Exam 2
... the membrane generate a pH gradient of DpH = 1.0 (interior higher by one unit) and a membrane potential of –120mv (interior negative). This “proton-motive” force can be used to synthesize ATP from ADP and phosphate inside the cell. Here is some more information that may be useful as you solve the pr ...
... the membrane generate a pH gradient of DpH = 1.0 (interior higher by one unit) and a membrane potential of –120mv (interior negative). This “proton-motive” force can be used to synthesize ATP from ADP and phosphate inside the cell. Here is some more information that may be useful as you solve the pr ...
Derived copy of Bis2A 07.3 Oxidation of Pyruvate and the Citric Acid
... that reduce NAD+ to NADH and release carboxyl groups that form CO2 molecules. α-Ketoglutarate is the product of step three, and a succinyl group is the product of step four. CoA binds the succinyl group to form succinyl CoA. The enzyme that catalyzes step four is regulated by feedback inhibition of ...
... that reduce NAD+ to NADH and release carboxyl groups that form CO2 molecules. α-Ketoglutarate is the product of step three, and a succinyl group is the product of step four. CoA binds the succinyl group to form succinyl CoA. The enzyme that catalyzes step four is regulated by feedback inhibition of ...
Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
... to pyruvate and then, via gluconeogenesis, to glucose. – Why would muscle transport lactate to the liver for conversion back to pyruvate? NAD+ is needed for that step, and the point of making lactate in the first place was because NAD+ was too low. ...
... to pyruvate and then, via gluconeogenesis, to glucose. – Why would muscle transport lactate to the liver for conversion back to pyruvate? NAD+ is needed for that step, and the point of making lactate in the first place was because NAD+ was too low. ...
Adenylate Energy Charge
... The events which occur in the 3 h period after harvesting starts and before sampling of starving bacteria commences are clearly of interest. The organisms do not all enter starvation simultaneously but do so continuously as they are removed from the culture medium over the 90 min required for harves ...
... The events which occur in the 3 h period after harvesting starts and before sampling of starving bacteria commences are clearly of interest. The organisms do not all enter starvation simultaneously but do so continuously as they are removed from the culture medium over the 90 min required for harves ...
Biological energy
... by substrate-level by oxidative phosphorylation, depending on which shuttle transports electrons phosphorylation from NADH in cytosol ...
... by substrate-level by oxidative phosphorylation, depending on which shuttle transports electrons phosphorylation from NADH in cytosol ...
07-Photosynthesis
... water into sugar, oxygen, and other organic compounds. This process is often summarized by the following reaction: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 H2O + 6 CO2 + light energy ...
... water into sugar, oxygen, and other organic compounds. This process is often summarized by the following reaction: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 H2O + 6 CO2 + light energy ...
Understanding oxidative stress and antioxidant functions in order to
... interactions between the AsA-GSH pathway and the PRXs demonstrate cross-talk between the individual ROS-metabolizing pathways of the chloroplasts. The AsA-GSH pathway has a higher specificity for H2O2 and the chloroplast APX has higher activities than PRXs but the PRXs have a broad specificity of to ...
... interactions between the AsA-GSH pathway and the PRXs demonstrate cross-talk between the individual ROS-metabolizing pathways of the chloroplasts. The AsA-GSH pathway has a higher specificity for H2O2 and the chloroplast APX has higher activities than PRXs but the PRXs have a broad specificity of to ...
I. Overview of Photosynthesis: 4 STAGES: 1. Light Absorption
... 3. Many plants have photorespiration 4. C4 plants maximize CO2 fixation using a C4 pathway that increase [CO2] conc. 5. CAM plants minimize water loss by fixing CO2 at night. ...
... 3. Many plants have photorespiration 4. C4 plants maximize CO2 fixation using a C4 pathway that increase [CO2] conc. 5. CAM plants minimize water loss by fixing CO2 at night. ...
