorophyll Chlorophyll a (main pigment) Chlorophyll b (accessory pigment) (2) In plants, chlorophyll is found in organelles called chloroplasts. What do accessory pigments do? They capture the radiant energy that chlorophyll ...
... (1) Chlorophyll is a molecule that absorbs light energy. (2) Two types of Chlorophyll Chlorophyll a (main pigment) Chlorophyll b (accessory pigment) (2) In plants, chlorophyll is found in organelles called chloroplasts. What do accessory pigments do? They capture the radiant energy that chlorophyll ...
Peroxisomal oxidation of fatty acids
... Thus there will be production of 7 FADH2, 7 NADH molecules during the b-oxidation cycles. ...
... Thus there will be production of 7 FADH2, 7 NADH molecules during the b-oxidation cycles. ...
Document
... • How did we get from glucose to lactic acid? • In the liver, the process is “reversed” using ATP from aerobic respiration ...
... • How did we get from glucose to lactic acid? • In the liver, the process is “reversed” using ATP from aerobic respiration ...
Cellular Respiration
... Cellular Respiration Cellular Energy •The Stages of Cellular Respiration Cellular respiration has two stages. •Glycolysis The first stage of cellular respiration is called glycolysis. •Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration The second stage of cellular respiration is either aerobic respiration (in the p ...
... Cellular Respiration Cellular Energy •The Stages of Cellular Respiration Cellular respiration has two stages. •Glycolysis The first stage of cellular respiration is called glycolysis. •Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration The second stage of cellular respiration is either aerobic respiration (in the p ...
Getting a good rate of exchange – the mitochondrial ADP
... Three repeating units form the closed pore At the narrowest constriction at the base of the carrier pore, a set of smaller α-helices connect each pair of TM α-helices and lie adjacent to the inner surface of the membrane (view-4). These smaller αhelices are called the matrix helices as they lie in t ...
... Three repeating units form the closed pore At the narrowest constriction at the base of the carrier pore, a set of smaller α-helices connect each pair of TM α-helices and lie adjacent to the inner surface of the membrane (view-4). These smaller αhelices are called the matrix helices as they lie in t ...
Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration
... than the covalent bonds in water and carbon dioxide. B) Electrons are being moved from atoms that have a lower affinity for electrons (such as C) to atoms with a higher affinity for electrons (such as O). C) The oxidation of organic compounds can be used to make ATP. D) The electrons have a higher p ...
... than the covalent bonds in water and carbon dioxide. B) Electrons are being moved from atoms that have a lower affinity for electrons (such as C) to atoms with a higher affinity for electrons (such as O). C) The oxidation of organic compounds can be used to make ATP. D) The electrons have a higher p ...
Flashback - Max-Planck
... ATP during muscle contraction, creatine phosphate can compensate for this loss by transferring a phosphate group to adenosine diphosphate (ADP), turning it back into ATP. The formation of ATP by the transfer of a phosphate group from an energy-rich chemical compound to ADP plays a decisive role in m ...
... ATP during muscle contraction, creatine phosphate can compensate for this loss by transferring a phosphate group to adenosine diphosphate (ADP), turning it back into ATP. The formation of ATP by the transfer of a phosphate group from an energy-rich chemical compound to ADP plays a decisive role in m ...
งานนำเสนอ PowerPoint
... • the first committed step is too slow to permit its substrate and product to equilibrate • most of other reactions in a pathway function close to equilibrium • committed step = rate-limiting step ...
... • the first committed step is too slow to permit its substrate and product to equilibrate • most of other reactions in a pathway function close to equilibrium • committed step = rate-limiting step ...
Problem Set 8 Key
... cycle and generate 3 NADH + 1 FADH2 + 1 ATP total 10 ATP sacrificed per Acetyl-CoA x 8 = 80 ATP 1st Acetyl-CoA does not need to be converted to Malonyl-CoA because it is directly transferred onto the KS domain. The other 7 are carboxylated by ACC, which requires 1 ATP each 7 ATP Each round of el ...
