Anaerobic-and-Aerobic
... atmosphere. This type of respiration is useful today because the atmosphere is now 21% oxygen. However, some anaerobic organisms that evolved before the atmosphere contained oxygen have survived to the present. Therefore, anaerobic respiration, which takes place without oxygen, must also have advant ...
... atmosphere. This type of respiration is useful today because the atmosphere is now 21% oxygen. However, some anaerobic organisms that evolved before the atmosphere contained oxygen have survived to the present. Therefore, anaerobic respiration, which takes place without oxygen, must also have advant ...
respiration revision quiz
... In the reactions of respiration, coenzymes become …………………. as substrates become …………………….. . These are necessary because the reactions are catalysed by inefficient dehydrogenase ………………… . Hydrogen ATO ...
... In the reactions of respiration, coenzymes become …………………. as substrates become …………………….. . These are necessary because the reactions are catalysed by inefficient dehydrogenase ………………… . Hydrogen ATO ...
Campbell`s Biology, 9e (Reece et al.) Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration
... 4) Why does the oxidation of organic compounds by molecular oxygen to produce CO2 and water release free energy? A) The covalent bonds in organic molecules and molecular oxygen have more kinetic energy than the covalent bonds in water and carbon dioxide. B) Electrons are being moved from atoms that ...
... 4) Why does the oxidation of organic compounds by molecular oxygen to produce CO2 and water release free energy? A) The covalent bonds in organic molecules and molecular oxygen have more kinetic energy than the covalent bonds in water and carbon dioxide. B) Electrons are being moved from atoms that ...
AMPK and mTOR: Antagonist ATP Sensors
... (ADP) and a phosphate ion as well as liberating 7.3 kcal of free energy to be used for work. ADP levels increase as ATP is used for energy. The body uses three energetic pathways to maintain cellular ATP levels, phosphocreatine, glycolysis, and oxidative phosphorylation. Two enzymes are responsible ...
... (ADP) and a phosphate ion as well as liberating 7.3 kcal of free energy to be used for work. ADP levels increase as ATP is used for energy. The body uses three energetic pathways to maintain cellular ATP levels, phosphocreatine, glycolysis, and oxidative phosphorylation. Two enzymes are responsible ...
Full Text PDF
... this means that the overlapping of metal and ligand orbitals provides a path by which metal electrons can, and do, escape to a certain extent from 3d-ion towards ligands and molecule boundaries. The effect has been named "nephelauxetic" (expanding cloud, from Greek) [6]. Summing up: β values, which ...
... this means that the overlapping of metal and ligand orbitals provides a path by which metal electrons can, and do, escape to a certain extent from 3d-ion towards ligands and molecule boundaries. The effect has been named "nephelauxetic" (expanding cloud, from Greek) [6]. Summing up: β values, which ...
Metabolism: Energy, Enzymes, and Regulation
... principles of thermodynamics is required. The science of thermodynamics analyzes energy changes in a collection of matter (e.g., a cell or a plant) called a system. All other matter in the universe is called the surroundings. Thermodynamics focuses on the energy differences between the initial state ...
... principles of thermodynamics is required. The science of thermodynamics analyzes energy changes in a collection of matter (e.g., a cell or a plant) called a system. All other matter in the universe is called the surroundings. Thermodynamics focuses on the energy differences between the initial state ...
Chapter 7: Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy
... each catalyzed by a specific enzyme. • Metabolic pathways are often compartmentalized and are highly regulated. ...
... each catalyzed by a specific enzyme. • Metabolic pathways are often compartmentalized and are highly regulated. ...
Dr. V. Main Powerpoint
... Stepwise Energy Harvest via NAD+ and the Electron Transport Chain • In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps • Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme ...
... Stepwise Energy Harvest via NAD+ and the Electron Transport Chain • In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps • Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme ...
Chapter 14
... • FMNH2 and FADH2 donate one electron at a time • All subsequent steps proceed by one e- transfers Prentice Hall c2002 ...
... • FMNH2 and FADH2 donate one electron at a time • All subsequent steps proceed by one e- transfers Prentice Hall c2002 ...
Unit 2 Biochemistry Chp 8 Metabolism Notes
... The overall sequence of reactions is kept going by the huge free-energy difference between glucose and oxygen at the top of the energy “hill” and carbon dioxide and water at the “downhill” ...
... The overall sequence of reactions is kept going by the huge free-energy difference between glucose and oxygen at the top of the energy “hill” and carbon dioxide and water at the “downhill” ...