Lecture 3: Glycolysis Part 2 - University of California, Berkeley
... A hydride moiety, the proton plus two electrons, is transferred onto NAD+. This is a strongly downhill reaction. The oxidation is on the carbon. This is aided by the abstraction of the proton on the -OH group, ending up with a thioester. Thioesters. The hydrolysis of thioesters is much more strongly ...
... A hydride moiety, the proton plus two electrons, is transferred onto NAD+. This is a strongly downhill reaction. The oxidation is on the carbon. This is aided by the abstraction of the proton on the -OH group, ending up with a thioester. Thioesters. The hydrolysis of thioesters is much more strongly ...
K - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... (1 ATP, 1 GTP)—these first two reactions are that expensive! ...
... (1 ATP, 1 GTP)—these first two reactions are that expensive! ...
Bis2A 07.3 Oxidation of Pyruvate and the Citric
... that reduce NAD+ to NADH and release carboxyl groups that form CO2 molecules. α-Ketoglutarate is the product of step three, and a succinyl group is the product of step four. CoA binds the succinyl group to form succinyl CoA. The enzyme that catalyzes step four is regulated by feedback inhibition of ...
... that reduce NAD+ to NADH and release carboxyl groups that form CO2 molecules. α-Ketoglutarate is the product of step three, and a succinyl group is the product of step four. CoA binds the succinyl group to form succinyl CoA. The enzyme that catalyzes step four is regulated by feedback inhibition of ...
Mutations in the Subunit of Photosystem II and Resistance to the
... the double m utant ID tow ard various herbicides. R/S is the ratio of the inhibitor concentration blocking half o f the PS II activity o f the m utant to that of the wild type. F or com parison, R/S of the single m utant 266 (Thr) and of the single m utant 264 (Ala) are also presented. Concerning io ...
... the double m utant ID tow ard various herbicides. R/S is the ratio of the inhibitor concentration blocking half o f the PS II activity o f the m utant to that of the wild type. F or com parison, R/S of the single m utant 266 (Thr) and of the single m utant 264 (Ala) are also presented. Concerning io ...
Name
... KEY CONCEPT Fermentation allows the production of a small amount of ATP without oxygen. When oxygen is not available in cells, fermentation takes place instead. Fermentation is an anaerobic process that allows glycolysis to continue, but does not produce ATP on its own. The main function of fermenta ...
... KEY CONCEPT Fermentation allows the production of a small amount of ATP without oxygen. When oxygen is not available in cells, fermentation takes place instead. Fermentation is an anaerobic process that allows glycolysis to continue, but does not produce ATP on its own. The main function of fermenta ...
lecture 6 ppt
... Electron transport chain (ETC) • ETC e- collection molecules • embedded on inner mitochondrial membrane • accept e- in turn • e- ultimately accepted by O2 ...
... Electron transport chain (ETC) • ETC e- collection molecules • embedded on inner mitochondrial membrane • accept e- in turn • e- ultimately accepted by O2 ...
Photosynthesis: CO assimilation and sugar metabolism
... Thus, soybean yields only 27% of the energy of corn. What about new energy crops? For Miscanthus, dry wt yields of cellulose is approaching 40,000 lb/acre, or about 10-times more energy than available in starch from corn seed. That is why long-term biofuel solutions from higher plants focus on cellu ...
... Thus, soybean yields only 27% of the energy of corn. What about new energy crops? For Miscanthus, dry wt yields of cellulose is approaching 40,000 lb/acre, or about 10-times more energy than available in starch from corn seed. That is why long-term biofuel solutions from higher plants focus on cellu ...
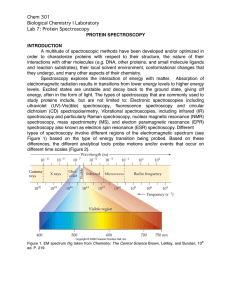
Chem 301 Biological Chemistry I Laboratory Lab 7: Protein
... configuration, giving off the energy that was just absorbed. Some of the states in the system, however will lose only some energy in non-radiative processes (those that do not emit radiation) and will decay to a lower (but still excited) energy state. Within each electronic energy level are all of t ...
