OverallQuiz2Ch5-8.doc
... 7. During photosynthesis, electrons are continuously lost from the reaction center of photosystem II. What source is used to replace these electrons? a. sunlight b. oxygen c. water d. carbon dioxide ...
... 7. During photosynthesis, electrons are continuously lost from the reaction center of photosystem II. What source is used to replace these electrons? a. sunlight b. oxygen c. water d. carbon dioxide ...
Chapter 5 Test Review
... 8. cellular respiration Section 2 1. photosynthesis 2. chlorophyll 3. red (675 nm) and blue (450 nm) 4. green wavelengths (525 nm) are reflected 5. oxygen gas (O2) 6. enter the electron transport chain of the thylakoid membrane 7. water is split to replace 2e- that enter the electron transport chain ...
... 8. cellular respiration Section 2 1. photosynthesis 2. chlorophyll 3. red (675 nm) and blue (450 nm) 4. green wavelengths (525 nm) are reflected 5. oxygen gas (O2) 6. enter the electron transport chain of the thylakoid membrane 7. water is split to replace 2e- that enter the electron transport chain ...
Photosynthesis
... provide almost all the energy for life on Earth. Autotrophs and Heterotrophs rely on this chemical energy to support their own growth and reproduction! ...
... provide almost all the energy for life on Earth. Autotrophs and Heterotrophs rely on this chemical energy to support their own growth and reproduction! ...
Chapter 1 Homework - due Tuesday, Sept
... ETC/chemiosmosis – 32-34 ATP – oxidative phosphorylation ...
... ETC/chemiosmosis – 32-34 ATP – oxidative phosphorylation ...
Chapter 1 Homework - due Tuesday, Sept
... ETC/chemiosmosis – 32-34 ATP – oxidative phosphorylation ...
... ETC/chemiosmosis – 32-34 ATP – oxidative phosphorylation ...
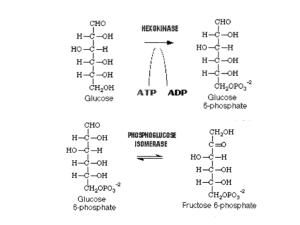
Glycolysis
... Energy for the body • Trapped in chemical bonds of fats, proteins, and carbs (potential) • liberate energy – break bonds – release energy, CO2 and H20 – Energy is transferred to ATP for use in the body ...
... Energy for the body • Trapped in chemical bonds of fats, proteins, and carbs (potential) • liberate energy – break bonds – release energy, CO2 and H20 – Energy is transferred to ATP for use in the body ...
CPS Activity: Photosynthesis Review
... following is required in order for photosynthesis to occur? water chlorophyll light energy all of the above ...
... following is required in order for photosynthesis to occur? water chlorophyll light energy all of the above ...
The Working Cell: Energy from Sunlight
... – Carotenoids are pigments that range in color from pale yellow to deep red • they are involved in the color changes of leaves in the fall • they funnel the energy from other wavelengths to chlorophyll a. ...
... – Carotenoids are pigments that range in color from pale yellow to deep red • they are involved in the color changes of leaves in the fall • they funnel the energy from other wavelengths to chlorophyll a. ...
Cellular Respiration 2
... Electron is passed to other molecules that have higher electronegativity • Reduces new acceptor ...
... Electron is passed to other molecules that have higher electronegativity • Reduces new acceptor ...
Unit 3 Study Guide: Energetics
... 7) What is the proton-motive force? How does it result in the formation of ATP? 8) How is chemiosmosis involved in cellular respiration? 9) During respiration, in what pathway does most energy flow? 10) Describe three ways in which fermentation differs from respiration. 11) Sketch and label a chloro ...
... 7) What is the proton-motive force? How does it result in the formation of ATP? 8) How is chemiosmosis involved in cellular respiration? 9) During respiration, in what pathway does most energy flow? 10) Describe three ways in which fermentation differs from respiration. 11) Sketch and label a chloro ...
Fermentation/ Citric Acid Cycle
... - Muscles are working hard (USING ATP) - You are breathing heavy (NOT GETTING ENOUGH OXYGEN) These are prefect conditions for FERMENTATION - After a hard workout, why are your muscles sore? o Answer: Lactic acid has built up in the CYTOSOL ...
... - Muscles are working hard (USING ATP) - You are breathing heavy (NOT GETTING ENOUGH OXYGEN) These are prefect conditions for FERMENTATION - After a hard workout, why are your muscles sore? o Answer: Lactic acid has built up in the CYTOSOL ...
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
... Photosystems Within the chloroplasts, chlorophyll is found in clusters within the thylakoid membranes. These clusters are called photosystems. When light hits the photosystem, energy is absorbed and electrons are promoted to an electron acceptor at a higher energy level. As the electrons fa ...
... Photosystems Within the chloroplasts, chlorophyll is found in clusters within the thylakoid membranes. These clusters are called photosystems. When light hits the photosystem, energy is absorbed and electrons are promoted to an electron acceptor at a higher energy level. As the electrons fa ...
Bioenergetics and Mitosis Review Sheet
... 24. What are the two types of fermentation? What are the products of each? Which organisms use what type of fermentation in the lack of oxygen? Chapter 10 25. What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis? 26. What are some photosynthetic pigments? What are the main ones? What color are they? 27. ...
