Preview as PDF - Pearson Higher Education
... comes from the sun. In photosynthesis, the energy of sunlight is used to rearrange the atoms of carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O), producing organic molecules and releasing oxygen (O2). In cellular respiration, O2 is consumed as organic molecules are broken down to CO2 and H2O, and the cell captu ...
... comes from the sun. In photosynthesis, the energy of sunlight is used to rearrange the atoms of carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O), producing organic molecules and releasing oxygen (O2). In cellular respiration, O2 is consumed as organic molecules are broken down to CO2 and H2O, and the cell captu ...
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical
... 4) Why does the oxidation of organic compounds by molecular oxygen to produce CO 2 and water release free energy? A) The covalent bonds in organic molecules are higher energy bonds than those in water and carbon dioxide. B) Electrons are being moved from atoms that have a lower affinity for electro ...
... 4) Why does the oxidation of organic compounds by molecular oxygen to produce CO 2 and water release free energy? A) The covalent bonds in organic molecules are higher energy bonds than those in water and carbon dioxide. B) Electrons are being moved from atoms that have a lower affinity for electro ...
Head-Gordon`s
... is scarcely the only important environment in which chemical processes occur, although it does have the merit of being simplest to model! In section 7, I give an overview of the ways in which environments such as those in solution, or for molecules interacting with extended surfaces, are currently t ...
... is scarcely the only important environment in which chemical processes occur, although it does have the merit of being simplest to model! In section 7, I give an overview of the ways in which environments such as those in solution, or for molecules interacting with extended surfaces, are currently t ...
Lactic Acid Fermentation
... fermentation, the pyruvate breaks down into Ethanol (alcohol) as it gives off one carbon dioxide (per pyruvate) while accepting two electrons from NADH. This breaks down NADH into NAD+ so that it can be used by Glycolysis again and again. In bacteria (prokaryotes), this has to happen because there a ...
... fermentation, the pyruvate breaks down into Ethanol (alcohol) as it gives off one carbon dioxide (per pyruvate) while accepting two electrons from NADH. This breaks down NADH into NAD+ so that it can be used by Glycolysis again and again. In bacteria (prokaryotes), this has to happen because there a ...
Glucose Metabolism
... B. When glucose in the bloodstream enters the cytosol (internal fluid) of our cells, it is immediately converted to glucose – 6 – phosphate. 1. This is an exergonic process and not reversible. Glucose + ATP Æ Glucose – 6 – phosphate + ADP ΔG = -4.0 kcal/mol ...
... B. When glucose in the bloodstream enters the cytosol (internal fluid) of our cells, it is immediately converted to glucose – 6 – phosphate. 1. This is an exergonic process and not reversible. Glucose + ATP Æ Glucose – 6 – phosphate + ADP ΔG = -4.0 kcal/mol ...
The TCA Cycle
... a. As far as oxidation of carbs goes, you’ll recall that most of the preparatory stage of changing glucose to pyruvate takes place in the cytosol. This is a unique feature of carbohydrates, as fatty acids and amino acids will be oxidized directly in the mitochondria. b. The ability of glucose to be ...
... a. As far as oxidation of carbs goes, you’ll recall that most of the preparatory stage of changing glucose to pyruvate takes place in the cytosol. This is a unique feature of carbohydrates, as fatty acids and amino acids will be oxidized directly in the mitochondria. b. The ability of glucose to be ...
(January 2005).
... ATP to ADP + Pi releases energy/exergonic or description; ADP + Pi to ATP needs energy/endergonic or description; easily reversible; transfers energy from place of release/one molecule to energy-requiring reactions; provides energy in 'small packets'/figure e.g. 30.6 or 31. ...
... ATP to ADP + Pi releases energy/exergonic or description; ADP + Pi to ATP needs energy/endergonic or description; easily reversible; transfers energy from place of release/one molecule to energy-requiring reactions; provides energy in 'small packets'/figure e.g. 30.6 or 31. ...
Energy Systems - Southwest High School
... Long Term Energy: The Oxygen System Used for most daily activities and longer duration physical activities and sports. In the aerobic system, a complex chemical reaction known as OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION is used to resynthesize ATP. This takes place in Cell organelles called Mitrochondria. A metabo ...
