During the light reactions, there are two possible routes of electron
... photosystem II to photosystem I via an electron transport chain. 3. As the electrons are passed down the ETC, energy is given off. This energy is used to pump hydrogen ions (protons) from the stroma into the thylakoid lumen, creating a H+ gradient for chemiosmosis. Four protons are translocated into ...
... photosystem II to photosystem I via an electron transport chain. 3. As the electrons are passed down the ETC, energy is given off. This energy is used to pump hydrogen ions (protons) from the stroma into the thylakoid lumen, creating a H+ gradient for chemiosmosis. Four protons are translocated into ...
Photosynthesis Part 1
... photon. This high energy electron is then transferred to an electron acceptor via a redox reaction. The final electron acceptor in this case is NADP+. When it accepts two electrons it becomes NADPH (very similar to what we learned for NAD+ and NADH). It takes two photons to excite two electrons to r ...
... photon. This high energy electron is then transferred to an electron acceptor via a redox reaction. The final electron acceptor in this case is NADP+. When it accepts two electrons it becomes NADPH (very similar to what we learned for NAD+ and NADH). It takes two photons to excite two electrons to r ...
SBI 4U photosynthesis 1
... thylakoid membrane with proteins in the centre of them and make up a photosystem. Chlorophyll molecules in these photosystems are able to absorb light energy at various wavelengths. A pigment absorbs a photon, the molecule passes the energy to a unique pair of chlorophyll a molecules called the ...
... thylakoid membrane with proteins in the centre of them and make up a photosystem. Chlorophyll molecules in these photosystems are able to absorb light energy at various wavelengths. A pigment absorbs a photon, the molecule passes the energy to a unique pair of chlorophyll a molecules called the ...
Chapter 8 and 9 review - Iowa State University
... between the outer and inner mitochondrial membrane, what would expect to see if there was an increase in electron transport. a. The pH would likely go up. b. The pH would likely go down. c. The pH would likely remain the same. 4.The proton motive force a. drives the rotation of the ATP synthase. b. ...
... between the outer and inner mitochondrial membrane, what would expect to see if there was an increase in electron transport. a. The pH would likely go up. b. The pH would likely go down. c. The pH would likely remain the same. 4.The proton motive force a. drives the rotation of the ATP synthase. b. ...
PHOTOSYNTHESIS READING GUIDE Directions—Address each of
... 9. Where do plants obtain electrons to replace those that are lost when light strikes chlorophyll? ...
... 9. Where do plants obtain electrons to replace those that are lost when light strikes chlorophyll? ...
Quizon ch5-6-7-8new.doc
... 6. In endergonic reactions, __________. a. the reactants have more potential energy than the products b. energy is released c. a net input of energy is not required d. all of the above e. none of the above 7. In most land plants, photosynthesis occurs in cells of the __________ of the leaves, becaus ...
... 6. In endergonic reactions, __________. a. the reactants have more potential energy than the products b. energy is released c. a net input of energy is not required d. all of the above e. none of the above 7. In most land plants, photosynthesis occurs in cells of the __________ of the leaves, becaus ...
Slide 1
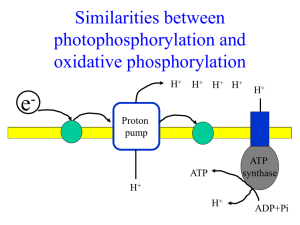
... • Imbedded in the inner mitochondria membrane are a series of electron carriers. These electron carriers pass electrons from NADH and FADH to one another down a red-ox stairway. The net result of this series of step-wise electron exchanges is to pump H+ (protons) out of the matrix into the outer com ...
... • Imbedded in the inner mitochondria membrane are a series of electron carriers. These electron carriers pass electrons from NADH and FADH to one another down a red-ox stairway. The net result of this series of step-wise electron exchanges is to pump H+ (protons) out of the matrix into the outer com ...
Unit 2 Test Review
... o Excited electron is passed through the first series of embedded membrane proteins Plastoquinone Cytochrome b6-f Complex Plastocyanin. Along the way, the free energy from the moving electron is used to pump 4 H+ from outside to inside the thylakoid, per 2 electrons (which travel in pairs always ...
... o Excited electron is passed through the first series of embedded membrane proteins Plastoquinone Cytochrome b6-f Complex Plastocyanin. Along the way, the free energy from the moving electron is used to pump 4 H+ from outside to inside the thylakoid, per 2 electrons (which travel in pairs always ...
Microbial Metabolism - ASAB-NUST
... matrix. • In eucaryotes they are found in the mitochondrial matrix. • The complete cycle appears to be functional in many aerobic bacteria, free-living protists, and fungi. ...
... matrix. • In eucaryotes they are found in the mitochondrial matrix. • The complete cycle appears to be functional in many aerobic bacteria, free-living protists, and fungi. ...
T/F 1. Pyruvate, the end product of glycolysis, is processed
... 6. How many molecules of CO2 are produced for each molecule of glucose that passes through glycolysis and the Krebs cycle? a. 2 b. 3 c. 6 d. 7 7. The electrons generated from the Krebs cycle are transferred to ____________ and then are shuttled to _______________. a. NAD+ / oxygen b. NAD+ / electron ...
... 6. How many molecules of CO2 are produced for each molecule of glucose that passes through glycolysis and the Krebs cycle? a. 2 b. 3 c. 6 d. 7 7. The electrons generated from the Krebs cycle are transferred to ____________ and then are shuttled to _______________. a. NAD+ / oxygen b. NAD+ / electron ...
