science background - CMA
... attraction between molecules. For instance: alcohols evaporate faster that water, because water molecules have stronger intermolecular forces of attraction than alcohols; one H2O molecule can form up to four hydrogen bonds, whereas CnH2n+1OH can only form two or three hydrogen bonds, because only on ...
... attraction between molecules. For instance: alcohols evaporate faster that water, because water molecules have stronger intermolecular forces of attraction than alcohols; one H2O molecule can form up to four hydrogen bonds, whereas CnH2n+1OH can only form two or three hydrogen bonds, because only on ...
Chapter-2-Human-Chemistry
... needed to disrupt and rearrange the stable electron configuration 2.Concentration and Temperature are main factors in influencing chemical reactions ...
... needed to disrupt and rearrange the stable electron configuration 2.Concentration and Temperature are main factors in influencing chemical reactions ...
Exam 3 Review - Iowa State University
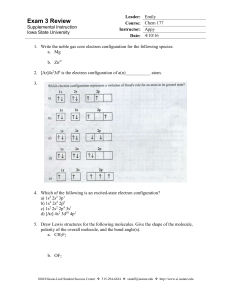
... 8. Which of the following has the smallest ionization energy. a. Mg b. Se c. Ba d. Po 9. Which has the largest 2nd Ionization energy between K and Ca? a. K b. Ca c. Both K and Ca have the same second Ionization energy d. It’s impossible to tell 10. In terms of electronegativity, determine whether th ...
... 8. Which of the following has the smallest ionization energy. a. Mg b. Se c. Ba d. Po 9. Which has the largest 2nd Ionization energy between K and Ca? a. K b. Ca c. Both K and Ca have the same second Ionization energy d. It’s impossible to tell 10. In terms of electronegativity, determine whether th ...
Chapter 14, Section 1, pages 494-501
... Reversible Reactions and Chemical Equilibrium Objectives To contrast reactions. To describe chemical equilibrium To give examples of chemical equilibrium Demo Burn sulfur in oxygen as an example of a completion reaction. Input Completion Reactions and Reversible Reactions What does reversible mean? ...
... Reversible Reactions and Chemical Equilibrium Objectives To contrast reactions. To describe chemical equilibrium To give examples of chemical equilibrium Demo Burn sulfur in oxygen as an example of a completion reaction. Input Completion Reactions and Reversible Reactions What does reversible mean? ...
Chemistry 221 - Oregon State chemistry
... Which unit is used to describe the chemical energy contained within the food you eat? ...
... Which unit is used to describe the chemical energy contained within the food you eat? ...
Slides for Chapter 1-4 - Department of Chemistry and Physics
... Nucleophiles will replace the halide in C-X bonds of many alkyl halides(reaction as Lewis base) Nucleophiles that are Brønsted bases produce elimination ...
... Nucleophiles will replace the halide in C-X bonds of many alkyl halides(reaction as Lewis base) Nucleophiles that are Brønsted bases produce elimination ...
South Pasadena • AP Chemistry
... 8. Explain why atoms become smaller as positive ions and why they become larger as negative ions. (Be specific!) ...
... 8. Explain why atoms become smaller as positive ions and why they become larger as negative ions. (Be specific!) ...
CHM_101_ASSIGNMENT_COPY_1_2
... Calculate the pressure equilibrium constant Kp for the reaction at this temperature. What is the partial pressure of chlorine in the vessel? 5. Write the expressions for the concentration equilibrium constant Kc and pressure equilibrium constant Kp for the following reactions: a) ...
... Calculate the pressure equilibrium constant Kp for the reaction at this temperature. What is the partial pressure of chlorine in the vessel? 5. Write the expressions for the concentration equilibrium constant Kc and pressure equilibrium constant Kp for the following reactions: a) ...
MATTER INTO ENERGY ENERGY INTO MATTER - TJ
... • Energy- The ability of a system or matter to do work. Determined by the breaking and forming of chemical bonds. Energy is required for all cellular biochemical reactions in a body. Energy causes molecules in the cells to be rearranged. This is a matter-energy relationship for biology. • Atom- The ...
... • Energy- The ability of a system or matter to do work. Determined by the breaking and forming of chemical bonds. Energy is required for all cellular biochemical reactions in a body. Energy causes molecules in the cells to be rearranged. This is a matter-energy relationship for biology. • Atom- The ...
MODULE 1: Chemistry for Life – The Elements of Life
... Contrast the benefits of chlorine use in water treatment (killing bacteria) with associated risks (hazards of toxic chlorine gas and possible risks from formation of chlorinated hydrocarbons). HOW SCIENCE WORKS (6a, 6b) Describe the precipitation reactions, including ionic equations, of the aqueous ...
... Contrast the benefits of chlorine use in water treatment (killing bacteria) with associated risks (hazards of toxic chlorine gas and possible risks from formation of chlorinated hydrocarbons). HOW SCIENCE WORKS (6a, 6b) Describe the precipitation reactions, including ionic equations, of the aqueous ...
Chapter 18 - Sarah Mahajan Study Guides
... Rate is a measure of speed of any change that occurs within an interval of time In chemistry, the reaction rate (rate of a chemical change) = amount of reactant per unit time o For example: 0.2 mol/1 month Collision theory- atoms, molecules, and ions can react to form products when they collide with ...
... Rate is a measure of speed of any change that occurs within an interval of time In chemistry, the reaction rate (rate of a chemical change) = amount of reactant per unit time o For example: 0.2 mol/1 month Collision theory- atoms, molecules, and ions can react to form products when they collide with ...