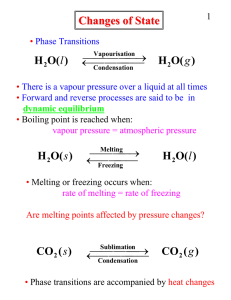
Chemical Reaction
... Beginning & ending substances have different properties Atoms are rearranged, chemical bonds are broken and new bonds are formed All reactions involve energy changes ...
... Beginning & ending substances have different properties Atoms are rearranged, chemical bonds are broken and new bonds are formed All reactions involve energy changes ...
Chemical Reactions presentation
... Chemical Bonds and Energy The heat produced by a propane grill is a form of energy. When you write the chemical equation for the combustion of propane, you can include “heat” on the right side of the equation. C3H8 + 5O2 3CO2 + 4H2O + Heat ...
... Chemical Bonds and Energy The heat produced by a propane grill is a form of energy. When you write the chemical equation for the combustion of propane, you can include “heat” on the right side of the equation. C3H8 + 5O2 3CO2 + 4H2O + Heat ...
exam #1 study guide
... 6. Elements / Compounds are made up of only one type of atom. 7. true / false An atom becomes an ion when its number of protons changes. 8. true / false Some ions are positively charged, and some ions have no charge. 9. true / false The formation of an ion results in a full outermost energy level. 1 ...
... 6. Elements / Compounds are made up of only one type of atom. 7. true / false An atom becomes an ion when its number of protons changes. 8. true / false Some ions are positively charged, and some ions have no charge. 9. true / false The formation of an ion results in a full outermost energy level. 1 ...
lect3
... (Housecroft/Sharpe p42) CO has (a) filled sigma () bonding orbital - the donor orbital (b) empty pi(*) antibonding orbital - acceptor orbital ...
... (Housecroft/Sharpe p42) CO has (a) filled sigma () bonding orbital - the donor orbital (b) empty pi(*) antibonding orbital - acceptor orbital ...
study guide first semester chemistry
... a. magnesium reacts with nitrogen to produce magnesium nitride. (3Mg(s) + N2(g) Mg3N2(s) b. silver nitrate reacts with copper to form copper(II) nitrate and silver. (2AgNO3(aq) + Cu Cu(NO3)2(aq) +2 Ag(s)) c. ammonia reacts with hydrochloric acid to form ammonium chloride. ...
... a. magnesium reacts with nitrogen to produce magnesium nitride. (3Mg(s) + N2(g) Mg3N2(s) b. silver nitrate reacts with copper to form copper(II) nitrate and silver. (2AgNO3(aq) + Cu Cu(NO3)2(aq) +2 Ag(s)) c. ammonia reacts with hydrochloric acid to form ammonium chloride. ...
worksheet 7b answers - Iowa State University
... Iowa State University 1) Effective Nuclear Charge: the net positive charge experienced by an electron in a many-electron atom. What is the equation? Zeff = Z – S Z = atoms number (# of protons or electrons) S = Shielding/Screening electrons Same n: 0.35 n-1: 0.85 n-2,3+: 1 ...
... Iowa State University 1) Effective Nuclear Charge: the net positive charge experienced by an electron in a many-electron atom. What is the equation? Zeff = Z – S Z = atoms number (# of protons or electrons) S = Shielding/Screening electrons Same n: 0.35 n-1: 0.85 n-2,3+: 1 ...
Basic Background Review: Acid-Base , Redox, and Stable Isotopes
... Reactions with kinetic component, always end up enriching in LIGHT isotope. • Note: Natural processes: often may have both a passive (diffusion) and active (biochemical reaction) component. BOTH parts will fractionate for light isotope. ...
... Reactions with kinetic component, always end up enriching in LIGHT isotope. • Note: Natural processes: often may have both a passive (diffusion) and active (biochemical reaction) component. BOTH parts will fractionate for light isotope. ...
Answer on Question#52196 - Chemistry
... due to the unrealized presence of free radical generating substances such as peroxides. The explanation is that HBr produces a Br radical, which then reacts with the double bond. Since the bromine atom is very large, it is more probable that it will encounter and react with the least substituted car ...
... due to the unrealized presence of free radical generating substances such as peroxides. The explanation is that HBr produces a Br radical, which then reacts with the double bond. Since the bromine atom is very large, it is more probable that it will encounter and react with the least substituted car ...
classification of chemical reactions
... What is the total number of atoms in the above formulas? 1) 3H2O= ___ hydrogen (H), ___ oxygen (O) = total of ___ atoms 2) 2H2SO4 = ___ hydrogen (H), ___sulfur (S), ___ oxygen (O) = total of ___atoms 3) 4Fe2 O3 = ____ iron (Fe), ___ oxygen (O) =total of ____ atoms ...
... What is the total number of atoms in the above formulas? 1) 3H2O= ___ hydrogen (H), ___ oxygen (O) = total of ___ atoms 2) 2H2SO4 = ___ hydrogen (H), ___sulfur (S), ___ oxygen (O) = total of ___atoms 3) 4Fe2 O3 = ____ iron (Fe), ___ oxygen (O) =total of ____ atoms ...
File
... amazing, but that’s not the only thing to consider. All the other three fuels are liquids whereas hydrogen is a gas. Although hydrogen stores more energy per gram, a gram of hydrogen takes a lot of space because of the low density of gases. How to store the hydrogen efficiently is a challenge for de ...
... amazing, but that’s not the only thing to consider. All the other three fuels are liquids whereas hydrogen is a gas. Although hydrogen stores more energy per gram, a gram of hydrogen takes a lot of space because of the low density of gases. How to store the hydrogen efficiently is a challenge for de ...
2. Covalent network
... o A cation is smaller than its parent atom Lattice energy: the change in energy when ions are packed together to form an ionic solid o Lattice energy=k(Q1 Q2/r) o K= constant o Q1, Q2 = charges on the ions ...
... o A cation is smaller than its parent atom Lattice energy: the change in energy when ions are packed together to form an ionic solid o Lattice energy=k(Q1 Q2/r) o K= constant o Q1, Q2 = charges on the ions ...
content review for prerequisite validation - laccd
... 4. Define kinetics, rate law, order of a reaction and activation energy; describe first-order and secondorder reactions; study the relationship between rate constant and equilibrium constant for a reversible reaction. 5. Define chemical equilibrium; calculate the equilibrium constant; study the effe ...
... 4. Define kinetics, rate law, order of a reaction and activation energy; describe first-order and secondorder reactions; study the relationship between rate constant and equilibrium constant for a reversible reaction. 5. Define chemical equilibrium; calculate the equilibrium constant; study the effe ...
nuc_alchemy_talk-fgs-dec07
... Making Gold : Nuclear Alchemy Dr. Paddy Regan Department of Physics University of Surrey Guildford, GU2 7XH [email protected] ...
... Making Gold : Nuclear Alchemy Dr. Paddy Regan Department of Physics University of Surrey Guildford, GU2 7XH [email protected] ...