Photosynthesis - Defiance City Schools
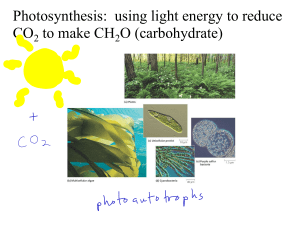
... converting carbon dioxide, water and light energy into oxygen and high energy sugar molecules. ...
... converting carbon dioxide, water and light energy into oxygen and high energy sugar molecules. ...
LEAVES AND PHOTOSYNTHESIS
... ! NADPH adds electrons ! Free energy of NADPH oxidation and ATP hydrolysis push the reaction forward ...
... ! NADPH adds electrons ! Free energy of NADPH oxidation and ATP hydrolysis push the reaction forward ...
the light reactions
... accessory pigments set in a protein matrix in the thylakoid membrane. The photon energy of the ant. pigment molecules transfer from pigment to pigment (resonance) until it reaches a chlorophyll a molecule in an area called the reaction centre. The excited electron of the chlorophyll a is captured by ...
... accessory pigments set in a protein matrix in the thylakoid membrane. The photon energy of the ant. pigment molecules transfer from pigment to pigment (resonance) until it reaches a chlorophyll a molecule in an area called the reaction centre. The excited electron of the chlorophyll a is captured by ...
Harvesting light
... antenna pigments transferring energy to each reaction centre. Plants found in full sunlight will tend to have antennae with fewer pigments. If the amount of light that is absorbed by plants exceeds their capacity for electron transfer, part of the photosynthetic electron transfer chain can be shut d ...
... antenna pigments transferring energy to each reaction centre. Plants found in full sunlight will tend to have antennae with fewer pigments. If the amount of light that is absorbed by plants exceeds their capacity for electron transfer, part of the photosynthetic electron transfer chain can be shut d ...
File
... Evidence of student learning is a demonstrated understanding of each of the following: 1. Electron transport chain reactions occur in chloroplasts (photosynthesis), mitochondria (cellular respiration) and prokaryotic plasma membranes. 2. In cellular respiration, electrons delivered by NADH and FADH2 ...
... Evidence of student learning is a demonstrated understanding of each of the following: 1. Electron transport chain reactions occur in chloroplasts (photosynthesis), mitochondria (cellular respiration) and prokaryotic plasma membranes. 2. In cellular respiration, electrons delivered by NADH and FADH2 ...
The light reactions
... Not all photosynthetic organisms use H2O as electron donor in photosynthesis; thus not all of them produce O2 while they produce ATP and NADPH. There are two types of photosynthesis: oxygenic (producing oxygen) photosynthesis and anoxygenic (not producing oxygen) photosynthesis. Only organisms wit ...
... Not all photosynthetic organisms use H2O as electron donor in photosynthesis; thus not all of them produce O2 while they produce ATP and NADPH. There are two types of photosynthesis: oxygenic (producing oxygen) photosynthesis and anoxygenic (not producing oxygen) photosynthesis. Only organisms wit ...
Where does a tree get its mass? - Biology 1510 Biological Principles
... Chlorophylls and other pigments form a lightharvesting complex in photosynthetic membranes ...
... Chlorophylls and other pigments form a lightharvesting complex in photosynthetic membranes ...
File
... • Light-dependent reaction: takes place in the thylakoid space and across the thylakoid membranes. • Light-independent reaction: takes place in the stroma. ...
... • Light-dependent reaction: takes place in the thylakoid space and across the thylakoid membranes. • Light-independent reaction: takes place in the stroma. ...
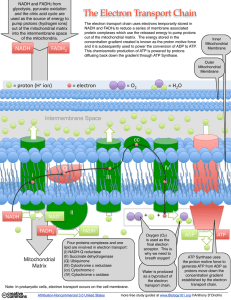
What is the Electron Transport Chain?
... The electron transport chain uses electrons temporarily stored in NADH and FADH2 to reduce a series of membrane associated protein complexes which use the released energy to pump protons out of the mitochondrial matrix. The energy stored in the concentration gradient created is known as the proton m ...
... The electron transport chain uses electrons temporarily stored in NADH and FADH2 to reduce a series of membrane associated protein complexes which use the released energy to pump protons out of the mitochondrial matrix. The energy stored in the concentration gradient created is known as the proton m ...
PHOTOSYNTHESIS • the light reaction involves three stages: • 1
... photosystem I contain chlorophyll a called P700 (absorption spectrum peaks at a wavelength of 700) photosystem II contain chlorophyll a called P680 the different peaks are due to the proteins associated with them at the reaction centre ...
... photosystem I contain chlorophyll a called P700 (absorption spectrum peaks at a wavelength of 700) photosystem II contain chlorophyll a called P680 the different peaks are due to the proteins associated with them at the reaction centre ...
Light Dependent Reactions
... were passed down the chain end up in the reaction centre of Photosystem I (P700), and another photon is needed to re-energize it so it can be released. * 5. The chain ends in the reduction of a molecule of NADP+ into NADPH. At this point, there is a large gradient of H+ across the membrane, as well ...
... were passed down the chain end up in the reaction centre of Photosystem I (P700), and another photon is needed to re-energize it so it can be released. * 5. The chain ends in the reduction of a molecule of NADP+ into NADPH. At this point, there is a large gradient of H+ across the membrane, as well ...