Recitation 6 The path of electron flow in photosynthesis from initial
... mitochondria and photosynthesis. For example, both involved a membrane-bound electron transport system, and the mechanisms of ATP production via proton gradients are similar. Electron transport in mitochondria, however, is from a good electron donor, NADH (or FADH2) to a good acceptor, O2. We have a ...
... mitochondria and photosynthesis. For example, both involved a membrane-bound electron transport system, and the mechanisms of ATP production via proton gradients are similar. Electron transport in mitochondria, however, is from a good electron donor, NADH (or FADH2) to a good acceptor, O2. We have a ...
Ch 6-1 Notes
... 3. The electrons are then transferred along a series of molecules called an electron transport chain ...
... 3. The electrons are then transferred along a series of molecules called an electron transport chain ...
CHLOROPLASTS, CALVIN CYCLE, PHOTOSYNTHETIC …
... There are three proton pumps 1) oxidation of water by PSII in the lumen releases protons 2) the cytochrome bf complex pumps protons from the stroma to the lumen 3) the reduction of NADP+ in the stroma removes protons ...
... There are three proton pumps 1) oxidation of water by PSII in the lumen releases protons 2) the cytochrome bf complex pumps protons from the stroma to the lumen 3) the reduction of NADP+ in the stroma removes protons ...
Oxidative phosphorylation (mitochondria)
... Two primary forms of energy are: Nucleotide triphosphate (e.g. ATP, GTP) Reducing power (NADH, NADPH) Two ways to make them: Through glycolysis (cytosol) Oxidative phosphorylation (mitochondria) ...
... Two primary forms of energy are: Nucleotide triphosphate (e.g. ATP, GTP) Reducing power (NADH, NADPH) Two ways to make them: Through glycolysis (cytosol) Oxidative phosphorylation (mitochondria) ...
REACTIONS OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS
... How is the Calvin cycle different from the light-dependent reactions? A. It takes place in the thylakoid membrane B. It takes place in the stroma. C. It requires light. D. It takes place in chloroplasts. Why does the space inside the thylakoid become positively charged during the light-dependent rea ...
... How is the Calvin cycle different from the light-dependent reactions? A. It takes place in the thylakoid membrane B. It takes place in the stroma. C. It requires light. D. It takes place in chloroplasts. Why does the space inside the thylakoid become positively charged during the light-dependent rea ...
PHOTOSYNTHESIS NOTES
... The light reactions of photosynthesis convert radiant (sunlight) energy into the potential chemical energy found between the carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen bonds in sugar (glucose). 1. Photosynthesis uses most of the energy in sunlight except green wavelengths (color that's reflected) 2. The light rea ...
... The light reactions of photosynthesis convert radiant (sunlight) energy into the potential chemical energy found between the carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen bonds in sugar (glucose). 1. Photosynthesis uses most of the energy in sunlight except green wavelengths (color that's reflected) 2. The light rea ...
Photosynthesis Light Dependent Reactions PPT
... molecule is now called NADPH, an electron carrier. 12 of these are created in all for this process… ...
... molecule is now called NADPH, an electron carrier. 12 of these are created in all for this process… ...
The light reactions
... Not all photosynthetic organisms use H2O as electron donor in photosynthesis; thus not all of them produce O2 while they produce ATP and NADPH. There are two types of photosynthesis: oxygenic (producing oxygen) photosynthesis and anoxygenic (not producing oxygen) photosynthesis. Only organisms wit ...
... Not all photosynthetic organisms use H2O as electron donor in photosynthesis; thus not all of them produce O2 while they produce ATP and NADPH. There are two types of photosynthesis: oxygenic (producing oxygen) photosynthesis and anoxygenic (not producing oxygen) photosynthesis. Only organisms wit ...
lecture1
... chlorophyll molecule which results in their excitation to higher energy levels. Thereafter, electrons from the excited chlorophyll molecules are transferred to specialized acceptor molecule and ultimately to NADP+ which is accompanied by ATP formation. Water serves as edonor (reducing agent) purpose ...
... chlorophyll molecule which results in their excitation to higher energy levels. Thereafter, electrons from the excited chlorophyll molecules are transferred to specialized acceptor molecule and ultimately to NADP+ which is accompanied by ATP formation. Water serves as edonor (reducing agent) purpose ...
Chemolithotrophs
... inorganic electron donor for energy and electrons. • Chemolithotrophs: reduced inorganic electron donor for energy and electrons. • Phototrophs: use light energy and an electron donor molecule (H2O, H2S, organic). • Both may be autotrophs: fix CO2 into organic carbon via the Calvin Cycle. ...
... inorganic electron donor for energy and electrons. • Chemolithotrophs: reduced inorganic electron donor for energy and electrons. • Phototrophs: use light energy and an electron donor molecule (H2O, H2S, organic). • Both may be autotrophs: fix CO2 into organic carbon via the Calvin Cycle. ...