A2 revision
... mitochondria where carbon dioxide is produced (in the Krebs cycle and the link reaction). Glucose cannot enter the mitochondria, and the enzymes for breaking down glucose are only found in the cytoplasm not in mitochondria. You can also gain a mark for saying that carbon dioxide is produced by decar ...
... mitochondria where carbon dioxide is produced (in the Krebs cycle and the link reaction). Glucose cannot enter the mitochondria, and the enzymes for breaking down glucose are only found in the cytoplasm not in mitochondria. You can also gain a mark for saying that carbon dioxide is produced by decar ...
Photosynthesis: Introduction
... Go’ = +2840 kJ/mol Unfavorable Go’ explains the need for energy input. That is the role of light. ...
... Go’ = +2840 kJ/mol Unfavorable Go’ explains the need for energy input. That is the role of light. ...
Chapter 8 Notes
... • Heat (thermal energy) is kinetic energy associated with random movement of atoms or molecules • Potential energy is energy that matter possesses because of its location or structure • Chemical energy is potential energy available for release in a chemical reaction • Energy can be converted from on ...
... • Heat (thermal energy) is kinetic energy associated with random movement of atoms or molecules • Potential energy is energy that matter possesses because of its location or structure • Chemical energy is potential energy available for release in a chemical reaction • Energy can be converted from on ...
Compare and Contrast Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
... Is energy captured or released? Where does the energy come from? Is carbon dioxide used or released? Is oxygen used or released? Does the process require light? ...
... Is energy captured or released? Where does the energy come from? Is carbon dioxide used or released? Is oxygen used or released? Does the process require light? ...
Chapter 9
... NADH, forming lactate as an end product, with no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
... NADH, forming lactate as an end product, with no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
Ch 8 Chapter Summary
... transferred to the water as the diver enters it. ○ Some energy is converted to heat due to friction. ...
... transferred to the water as the diver enters it. ○ Some energy is converted to heat due to friction. ...
Chapter 8 Notes
... transferred to the water as the diver enters it. ○ Some energy is converted to heat due to friction. ...
... transferred to the water as the diver enters it. ○ Some energy is converted to heat due to friction. ...
Chemistry - Textbooks Online
... on the basis of their size, shape and orientation in space by using principal, azimuthal, magnetic and spin quantum numbers. ...
... on the basis of their size, shape and orientation in space by using principal, azimuthal, magnetic and spin quantum numbers. ...
Powerpoint
... Two sets of reactions: Light harvesting - converts light energy to chemical energy (ATP, NADPH) - splits H2O and produces O2 as byproduct ...
... Two sets of reactions: Light harvesting - converts light energy to chemical energy (ATP, NADPH) - splits H2O and produces O2 as byproduct ...
BCHM 463 Supplemental Problems for Friday, April 2, 2004 1. Write
... 2. During glycolysis, how many ADP molecules are converted to ATP. Explain this answer with regard to your answer to #1. 4 ADP molecules are converted into ATP. There is a net gain of only 2 ATP molecules because 2 are consumed during the first stage of glycolysis. 3. What are the three metabolicall ...
... 2. During glycolysis, how many ADP molecules are converted to ATP. Explain this answer with regard to your answer to #1. 4 ADP molecules are converted into ATP. There is a net gain of only 2 ATP molecules because 2 are consumed during the first stage of glycolysis. 3. What are the three metabolicall ...
Week 6 Lesson 1 Artificial photosynthesis
... chloroplasts during photosynthesis. Manganese does not work in the lab. It is rather unstable and does not dissolve in water. Researchers have tried other catalysts but these are also unstable and can cause extra, unwanted chemical reactions. Some inorganic metal oxides have been tried as catalysts. ...
... chloroplasts during photosynthesis. Manganese does not work in the lab. It is rather unstable and does not dissolve in water. Researchers have tried other catalysts but these are also unstable and can cause extra, unwanted chemical reactions. Some inorganic metal oxides have been tried as catalysts. ...
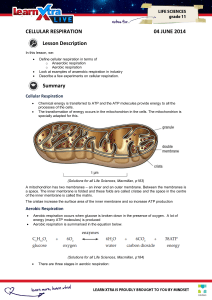
CELLULAR RESPIRATION 04 JUNE 2014 Lesson Description
... carbon dioxide. The hydrogens will be used in oxidative phosphorylation and the carbon dioxide will be breathed out. ...
... carbon dioxide. The hydrogens will be used in oxidative phosphorylation and the carbon dioxide will be breathed out. ...