... cycle and generate 3 NADH + 1 FADH2 + 1 ATP total 10 ATP sacrificed per Acetyl-CoA x 8 = 80 ATP 1st Acetyl-CoA does not need to be converted to Malonyl-CoA because it is directly transferred onto the KS domain. The other 7 are carboxylated by ACC, which requires 1 ATP each 7 ATP Each round of el ...
Hexokinase
... Figure 18.2 Pyruvate produced in glycolysis can be utilized by cells in several ways. In animals, pyruvate is normally converted to acetylcoenzyme A, which is then oxidized in the TCA cycle to produce CO2. When oxygen is limited, pyruvate can be converted to lactate. Alcoholic fermentation in yeast ...
... Figure 18.2 Pyruvate produced in glycolysis can be utilized by cells in several ways. In animals, pyruvate is normally converted to acetylcoenzyme A, which is then oxidized in the TCA cycle to produce CO2. When oxygen is limited, pyruvate can be converted to lactate. Alcoholic fermentation in yeast ...
8.2 What Happens During Glycolysis?
... the cell captures many high-energy electrons in carrier molecules: 10 NADH and 2 FADH2 for every glucose molecule that was broken down – These carriers each release two electrons into an electron transport chain (ETC), many copies of which are embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane ...
... the cell captures many high-energy electrons in carrier molecules: 10 NADH and 2 FADH2 for every glucose molecule that was broken down – These carriers each release two electrons into an electron transport chain (ETC), many copies of which are embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane ...
Pre AP Bio Nov 8 2016
... • How did we get from glucose to lactic acid? • In the liver, the process is “reversed” using ATP from aerobic respiration ...
... • How did we get from glucose to lactic acid? • In the liver, the process is “reversed” using ATP from aerobic respiration ...
Document
... If coupled directly to ADP ATP (7 kcal cost), 46 kcal/mole waste, and heat So the electrons on NADH (and FADH2) are not passed directly to oxygen, but to intermediate ...
... If coupled directly to ADP ATP (7 kcal cost), 46 kcal/mole waste, and heat So the electrons on NADH (and FADH2) are not passed directly to oxygen, but to intermediate ...
Krebs cycle
... • Electrons are transferred from succinate to FAD and then to ubiquinone (Q) in electron transport chain • Dehydrogenation is stereospecific; only the trans isomer is formed ...
... • Electrons are transferred from succinate to FAD and then to ubiquinone (Q) in electron transport chain • Dehydrogenation is stereospecific; only the trans isomer is formed ...
Exam #1
... Synthase. From chap 20: dehydrogenase, reductase, Lipases. There could also be questions pertaining to Case study 23, 25 and exercise #1 and #2. Also, Know how to draw Pyruvate. Chapter 18 –Know the basic structure of the mitochondria—what locations do glycolysis, citric acid cycle, electron transpo ...
... Synthase. From chap 20: dehydrogenase, reductase, Lipases. There could also be questions pertaining to Case study 23, 25 and exercise #1 and #2. Also, Know how to draw Pyruvate. Chapter 18 –Know the basic structure of the mitochondria—what locations do glycolysis, citric acid cycle, electron transpo ...
Anaerobic respiration with elemental sulfur and with disulfides
... ic matter [55,57,58]. Mesophilic and thermophilic sulfur reducers, mostly from the bacterial domain [59], have been isolated from environments such as anoxic marine or brackish sediments, fresh water sediments, bovine rumen, hot water pools from solfataric ¢elds, and volcanic hot springs. Among sulf ...
... ic matter [55,57,58]. Mesophilic and thermophilic sulfur reducers, mostly from the bacterial domain [59], have been isolated from environments such as anoxic marine or brackish sediments, fresh water sediments, bovine rumen, hot water pools from solfataric ¢elds, and volcanic hot springs. Among sulf ...
Chapter 8 - Plant Biology
... The results of some plant enzyme activities are easy to detect. The darkening of an apple fruit after it has been cut or bitten results from the action of the enzyme polyphenol oxidase on chemicals released from the cells. The softening of a tomato fruit as it ripens is caused by the action of seve ...
... The results of some plant enzyme activities are easy to detect. The darkening of an apple fruit after it has been cut or bitten results from the action of the enzyme polyphenol oxidase on chemicals released from the cells. The softening of a tomato fruit as it ripens is caused by the action of seve ...
