* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organic Macromolecules
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
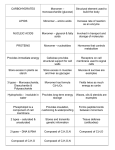
The Chemicals of Life Organic molecules contain carbon-carbon bonds, and are usually found in living things. Because of its atomic structure, carbon bonds easily with other carbon atoms, and many other substances Carbon can form single bonds (one electron is shared), double bonds (two electrons are shared), or triple bonds (three electrons are shared) Carbon can form straight chains, branched chains, or rings; many different compounds are possible A polymer is a large molecule made of many small molecules (monomers) Isomers are molecules with the same chemical formula(C6H12O6), but different structures Macromolecule=Large molecule or polymer Four main types of organic macromolecules are required for all living things Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Monomer=Glucose (monosaccharide) Carbohydrates are used for a quick energy source (glucose) or cell walls of plants (cellulose) Ex.:Polysaccharides (starch,glycogen, cellulose), disaccharides (sucrose),monosaccharide (glucose) Monomer=Fatty Acid Cells use lipids for energy storage, insulation, cell membranes, protective coatings Examples include saturated and unsaturated fats, oils, waxes Also called polypeptides Monomer=Amino Acids; there are 20 different amino acids, held together by peptide bonds Used for building structures (skin, muscles)or speeding up chemical reactions (enzymes) Ex.: keratin (hair, nails, skin), actin and myosin (muscles), meat Enzymes are a special kind of protein that act as a catalyst (speed up chemical reactions) They speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy (the amount of energy needed to start a chemical reaction) Ex.: Amylase (enzyme in saliva that breaks down starch, or amylose), Lactase (enzyme that breaks down lactose) Monomer=Nucleotide (made of a phosphate, sugar, nitrogen base) Only two types: DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid) Stores instructions for cellular functions and contains genetic information