Chapter 7, 8, and 9 Exam 2014 Name I. 50% of your grade will come
... Select the one lettered choice that best fits each statement and then fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. A choice may be used once, more than once, or not at all in each set. Questions 1–4 refer to the following types of energy. (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) ...
... Select the one lettered choice that best fits each statement and then fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. A choice may be used once, more than once, or not at all in each set. Questions 1–4 refer to the following types of energy. (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) ...
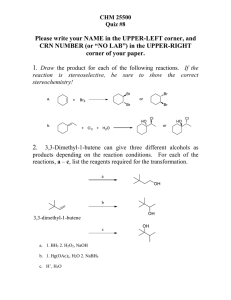
CM1121 - ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 1
... Ideal or perfect gases – Boyle’s Law; Charles Law; Amonton’s Law; Avogadro’s Law; Ideal gas law; Dalton’s law of partial pressures; postulates of the kinetic molecular theory; molecular view of gas laws; effusion; diffusion Real gases – deviation from ideal behavior; various types of intermolecular ...
... Ideal or perfect gases – Boyle’s Law; Charles Law; Amonton’s Law; Avogadro’s Law; Ideal gas law; Dalton’s law of partial pressures; postulates of the kinetic molecular theory; molecular view of gas laws; effusion; diffusion Real gases – deviation from ideal behavior; various types of intermolecular ...
Unit 1 Tro Textbook Enlow`s Brief: Chapter 1: Matter, Measurement
... Temperature – a measure of the average KE of the atoms (it’s a measure of molecular motion) ; it determines the direction of thermal energy transfer (always from hotter to colder systems) ; Kelvin is the absolute temperature scale and does not utilize negative #s ...
... Temperature – a measure of the average KE of the atoms (it’s a measure of molecular motion) ; it determines the direction of thermal energy transfer (always from hotter to colder systems) ; Kelvin is the absolute temperature scale and does not utilize negative #s ...
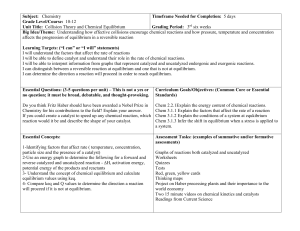
Subject:
... I can distinguish between a reversible reaction at equilibrium and one that is not at equilibrium. I can determine the direction a reaction will proceed in order to reach equilibrium. Essential Questions: (3-5 questions per unit) – This is not a yes or no question; it must be broad, debatable, and t ...
... I can distinguish between a reversible reaction at equilibrium and one that is not at equilibrium. I can determine the direction a reaction will proceed in order to reach equilibrium. Essential Questions: (3-5 questions per unit) – This is not a yes or no question; it must be broad, debatable, and t ...
ap chemistry review – multiple choice
... 3. The energy in a chemical or physical change that is available to do useful work, 4. The energy required to form the transition state in a chemical reaction. Questions 5-8 refer to atoms for which the occupied atomic orbitals are shown below: (a) 1s ___ (b) 1s (c) 1s (d) 1s (e) [Ar] 4s ...
... 3. The energy in a chemical or physical change that is available to do useful work, 4. The energy required to form the transition state in a chemical reaction. Questions 5-8 refer to atoms for which the occupied atomic orbitals are shown below: (a) 1s ___ (b) 1s (c) 1s (d) 1s (e) [Ar] 4s ...
5 - BrainMass
... smaller than that for a 3p electron. In light of this fact, which orbital is higher in energy? b. Would you expect it to require more or less energy to remove a 3s electron from the chlorine atom, as compared with a 2p electron? Explain. ...
... smaller than that for a 3p electron. In light of this fact, which orbital is higher in energy? b. Would you expect it to require more or less energy to remove a 3s electron from the chlorine atom, as compared with a 2p electron? Explain. ...
Chemical Kinetics - Review
... S2O82-(aq) + 2 I–(aq) → 2 SO42-(aq) + I2 (s) Ba2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → BaSO4 (s) ...
... S2O82-(aq) + 2 I–(aq) → 2 SO42-(aq) + I2 (s) Ba2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → BaSO4 (s) ...
Chem 1151
... The electron configuration [Kr] describes the electron configuration for all of the following except A. **B. C. D. ...
... The electron configuration [Kr] describes the electron configuration for all of the following except A. **B. C. D. ...
The Nature of Chemical Reactions
... The Law of Conservation of Mass: the mass of what you start with has to be equal to the mass of what you end with This is why equations must be balanced!!! A balanced equation says the number of atoms you started with has to be equal to the number of atoms you end with ...
... The Law of Conservation of Mass: the mass of what you start with has to be equal to the mass of what you end with This is why equations must be balanced!!! A balanced equation says the number of atoms you started with has to be equal to the number of atoms you end with ...
Culver City H.S. • AP Chemistry Name Period ___ Date ___/___/___
... An electron is excited from the n=1 ground state to the n=3 state in a hydrogen atom. Which of the following statements are true? Correct the false statements to make them true. It takes more energy to ionize (completely remove) the electron from n=3 than from the ground state. The electron is farth ...
... An electron is excited from the n=1 ground state to the n=3 state in a hydrogen atom. Which of the following statements are true? Correct the false statements to make them true. It takes more energy to ionize (completely remove) the electron from n=3 than from the ground state. The electron is farth ...
C1_5_products_from_oils_crossword
... 9. The reaction in which the enzymes in yeast turn glucose into ethanol and carbon dioxide. 10. An alkene with the formula C3H6. 11. Polymers that change in response to changes in their environment. 12. A hydrocarbon whose molecules contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond. Down 1. Something t ...
... 9. The reaction in which the enzymes in yeast turn glucose into ethanol and carbon dioxide. 10. An alkene with the formula C3H6. 11. Polymers that change in response to changes in their environment. 12. A hydrocarbon whose molecules contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond. Down 1. Something t ...
Review - The University of Texas at Dallas
... Slowest rate = “rate limiting step” and determines overall rate expression Intermediates produced and consumed in steady state Fast equilibrium steps honor K = kf / kr ...
... Slowest rate = “rate limiting step” and determines overall rate expression Intermediates produced and consumed in steady state Fast equilibrium steps honor K = kf / kr ...
A.P. Chemistry Complexation Reactions
... Two compounds switch partners and form two new compounds. ...
... Two compounds switch partners and form two new compounds. ...