KTH | KD1500 Physical Biochemistry 7.5 credits
... This course is aimed at giving biotechnology students basic knowledge in physical biochemistry, and to show how thermodynamics and kinetics is applied in biology. The course contains different part that systematically point out the most important aspects of physical chemistry for biological applicat ...
... This course is aimed at giving biotechnology students basic knowledge in physical biochemistry, and to show how thermodynamics and kinetics is applied in biology. The course contains different part that systematically point out the most important aspects of physical chemistry for biological applicat ...
equilibrium and activation energy
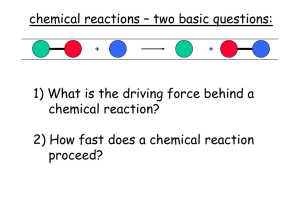
... Rates of chemical reactions are related to the properties of atoms, ions, and molecules through a model called collision theory. According to collision theory, atoms, ions, and molecules can react to form products when they collide, provided they have enough kinetic energy. ...
... Rates of chemical reactions are related to the properties of atoms, ions, and molecules through a model called collision theory. According to collision theory, atoms, ions, and molecules can react to form products when they collide, provided they have enough kinetic energy. ...
Midterm Exam 2
... 2) (10 points) In a particular photoelectron spectrum using 22.00 eV photons, electrons were ejected with kinetic energies of 10.00 eV, 8.25 eV, and 5.50 eV. Sketch an energy level diagram for the species, showing the ionization energies of the three identifiable ...
... 2) (10 points) In a particular photoelectron spectrum using 22.00 eV photons, electrons were ejected with kinetic energies of 10.00 eV, 8.25 eV, and 5.50 eV. Sketch an energy level diagram for the species, showing the ionization energies of the three identifiable ...
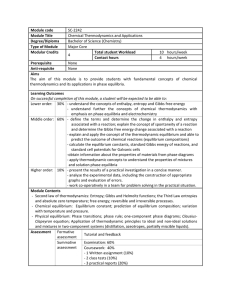
Module code SC-2242 Module Title Chemical Thermodynamics and
... Bachelor of Science (Chemistry) Major Core Total student Workload ...
... Bachelor of Science (Chemistry) Major Core Total student Workload ...
CHAPTER 2: THE ATOMS AND MOLECULES OF ANCIENT EARTH
... b. Reduction of CO2 by H2 forms H2CO, which is used as a building block to form organic compounds (compounds containing at least one C–C bond). (Fig. 2.13) B. For carbon to be reduced, early atmosphere must have contained CH 4, H2, and NH3 (molecules that can give up electrons). 1. Volcanic ash is k ...
... b. Reduction of CO2 by H2 forms H2CO, which is used as a building block to form organic compounds (compounds containing at least one C–C bond). (Fig. 2.13) B. For carbon to be reduced, early atmosphere must have contained CH 4, H2, and NH3 (molecules that can give up electrons). 1. Volcanic ash is k ...
32 . R $ [ ~ % % + l
... down the stairs and finally comes to a rest by the outside door. Which sequence best describes the energy transformations for the piano form the moment it is being brought upstairs, to when it stops by the door? (a) Potential energy Kinetic energy 3 Thermal energy of the ground and piano (b) Ground ...
... down the stairs and finally comes to a rest by the outside door. Which sequence best describes the energy transformations for the piano form the moment it is being brought upstairs, to when it stops by the door? (a) Potential energy Kinetic energy 3 Thermal energy of the ground and piano (b) Ground ...
Chapter 19 Reaction Rates And Equilibrium
... than the reactants, and the ΔH is negative. (2) The products have higher potential energy than the reactants, and the ΔH is positive. (3) The products have lower potential energy than the reactants, and the ΔH is negative. (4) The products have lower potential energy than the reactants, and the ΔH i ...
... than the reactants, and the ΔH is negative. (2) The products have higher potential energy than the reactants, and the ΔH is positive. (3) The products have lower potential energy than the reactants, and the ΔH is negative. (4) The products have lower potential energy than the reactants, and the ΔH i ...
Atomic number or proton number is the total number of protons in
... Atomic number or proton number is the total number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. Mass Number or nucleon number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. The relative isotopic ma ...
... Atomic number or proton number is the total number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. Mass Number or nucleon number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. The relative isotopic ma ...
File
... • The following three statements summarize the collision theory. 1) Particles must collide in order to react. 2) The particles must collide with the correct orientation. 3) The particles must collide with enough energy to form an activated complex, which is an intermediate particle made up of the jo ...
... • The following three statements summarize the collision theory. 1) Particles must collide in order to react. 2) The particles must collide with the correct orientation. 3) The particles must collide with enough energy to form an activated complex, which is an intermediate particle made up of the jo ...
Trends in the periodic table - Brigham Young University
... • Shielding effect of core electrons (S) • Nuclear effective charge, Zeff • Zeff = Z – S – What is Z? What is S? ...
... • Shielding effect of core electrons (S) • Nuclear effective charge, Zeff • Zeff = Z – S – What is Z? What is S? ...
Periodic Trends
... First ionization energy increases from left to right across a period. First ionization energy decreases down a group because atomic size increases and less energy is required to remove an electron farther from the nucleus. ...
... First ionization energy increases from left to right across a period. First ionization energy decreases down a group because atomic size increases and less energy is required to remove an electron farther from the nucleus. ...
Document
... More energy is needed to break chemical bonds, so it absorbs energy from its surroundings! It’s surroundings would feel cold, because heat (energy) is being taken from it. Example: Melting ice….. Energy is absorbed from the surroundings to melt the ice, which makes the air nearby feel cold. ...
... More energy is needed to break chemical bonds, so it absorbs energy from its surroundings! It’s surroundings would feel cold, because heat (energy) is being taken from it. Example: Melting ice….. Energy is absorbed from the surroundings to melt the ice, which makes the air nearby feel cold. ...
HS-PS1-6
... concentration of the reacting particles on the rate at which a reaction occurs. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on student reasoning that focuses on the number and energy of collisions between molecules.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment is limited to simple reactions in which there are only t ...
... concentration of the reacting particles on the rate at which a reaction occurs. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on student reasoning that focuses on the number and energy of collisions between molecules.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment is limited to simple reactions in which there are only t ...