... Long Term Energy: The Oxygen System Used for most daily activities and longer duration physical activities and sports. In the aerobic system, a complex chemical reaction known as OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION is used to resynthesize ATP. This takes place in Cell organelles called Mitrochondria. A metabo ...
Product Data Sheet
... Mitochondria are the cellular components responsible for generating the energy required to sustain life. Energy is produced from the flow of free electrons through the electron transport chain produced by oxidative phosphorylation. Because mitochondria serve as the powerhouse of the cell, their prop ...
... Mitochondria are the cellular components responsible for generating the energy required to sustain life. Energy is produced from the flow of free electrons through the electron transport chain produced by oxidative phosphorylation. Because mitochondria serve as the powerhouse of the cell, their prop ...
Cellular Respiration
... acid enters the pathways of aerobic respiration. (Aerobic respiration is covered in detail in the next section.) In anaerobic conditions (when oxygen is absent), however, some cells can convert pyruvic acid into other compounds through additional biochemical pathways that occur in the cytosol. The c ...
... acid enters the pathways of aerobic respiration. (Aerobic respiration is covered in detail in the next section.) In anaerobic conditions (when oxygen is absent), however, some cells can convert pyruvic acid into other compounds through additional biochemical pathways that occur in the cytosol. The c ...
9/2/08 Transcript I - UAB School of Optometry
... Utilized in "Fight or Flight"- If confronted by a lion then you will fight or flee and use this type of process because it does not require any set up time or oxygen. There are 10 rxns which are the same in all cells, but may not happen at same rate. 2 Phases: 1. Converts glucose to two Glycer ...
... Utilized in "Fight or Flight"- If confronted by a lion then you will fight or flee and use this type of process because it does not require any set up time or oxygen. There are 10 rxns which are the same in all cells, but may not happen at same rate. 2 Phases: 1. Converts glucose to two Glycer ...
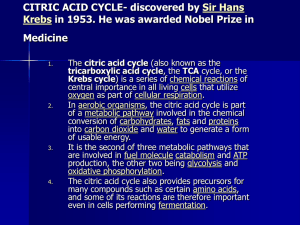
CITRIC ACID CYCLE
... It is the second of three metabolic pathways that are involved in fuel molecule catabolism and ATP production, the other two being glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation. The citric acid cycle also provides precursors for many compounds such as certain amino acids, and some of its reactions are th ...
... It is the second of three metabolic pathways that are involved in fuel molecule catabolism and ATP production, the other two being glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation. The citric acid cycle also provides precursors for many compounds such as certain amino acids, and some of its reactions are th ...
SOLUTE TRANSPORT
... Characterize each of the transport systems diagrammed below. [antiport vs. symport; electroneutral vs. electrogenic] ...
... Characterize each of the transport systems diagrammed below. [antiport vs. symport; electroneutral vs. electrogenic] ...
respiration_how cell..
... Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
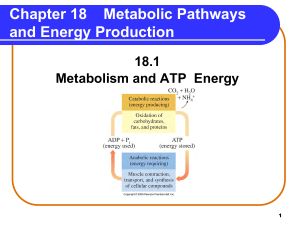
Metabolic Pathways and Energy Production
... • protons (H+) from Complexes I, III, and IV move into the intermembrane space. • a proton gradient is created. • protons return to matrix through ATP synthase, a protein complex. • the flow of protons provides energy for ATP synthesis (oxidative phosphorylation). ADP + Pi + Energy ...
... • protons (H+) from Complexes I, III, and IV move into the intermembrane space. • a proton gradient is created. • protons return to matrix through ATP synthase, a protein complex. • the flow of protons provides energy for ATP synthesis (oxidative phosphorylation). ADP + Pi + Energy ...
key - Scioly.org
... glycolysis can occur with or without oxygen glycolysis occurs in the mitochondria glycolysis is the first step in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration glycolysis produces 2 ATP, 2 NADH, and 2 pyruvate ...
... glycolysis can occur with or without oxygen glycolysis occurs in the mitochondria glycolysis is the first step in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration glycolysis produces 2 ATP, 2 NADH, and 2 pyruvate ...