Chapter 2 – The Molecules of Cells
... substances with different properties; composed of only one type of atom Atom – Smallest unit of matter that cannot be divided by chemical means Structure of an atom Composed of three subatomic (SA) particles Protons – positively charged SA particles; mass of 1 Dalton (mass of a hydrogen atom) Neutro ...
... substances with different properties; composed of only one type of atom Atom – Smallest unit of matter that cannot be divided by chemical means Structure of an atom Composed of three subatomic (SA) particles Protons – positively charged SA particles; mass of 1 Dalton (mass of a hydrogen atom) Neutro ...
Leaf Disk Assay
... obtain this energy from sunlight and convert it into sugars in the process called photosynthesis. Plants capture sunlight using chlorophyll molecules found in the chloroplasts of their cells. Chlorophyll gives plants their green color. The highest concentration of chloroplasts is found in plant leav ...
... obtain this energy from sunlight and convert it into sugars in the process called photosynthesis. Plants capture sunlight using chlorophyll molecules found in the chloroplasts of their cells. Chlorophyll gives plants their green color. The highest concentration of chloroplasts is found in plant leav ...
List of Possible Research Questions
... Na+/K+: How do enzymes differentiate between Na+ and K+? What is the physiological reason that 3Na+ are transported across neural membranes and only 2K+ are transported? Muscle cells: Ca2+ is required for muscle contraction. When the muscle contracts, Ca2+ rushes out of the sarcoplasmic reticulum an ...
... Na+/K+: How do enzymes differentiate between Na+ and K+? What is the physiological reason that 3Na+ are transported across neural membranes and only 2K+ are transported? Muscle cells: Ca2+ is required for muscle contraction. When the muscle contracts, Ca2+ rushes out of the sarcoplasmic reticulum an ...
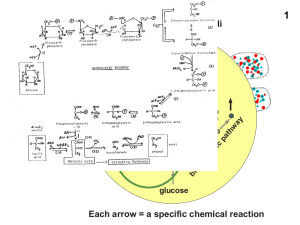
2, The Glyoxylate Pathway
... intermediates. GAP and F6P are consumed through glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation or recycled by gluconeogenesis to form G6P. In the latter case, 1 G6P can be converted, via 6 cycles of pentose phosphate pathway and gluconeogenesis, to 6 CO2 and 12 NADPH. • When R5P is needed more than NADPH, ...
... intermediates. GAP and F6P are consumed through glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation or recycled by gluconeogenesis to form G6P. In the latter case, 1 G6P can be converted, via 6 cycles of pentose phosphate pathway and gluconeogenesis, to 6 CO2 and 12 NADPH. • When R5P is needed more than NADPH, ...
Document
... intermediates. GAP and F6P are consumed through glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation or recycled by gluconeogenesis to form G6P. In the latter case, 1 G6P can be converted, via 6 cycles of pentose phosphate pathway and gluconeogenesis, to 6 CO2 and 12 NADPH. • When R5P is needed more than NADPH, ...
... intermediates. GAP and F6P are consumed through glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation or recycled by gluconeogenesis to form G6P. In the latter case, 1 G6P can be converted, via 6 cycles of pentose phosphate pathway and gluconeogenesis, to 6 CO2 and 12 NADPH. • When R5P is needed more than NADPH, ...
Knocking Down of Isoprene Emission Modiies the
... Plant PhysiologyÒ, July 2015, Vol. 168, pp. 859–870, www.plantphysiol.org Ó 2015 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved. ...
... Plant PhysiologyÒ, July 2015, Vol. 168, pp. 859–870, www.plantphysiol.org Ó 2015 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved. ...
Document
... The diagram represents a system in a space station that includes a tank containing algae. An astronaut from a spaceship boards the space station. A- State two changes in the chemical composition of the space station atmosphere that would result from turning on more lights. B- State two changes in t ...
... The diagram represents a system in a space station that includes a tank containing algae. An astronaut from a spaceship boards the space station. A- State two changes in the chemical composition of the space station atmosphere that would result from turning on more lights. B- State two changes in t ...