Chem 400 Chem 150 REVIEW SHEET Amanda R
... Trends in Periodic Table – trends of elements to predict formation of bonds o Counting valence electrons, electron configuration o Atomic radii increases to the left and down o Electron Affinity/Ionization Energy and electronegativity increases going up and to the right Types of Bonds – must know wh ...
... Trends in Periodic Table – trends of elements to predict formation of bonds o Counting valence electrons, electron configuration o Atomic radii increases to the left and down o Electron Affinity/Ionization Energy and electronegativity increases going up and to the right Types of Bonds – must know wh ...
Notes on Chapter 12 Chemical Equilibrium
... c. catalyst = anything that speeds up the rate of reactions by lowering the energy of activation for the reaction. The catalyst is not changed or used up during the chemical reaction. ...
... c. catalyst = anything that speeds up the rate of reactions by lowering the energy of activation for the reaction. The catalyst is not changed or used up during the chemical reaction. ...
Exam #2
... mass of the nucleus is concentrated in a very small volume. The electron diffraction experiment demonstrated Heisenberg’s hypothesis that matter and energy are interconvertable. The solution to the Schrodinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom does not provide a detailed description of the electro ...
... mass of the nucleus is concentrated in a very small volume. The electron diffraction experiment demonstrated Heisenberg’s hypothesis that matter and energy are interconvertable. The solution to the Schrodinger wave equation for the hydrogen atom does not provide a detailed description of the electro ...
Chemical Reactions and Enzymes What is a chemical reaction?
... reaction as either endothermic or exothermic by the graphs to the right: ...
... reaction as either endothermic or exothermic by the graphs to the right: ...
Document
... a bond to this atom. The initial cleavage does not cause fragmentation, only rearrangement and transfer of the radical site. This new radical site then initiates an alpha cleavage, resulting in the formation of the oddelectron ion. This rearrangement occurs at unsaturated functional groups, notably ...
... a bond to this atom. The initial cleavage does not cause fragmentation, only rearrangement and transfer of the radical site. This new radical site then initiates an alpha cleavage, resulting in the formation of the oddelectron ion. This rearrangement occurs at unsaturated functional groups, notably ...
topic-2.doc
... Electrons are in orbit around the nucleus, are involved in chemical reactions. o Orbital: three-dimensional space where an electron will most likely be found 90% of the time o First energy level: one s orbital, holds 2 electrons o Second energy level: one s and three p orbitals, holds 8 electrons Ch ...
... Electrons are in orbit around the nucleus, are involved in chemical reactions. o Orbital: three-dimensional space where an electron will most likely be found 90% of the time o First energy level: one s orbital, holds 2 electrons o Second energy level: one s and three p orbitals, holds 8 electrons Ch ...
Exam #2
... Given that Hf for MgCl2 is -641.6 kJ/mol and Hf for KCl is -435.9 kJ/mol, calculate Hrxn for the following equation: ...
... Given that Hf for MgCl2 is -641.6 kJ/mol and Hf for KCl is -435.9 kJ/mol, calculate Hrxn for the following equation: ...
Ground State
... Many-body effect caused by electron-electron interaction Open shell atoms Hund’s rule: the ground state has the maximum total spin and maximum orbital moment ...
... Many-body effect caused by electron-electron interaction Open shell atoms Hund’s rule: the ground state has the maximum total spin and maximum orbital moment ...
CHM 101 - Academic Computer Center
... high, positive or slightly negative low, positive or slightly negative high, very negative None of these is generally correct. ...
... high, positive or slightly negative low, positive or slightly negative high, very negative None of these is generally correct. ...
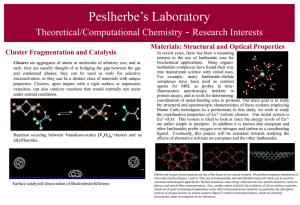
Cluster Fragmentation and Catalysis
... useful to study basic processes such as the role of microsolvation in chemical reactions. For example, the study of simple ion-cluster properties can show the role played by the microscopic interactions between species. As well, when exploring properties of ion pairs in clusters, it is possible to i ...
... useful to study basic processes such as the role of microsolvation in chemical reactions. For example, the study of simple ion-cluster properties can show the role played by the microscopic interactions between species. As well, when exploring properties of ion pairs in clusters, it is possible to i ...
Organic Macromolecules
... and are usually found in living things. Because of its atomic structure, carbon bonds easily with other carbon atoms, and many other substances Carbon can form single bonds (one electron is shared), double bonds (two electrons are shared), or triple bonds (three electrons are shared) ...
... and are usually found in living things. Because of its atomic structure, carbon bonds easily with other carbon atoms, and many other substances Carbon can form single bonds (one electron is shared), double bonds (two electrons are shared), or triple bonds (three electrons are shared) ...
General Chemistry - Review for final exam: (Make sure you bring
... d. Ionization energy e. 2nd ionization energy 41. What are cations and anions? Which type of elements form each? 42. Write the ions formed by the following: State how many electrons were gained or lost. a. F b. Ca c. H d. S e. Al 43. What is the octet rule? 44. What are some basic properties of ioni ...
... d. Ionization energy e. 2nd ionization energy 41. What are cations and anions? Which type of elements form each? 42. Write the ions formed by the following: State how many electrons were gained or lost. a. F b. Ca c. H d. S e. Al 43. What is the octet rule? 44. What are some basic properties of ioni ...
Chem 2641 Chapter 5 Understanding Organic Reactions I. Writing
... III. Making and breaking bonds A. The description of how bonds are broken and formed in a chemical reaction is called the mechanism of the reaction. B. Reactions can be one step or more than one step. 1. Reactions that are one step are called concerted reactions. The reactant is converted directly t ...
... III. Making and breaking bonds A. The description of how bonds are broken and formed in a chemical reaction is called the mechanism of the reaction. B. Reactions can be one step or more than one step. 1. Reactions that are one step are called concerted reactions. The reactant is converted directly t ...
Activation energy
... • Activation energy is the energy needed to start a reaction and break chemical bonds in the reactants. – This is why a flammable material, like gasoline, does not burn without a spark or flame. – The spark supplies the activation energy to start the reaction. ...
... • Activation energy is the energy needed to start a reaction and break chemical bonds in the reactants. – This is why a flammable material, like gasoline, does not burn without a spark or flame. – The spark supplies the activation energy to start the reaction. ...
Chapter 2
... -Building blocks of proteins are amino acids -can range from 50 to 1000’s of amino acids in structure. -The sequence in which the amino acids are placed determines the structure and function of that specific protein. -Fibrous or Structural Proteins-Globular or Functional ProteinsEnzymes-contain a sp ...
... -Building blocks of proteins are amino acids -can range from 50 to 1000’s of amino acids in structure. -The sequence in which the amino acids are placed determines the structure and function of that specific protein. -Fibrous or Structural Proteins-Globular or Functional ProteinsEnzymes-contain a sp ...