Photocatalysis on TiOn Surfaces: Principles, Mechanisms, and
... for a molecule are given in the energy level diagram in Figure 2.2. The ground state singlet energy level of the molecule is represented by SOand illustrates the energy of the molecule at room temperature in solution. The ground vibrational states for the three excited electronic states shown in Fig ...
... for a molecule are given in the energy level diagram in Figure 2.2. The ground state singlet energy level of the molecule is represented by SOand illustrates the energy of the molecule at room temperature in solution. The ground vibrational states for the three excited electronic states shown in Fig ...
Citrate Cycle
... Reaction 6: Oxidation of succinate by succinate dehydrogenase to form fumarate This coupled redox reaction directly links the citrate cycle to the electron transport system through the redox conjugate pair FAD/FADH2 which is covalently linked to the enzyme succinate dehydrogenase, an inner mitochond ...
... Reaction 6: Oxidation of succinate by succinate dehydrogenase to form fumarate This coupled redox reaction directly links the citrate cycle to the electron transport system through the redox conjugate pair FAD/FADH2 which is covalently linked to the enzyme succinate dehydrogenase, an inner mitochond ...
Chapter 7
... Glycolysis in Aerobic Respiration • Uses 2 ATP, produces 2 molecules of the more reactive, higher energy PGAL 2 ATP ...
... Glycolysis in Aerobic Respiration • Uses 2 ATP, produces 2 molecules of the more reactive, higher energy PGAL 2 ATP ...
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
... • The chain’s function is to break the large freeenergy drop from food to O2 into smaller steps that release energy in manageable amounts ...
... • The chain’s function is to break the large freeenergy drop from food to O2 into smaller steps that release energy in manageable amounts ...
Key - UCSB CLAS
... 1. What role do cofactors play? Give 2 examples of cofactors. Cofactors are molecules or metal ions that work with enzymes in biochemical reactions – examples include NAD+, FAD, TPP, biotin, PLP, lipoate, and CoASH 2. Niacin is required to make the coenzymes NAD+, NADP+, NADH and NADPH which are nec ...
... 1. What role do cofactors play? Give 2 examples of cofactors. Cofactors are molecules or metal ions that work with enzymes in biochemical reactions – examples include NAD+, FAD, TPP, biotin, PLP, lipoate, and CoASH 2. Niacin is required to make the coenzymes NAD+, NADP+, NADH and NADPH which are nec ...
Final Exam - KFUPM Faculty List
... Since O2 is a diatomic gas, here we have 40 million O atoms, corresponding to 40 x 106/(6.022 x 1023) mol O atoms = 6.64 x 10-17 mol O atoms choice E 2. The element oxygen consists of three naturally occurring isotopes: 16O, 17O, and 18O. The average atomic mass of oxygen is 16.00 amu. What does thi ...
... Since O2 is a diatomic gas, here we have 40 million O atoms, corresponding to 40 x 106/(6.022 x 1023) mol O atoms = 6.64 x 10-17 mol O atoms choice E 2. The element oxygen consists of three naturally occurring isotopes: 16O, 17O, and 18O. The average atomic mass of oxygen is 16.00 amu. What does thi ...
Slide 1
... Energy is released when a high-energy phosphate bond in ATP is broken. Just as a battery can be used to provide energy for a variety of uses, the energy from ATP can be used to do most of the body’s work—contract muscles, transport compounds, make new molecules, and more. With the loss of a phosphat ...
... Energy is released when a high-energy phosphate bond in ATP is broken. Just as a battery can be used to provide energy for a variety of uses, the energy from ATP can be used to do most of the body’s work—contract muscles, transport compounds, make new molecules, and more. With the loss of a phosphat ...
Chapter 5-7
... Catalyst Summary Four important principles about all catalysts • They speed up reactions that would occur anyway, if their activation energy could be surmounted. • Catalysts lower activation energy. • The lowered activation energy allows reactions to move forward more quickly. • Catalysts are not ...
... Catalyst Summary Four important principles about all catalysts • They speed up reactions that would occur anyway, if their activation energy could be surmounted. • Catalysts lower activation energy. • The lowered activation energy allows reactions to move forward more quickly. • Catalysts are not ...