... configuration, giving off the energy that was just absorbed. Some of the states in the system, however will lose only some energy in non-radiative processes (those that do not emit radiation) and will decay to a lower (but still excited) energy state. Within each electronic energy level are all of t ...
BSCS Chapter 04
... clusters, called photosystems (PS) I and II. • The chlorophyll and other pigments in each photosystem absorb light energy and transfer it from one molecule to the next. • All this energy is funneled to a specific chlorophyll a molecule called the reaction center. ...
... clusters, called photosystems (PS) I and II. • The chlorophyll and other pigments in each photosystem absorb light energy and transfer it from one molecule to the next. • All this energy is funneled to a specific chlorophyll a molecule called the reaction center. ...
C h e m g u id e –... DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... carrying a glycine attaches to the chain next door to the molecule carrying the methionine. Its anticodon will be CCA. The ribosome now moves along the chain to the next codon – GUA. At the same time a peptide bond is formed between the methionine and the glycine, and the methionine breaks away from ...
... carrying a glycine attaches to the chain next door to the molecule carrying the methionine. Its anticodon will be CCA. The ribosome now moves along the chain to the next codon – GUA. At the same time a peptide bond is formed between the methionine and the glycine, and the methionine breaks away from ...
Medical Biochemistry Review #2 By
... – Basically coupling electron flow through the ETC to ATP synthesis – The Respiratory complexes are proton pumps. As electrons pass through complexes I, III, and IV, hydrogen ions are pumped across the inner mitochondrial membrane into the intermembrane space. – The proton concentration in the inter ...
... – Basically coupling electron flow through the ETC to ATP synthesis – The Respiratory complexes are proton pumps. As electrons pass through complexes I, III, and IV, hydrogen ions are pumped across the inner mitochondrial membrane into the intermembrane space. – The proton concentration in the inter ...
Chapter 18 Metabolic Pathways and Energy Production
... • oxidized and reduced as hydrogen and/or electrons are transferred from one carrier to the next • FMN, Fe-S, coenzyme Q, and cytochromes • embedded in four enzyme complexes: I, II, III, and IV ...
... • oxidized and reduced as hydrogen and/or electrons are transferred from one carrier to the next • FMN, Fe-S, coenzyme Q, and cytochromes • embedded in four enzyme complexes: I, II, III, and IV ...
... two α-helical segments that are imbedded in the membrane. A “top view” of this protein is shown on the right. Briefly discuss the following aspects of the structure of this protein. i) What other type of secondary or super-secondary structures are seen in membrane proteins. Why? ii) What is the dist ...
Chapter 9: Pathways that Harvest Chemical
... Energy is stored in the covalent bonds of fuels, and it can be released and transformed. Wood burning in a campfire releases energy as heat and light. In cells, fuel molecules release chemical energy that is used to make ATP, which in turn drives endergonic reactions. ATP is central to the energy tr ...
... Energy is stored in the covalent bonds of fuels, and it can be released and transformed. Wood burning in a campfire releases energy as heat and light. In cells, fuel molecules release chemical energy that is used to make ATP, which in turn drives endergonic reactions. ATP is central to the energy tr ...
Key enzymes in glycolysis
... - Pyruvate: enters the mitochondria & is converted into acetyl CoA. Acetyl CoA enters citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to yield energy in the form of ATP - NADH: utilizes mitochondria & oxygen to yield energy 2- In cells with no mitochondria or adequate oxygen (or Both) (Anaerobic glycolysis) Lactate ...
... - Pyruvate: enters the mitochondria & is converted into acetyl CoA. Acetyl CoA enters citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to yield energy in the form of ATP - NADH: utilizes mitochondria & oxygen to yield energy 2- In cells with no mitochondria or adequate oxygen (or Both) (Anaerobic glycolysis) Lactate ...