Alkenes
... The electron configuration of carbon is When carbon bonds in alkenes, the electron configuration changes The 2s electron and two of the 2p electrons combine to form three sp2 hybrid orbitals, leaving a spare porbital on each of the carbon atoms ...
... The electron configuration of carbon is When carbon bonds in alkenes, the electron configuration changes The 2s electron and two of the 2p electrons combine to form three sp2 hybrid orbitals, leaving a spare porbital on each of the carbon atoms ...
CHAPTER 8
... 2. Quantum mechanics: electromagnetic radiation, quantum mechanics, quantum numbers, shape and energy of orbitals, Pauli Exclusion Principle, multi-electron atoms, Aufbau method, valence bond theory, hybridization, simple molecular orbital theory. 3. Solutions: homogeneous/heterogeneous mixtures, co ...
... 2. Quantum mechanics: electromagnetic radiation, quantum mechanics, quantum numbers, shape and energy of orbitals, Pauli Exclusion Principle, multi-electron atoms, Aufbau method, valence bond theory, hybridization, simple molecular orbital theory. 3. Solutions: homogeneous/heterogeneous mixtures, co ...
Primary electrons make random elastic and inelastic collision either
... Secondary electron, (<50 eV, normally around 2-6 eV, larger than sample’s work function) excitations result to loose bound valence electrons, which are promoted from the valence band to the conduction band in insulators and semiconductors, or directly from the conduction band in metals. … Auger elec ...
... Secondary electron, (<50 eV, normally around 2-6 eV, larger than sample’s work function) excitations result to loose bound valence electrons, which are promoted from the valence band to the conduction band in insulators and semiconductors, or directly from the conduction band in metals. … Auger elec ...
Section 2-4 “Chemical Reactions and Enzymes”
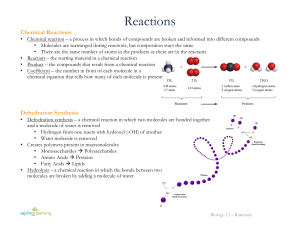
... Products – Elements or compounds produced by a chemical reaction ...
... Products – Elements or compounds produced by a chemical reaction ...
Organic Tutorial 1st Year MT03
... If there is no reaction, explain why! And now some Prelim questions… 5. How can the structure of the alkyl halide influence its reactivity in SN1 and SN2 reactions? Comment on the reactivity of all of the following in nucleophilic substitution reactions. [25] ...
... If there is no reaction, explain why! And now some Prelim questions… 5. How can the structure of the alkyl halide influence its reactivity in SN1 and SN2 reactions? Comment on the reactivity of all of the following in nucleophilic substitution reactions. [25] ...
Slide 1
... Ox1 + Red2 = Red1 + Ox2 In this case Red2 is the electron donor, passing electrons to Ox1 which is the electron acceptor. Thus Red2 is oxidized to Ox2 and Ox1 is reduced to Red1. The equilibrium constant for an oxidation-reduction reaction can be determined by combining the constants from Table 1 as ...
... Ox1 + Red2 = Red1 + Ox2 In this case Red2 is the electron donor, passing electrons to Ox1 which is the electron acceptor. Thus Red2 is oxidized to Ox2 and Ox1 is reduced to Red1. The equilibrium constant for an oxidation-reduction reaction can be determined by combining the constants from Table 1 as ...
Unit 3 Goals - kimscience.com
... o complete and balance combustion reactions of organic molecules containing carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, and explain the reaction in terms of bonds breaking and forming, enthalpy, and entropy change. o distinguish between complete and incomplete combustion in terms of reaction conditions, resulting ...
... o complete and balance combustion reactions of organic molecules containing carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, and explain the reaction in terms of bonds breaking and forming, enthalpy, and entropy change. o distinguish between complete and incomplete combustion in terms of reaction conditions, resulting ...
Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change
... 1. Acid-base reactions; concepts of Arrhenius, BrønstedLowry, and Lewis; coordination complexes, amphoterism 2. Precipitation reactions 3. Oxidation-reduction reactions a. Oxidation number b. The role of the electron in oxidation-reduction c. Electrochemistry: electrolytic and galvanic cells; Farada ...
... 1. Acid-base reactions; concepts of Arrhenius, BrønstedLowry, and Lewis; coordination complexes, amphoterism 2. Precipitation reactions 3. Oxidation-reduction reactions a. Oxidation number b. The role of the electron in oxidation-reduction c. Electrochemistry: electrolytic and galvanic cells; Farada ...
File - Ingolstadt Academy
... Density (definition and equation) Dimensional analysis Instruments that measure mass, volume, pressure, etc. (lab stuff!) The Scientific Method Atomic Structure: ...
... Density (definition and equation) Dimensional analysis Instruments that measure mass, volume, pressure, etc. (lab stuff!) The Scientific Method Atomic Structure: ...
Ch. 2 The Chemistry of Life
... - _____ contains the sugar _________, _____ contains the sugar _______________ ...
... - _____ contains the sugar _________, _____ contains the sugar _______________ ...
AP CHEMISTRY Chang -Chemistry 9
... Use of experimental data and graphical analysis to determine reactant order, rate constants, and reaction rate laws Effect of temperature change on rates Energy of activation; the role of catalysts Relationship between the rate-determining step and a ...
... Use of experimental data and graphical analysis to determine reactant order, rate constants, and reaction rate laws Effect of temperature change on rates Energy of activation; the role of catalysts Relationship between the rate-determining step and a ...
1. Millikan did his experiments with the balance of
... 6. a.) The condensed ground-state electron configuration of Mo3+ : [Kr] 5s2, 4d1 Mo3+ is paramagnetic because in the d orbital there are unpaired electrons. b.) The condensed ground-state electron configuration of Au+ : [Xe] 6s2, 4f14,5d8 Au+ is paramagnetic because in the d orbital there are unpai ...
... 6. a.) The condensed ground-state electron configuration of Mo3+ : [Kr] 5s2, 4d1 Mo3+ is paramagnetic because in the d orbital there are unpaired electrons. b.) The condensed ground-state electron configuration of Au+ : [Xe] 6s2, 4f14,5d8 Au+ is paramagnetic because in the d orbital there are unpai ...
Bioenergetics Key
... Chemistry 160 Bioenergetics Homework key 1. Give the equation that relates free energy to the equilibrium constant. ΔG = -RTlnK 2. What does it mean that ΔG are additive. Why is this important in metabolism? It means that if there are several reactions in a process (such as metabolism) that the ΔG f ...
... Chemistry 160 Bioenergetics Homework key 1. Give the equation that relates free energy to the equilibrium constant. ΔG = -RTlnK 2. What does it mean that ΔG are additive. Why is this important in metabolism? It means that if there are several reactions in a process (such as metabolism) that the ΔG f ...
ChemicalBondingPowerpoint
... • Energy is the ability to do work or supply heat. Stored energy is called potential energy, and the energy of movement is called kinetic energy or thermal energy, which is measured as temperature. ...
... • Energy is the ability to do work or supply heat. Stored energy is called potential energy, and the energy of movement is called kinetic energy or thermal energy, which is measured as temperature. ...
Syllabus
... There will be 12 homework assignments, a midterm and a final. All are given on a take-home basis. If you have any question about a problem before starting to work, you are strongly encouraged to discuss the matter with the professor or fellow students. That is, students are encouraged to discuss and ...
... There will be 12 homework assignments, a midterm and a final. All are given on a take-home basis. If you have any question about a problem before starting to work, you are strongly encouraged to discuss the matter with the professor or fellow students. That is, students are encouraged to discuss and ...