... 24. What are the two types of fermentation? What are the products of each? Which organisms use what type of fermentation in the lack of oxygen? Chapter 10 25. What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis? 26. What are some photosynthetic pigments? What are the main ones? What color are they? 27. ...
Ch08Photosynthesis
... 4. Grana and stroma 5. Thylakoid membrane and compartment 6. Pigments Photosynthesis occurs in two essential phases. 1. Light-dependent: “photo” of photosynthesis. a. Power of sunlight excites electrons in pigment molecules. b. Excited electrons are carried down transport chain of redox reactions li ...
... 4. Grana and stroma 5. Thylakoid membrane and compartment 6. Pigments Photosynthesis occurs in two essential phases. 1. Light-dependent: “photo” of photosynthesis. a. Power of sunlight excites electrons in pigment molecules. b. Excited electrons are carried down transport chain of redox reactions li ...
Ch. 9 – Cellular Respiration Why does the energy stored in different
... In the ETC, the electron carriers, NADH and FADH2 that were produced in Glycolysis and Kreb’s are now going to drop off their high energy electrons and H+ ions onto the mitochondrial membrane. Once there, the energy of the electrons, with help from electron carrier proteins, will pump the H+ ions a ...
... In the ETC, the electron carriers, NADH and FADH2 that were produced in Glycolysis and Kreb’s are now going to drop off their high energy electrons and H+ ions onto the mitochondrial membrane. Once there, the energy of the electrons, with help from electron carrier proteins, will pump the H+ ions a ...
Electron transport chains in mitochondria
... called NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase; EC 1.6.5.3) two electrons are removed from NADH and transferred to a lipid-soluble carrier, ubiquinone (Q). The reduced product, ubiquinol (QH2) freely diffuses within the membrane, and Complex I translocates four protons (H+) across the membrane, thus producin ...
... called NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase; EC 1.6.5.3) two electrons are removed from NADH and transferred to a lipid-soluble carrier, ubiquinone (Q). The reduced product, ubiquinol (QH2) freely diffuses within the membrane, and Complex I translocates four protons (H+) across the membrane, thus producin ...
Photosynthesis - Weizmann Institute of Science
... enough to remove two electrons from each of two water molecules, making a molecule of O2 at a cost of four photons — one for each electron moved. Photosystem II performs this remarkable feat only when photosystem I is present to dispose of the electrons. Photosystem I grabs the four electrons and us ...
... enough to remove two electrons from each of two water molecules, making a molecule of O2 at a cost of four photons — one for each electron moved. Photosystem II performs this remarkable feat only when photosystem I is present to dispose of the electrons. Photosystem I grabs the four electrons and us ...
File
... light strikes PS II causing electrons in chlorophyll a in the reaction center to become excited the excited electrons are picked up by the primary electron acceptor & passed down an electron transport chain which drives the synthesis of ATP by chemiosmosis meanwhile, light strikes PS I causing e ...
... light strikes PS II causing electrons in chlorophyll a in the reaction center to become excited the excited electrons are picked up by the primary electron acceptor & passed down an electron transport chain which drives the synthesis of ATP by chemiosmosis meanwhile, light strikes PS I causing e ...
Electron Transport Chain _ETC
... transport chain, as electrons are passed down the electron transport chain, they lose much of their free energy. Part of this energy can be captured and stored by the production of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi). This process is called oxidative phosphorylation. The remainder of the free ...
... transport chain, as electrons are passed down the electron transport chain, they lose much of their free energy. Part of this energy can be captured and stored by the production of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi). This process is called oxidative phosphorylation. The remainder of the free ...
File
... 2) The electrons are not passed on to NADP+ Reductase (which would produce NADPH). Instead the electrons are passed down the ETC back to P700. [Fig. 10.14] This process is called cyclic photophosphorylation ...
... 2) The electrons are not passed on to NADP+ Reductase (which would produce NADPH). Instead the electrons are passed down the ETC back to P700. [Fig. 10.14] This process is called cyclic photophosphorylation ...
Simplified Photosynthesis
... the thylakoid. This make the inside of the thylakoid positive and the outside negative. H+ ions are also passing thru ATP Synthase ( an enzyme) and changing ADP ATP ...
... the thylakoid. This make the inside of the thylakoid positive and the outside negative. H+ ions are also passing thru ATP Synthase ( an enzyme) and changing ADP ATP ...
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
... • is a nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer.[1] ATP transports chemical energy within cells for ...
... • is a nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer.[1] ATP transports chemical energy within cells for ...
Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration
... o Chloroplasts: The Sites of Photosynthesis in Plants o Tracking Atoms Through Photosynthesis o The Two Stages of Photosynthesis: A Preview Concept 10.2: The Light Reactions Convert Solar Energy To Chemical Energy o The Nature of Sunlight o Photosynthetic Pigments: The Light Receptors o Excitation o ...
... o Chloroplasts: The Sites of Photosynthesis in Plants o Tracking Atoms Through Photosynthesis o The Two Stages of Photosynthesis: A Preview Concept 10.2: The Light Reactions Convert Solar Energy To Chemical Energy o The Nature of Sunlight o Photosynthetic Pigments: The Light Receptors o Excitation o ...