Name
... THAN NADPH; ELECTRONS BACK UP IN THE ETC THAT SENDS ELECTRONS TO NADP+ REDUCTASE SO 1ST PROTEIN IN THAT ETC CYCLES BACK AND SENDS EXCIRTED ELECTRONS DOWN ETC BETWEEN PHOTOSYSTEM II AND PHOTOSYSTEM I (GENERATES ATP) 8c) How is NADPH concentration involved in feedback inhibition of noncyclic electron ...
... THAN NADPH; ELECTRONS BACK UP IN THE ETC THAT SENDS ELECTRONS TO NADP+ REDUCTASE SO 1ST PROTEIN IN THAT ETC CYCLES BACK AND SENDS EXCIRTED ELECTRONS DOWN ETC BETWEEN PHOTOSYSTEM II AND PHOTOSYSTEM I (GENERATES ATP) 8c) How is NADPH concentration involved in feedback inhibition of noncyclic electron ...
Document
... • Menaquinone in the QA site is singly reduced by an electron initially derived from the ChlSP (primary electron donor). • Ubiquinone in the QB site is then sequentially reduced (2 e-) and protonated (2H+ ) via QA forming UQH2. • UQH2 then exits from the QB binding pocket as a mobile 2 electron and ...
... • Menaquinone in the QA site is singly reduced by an electron initially derived from the ChlSP (primary electron donor). • Ubiquinone in the QB site is then sequentially reduced (2 e-) and protonated (2H+ ) via QA forming UQH2. • UQH2 then exits from the QB binding pocket as a mobile 2 electron and ...
Chloroplasts
... Photosystem II, the oxygens of two water molecules bind to a cluster of manganese atoms in an enzyme that enables electrons to be moved one at a time to fill the holes created by light in the chlorophyll molecules in the reaction centre. As soon as four electrons have been removed (requiring four qu ...
... Photosystem II, the oxygens of two water molecules bind to a cluster of manganese atoms in an enzyme that enables electrons to be moved one at a time to fill the holes created by light in the chlorophyll molecules in the reaction centre. As soon as four electrons have been removed (requiring four qu ...
Puzzle - UBC Blogs
... 18 time of day stomata are open in CAM plants 19 _____________ separation of fixation and Calvin cycle occurs in C4 plants 21 electron donor 22 conversion of light energy to chemical energy 23 pores that facilitate gas exchange 24 unit of organized pigments (mostly chlorophyll) that collect light en ...
... 18 time of day stomata are open in CAM plants 19 _____________ separation of fixation and Calvin cycle occurs in C4 plants 21 electron donor 22 conversion of light energy to chemical energy 23 pores that facilitate gas exchange 24 unit of organized pigments (mostly chlorophyll) that collect light en ...
Photosyn online lab
... 2. During photosynthesis a plant produces oxygen, carbon compounds, ATP, and NADPH. What is the function for each of those compounds? ...
... 2. During photosynthesis a plant produces oxygen, carbon compounds, ATP, and NADPH. What is the function for each of those compounds? ...
File
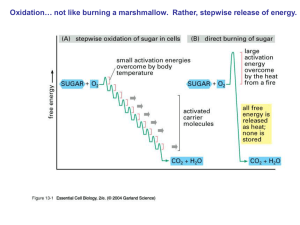
... added eg. ADP + Pi ATP because ATP is continuously being made at the same rate as it is being used up it is converted into Glucose-6phosphate (high energy) ...
... added eg. ADP + Pi ATP because ATP is continuously being made at the same rate as it is being used up it is converted into Glucose-6phosphate (high energy) ...
Thiobacillus thiooxidans
... • Pathways of oxygenic light reaction – Pair of chlorophyll based photosystems embedded in membrane • Chloroplast or plasma membrane ...
... • Pathways of oxygenic light reaction – Pair of chlorophyll based photosystems embedded in membrane • Chloroplast or plasma membrane ...
What role do pigments play in the process of photosynthesis
... 2. Electron carriers transport electrons to the next power station (photosystem I) and hydrogen is pumped into the thylakoid. Some energy is used pumping the hydrogen into the thylakoid thus creating a concentration gradient 3. Light energy is once again used for recharging the electron to a higher ...
... 2. Electron carriers transport electrons to the next power station (photosystem I) and hydrogen is pumped into the thylakoid. Some energy is used pumping the hydrogen into the thylakoid thus creating a concentration gradient 3. Light energy is once again used for recharging the electron to a higher ...
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
... chloroplasts and is stored through the synthesis of sugar (glucose) from carbon dioxide 1i – In the mitochondria and chloroplasts energy from electrons is stored for ATP production (Chemiosmosis) ...
... chloroplasts and is stored through the synthesis of sugar (glucose) from carbon dioxide 1i – In the mitochondria and chloroplasts energy from electrons is stored for ATP production (Chemiosmosis) ...
CH 8 Test Review
... 10. An electron carrier is a compound that can accept a pair of high-energy electrons and transfer them, along with most of their energy, to another molecule. 11. One of these carrier molecules is a compound known as NADP+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate). 12. Photosynthesis uses the en ...
... 10. An electron carrier is a compound that can accept a pair of high-energy electrons and transfer them, along with most of their energy, to another molecule. 11. One of these carrier molecules is a compound known as NADP+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate). 12. Photosynthesis uses the en ...