ExamView - Untitled.tst
... ____ 13. Thomson made his discovery about the atom during an experiment using a. thermal energy. c. cathode rays b. kinetic energy. d. X rays. ____ 14. In _____ atomic model, negative electrons orbit the positively charged nucleus. a. Dalton’s c. Rutherford’s b. Thomson’s d. Democritus’s ____ 15. Wh ...
... ____ 13. Thomson made his discovery about the atom during an experiment using a. thermal energy. c. cathode rays b. kinetic energy. d. X rays. ____ 14. In _____ atomic model, negative electrons orbit the positively charged nucleus. a. Dalton’s c. Rutherford’s b. Thomson’s d. Democritus’s ____ 15. Wh ...
Sem 1 Final
... • Look over your notes from the last couple days of class. • Remember to read the questions completely AND use units when solving the “math” questions. ...
... • Look over your notes from the last couple days of class. • Remember to read the questions completely AND use units when solving the “math” questions. ...
Chapter 8 Notes - Bonding: General Concepts 8.1 Types of
... 2. See table 8.2 in your text 8.10 Lewis Structures A. Electrons and Stability 1. "the most important requirement for the formation of a stable compound is that the atoms achieve noble gas configurations 2. Duet rule a. Hydrogen, lithium, beryllium, and boron form stable molecules when they share tw ...
... 2. See table 8.2 in your text 8.10 Lewis Structures A. Electrons and Stability 1. "the most important requirement for the formation of a stable compound is that the atoms achieve noble gas configurations 2. Duet rule a. Hydrogen, lithium, beryllium, and boron form stable molecules when they share tw ...
Chemical Bond – a force that holds two atoms together, the bond
... Chemical Bond – a force that holds two atoms together, the bond could be between two elements that are the same element or different elements. Ionic Bond – an electrostatic force between two different atomic elements (atomic nonmetal and an atomic metal) in which the atomic nonmetal steals the avail ...
... Chemical Bond – a force that holds two atoms together, the bond could be between two elements that are the same element or different elements. Ionic Bond – an electrostatic force between two different atomic elements (atomic nonmetal and an atomic metal) in which the atomic nonmetal steals the avail ...
Chemical Basis of Life
... Composed of 1 or more elements Found in 1 of 3 states Gas – no definite shape or volume Liquid – shape conforms to container ...
... Composed of 1 or more elements Found in 1 of 3 states Gas – no definite shape or volume Liquid – shape conforms to container ...
AP Review – Life and Chemistry Name: Date: ___B_ 1. The atomic
... ___B__ 2. Which of the following statements concerning electrons is not correct? a. b. c. d. ...
... ___B__ 2. Which of the following statements concerning electrons is not correct? a. b. c. d. ...
Chapter 19: Molecules and Compounds
... Mg loses 2 electrons so it has an oxidation number of +2 Oxygen gains 2 electrons so it has an oxidation number of –2. ...
... Mg loses 2 electrons so it has an oxidation number of +2 Oxygen gains 2 electrons so it has an oxidation number of –2. ...
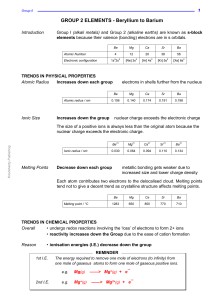
GROUP 2 ELEMENTS - Beryllium to Barium
... basic strength also increases down group this is because the solubility increases the metal ions get larger so charge density decreases there is a lower attraction between the OH¯ ions and larger dipositive ions the ions will split away from each other more easily there will be a greater concentrati ...
... basic strength also increases down group this is because the solubility increases the metal ions get larger so charge density decreases there is a lower attraction between the OH¯ ions and larger dipositive ions the ions will split away from each other more easily there will be a greater concentrati ...
Unit A Review Questions
... The zinc electrode is gaining mass because the copper ions are coming out of the solution and are being reduced by the zinc metal being oxidized. This would also account for the colour change in the copper nitrate solution. As the copper ions come out of the solution, the solution becomes a fainter ...
... The zinc electrode is gaining mass because the copper ions are coming out of the solution and are being reduced by the zinc metal being oxidized. This would also account for the colour change in the copper nitrate solution. As the copper ions come out of the solution, the solution becomes a fainter ...
Bonding
... and, therefore, does not produce a conducting solution. Silver nitrate has an ionic bond between the silver cation and the nitrate anion that is hydrated in water producing a conducting ionic solution. (b) Silver nitrate has covalent bonds in the nitrate anion and an ionic bond between the cation an ...
... and, therefore, does not produce a conducting solution. Silver nitrate has an ionic bond between the silver cation and the nitrate anion that is hydrated in water producing a conducting ionic solution. (b) Silver nitrate has covalent bonds in the nitrate anion and an ionic bond between the cation an ...
Study Guide Matter: Building Blocks of the Universe
... * Know the atomic particles: electron, neutron, and proton. where are they in the atom? What is their charge? What is their mass? How are electrons arranged in the electron cloud? * Know the four forces in the atom: strong, electromagnetic, weak, & gravity What are each of the forces responsible for ...
... * Know the atomic particles: electron, neutron, and proton. where are they in the atom? What is their charge? What is their mass? How are electrons arranged in the electron cloud? * Know the four forces in the atom: strong, electromagnetic, weak, & gravity What are each of the forces responsible for ...
Advanced Chemistry Midterm
... 36. What are parts of the electromagnetic spectrum in order from lowest frequency/lowest energy to highest frequency/highest energy? ...
... 36. What are parts of the electromagnetic spectrum in order from lowest frequency/lowest energy to highest frequency/highest energy? ...
Atomic Structure
... neutral atom in its ground state in order to form a cation. • Electron affinity - The energy given off when a neutral atom in the gas phase gains an extra electron to form a negatively charged ion. • Electronegativity - a measure of the attraction of an atom for the electrons in a chemical bond. ...
... neutral atom in its ground state in order to form a cation. • Electron affinity - The energy given off when a neutral atom in the gas phase gains an extra electron to form a negatively charged ion. • Electronegativity - a measure of the attraction of an atom for the electrons in a chemical bond. ...
Introduction to Chemistry for Coach Keith`s Biology
... The force of attraction between molecules is so strong that the oxygen atom of one molecule can actually remove the hydrogen from other water molecules; called Dissociation H20-----GOES TO----- H+ + OHOH- called hydroxide ion; H+ called hydrogen ion Free H+ ion can react with another water molecule ...
... The force of attraction between molecules is so strong that the oxygen atom of one molecule can actually remove the hydrogen from other water molecules; called Dissociation H20-----GOES TO----- H+ + OHOH- called hydroxide ion; H+ called hydrogen ion Free H+ ion can react with another water molecule ...
EXAM 007534RR Acids, Bases, and Redox Reactions
... 8. B. Cohesion is exhibited as water molecules are attracted to the molecules in the glass. 9. C. the salt breaks into positive chlorine ions and negative sodium ions. 10. D. high specific heat. 11. C. atoms must not be able to closely approach the hydrogen. 12. B. Three 13. B. None 14. C. Lithium i ...
... 8. B. Cohesion is exhibited as water molecules are attracted to the molecules in the glass. 9. C. the salt breaks into positive chlorine ions and negative sodium ions. 10. D. high specific heat. 11. C. atoms must not be able to closely approach the hydrogen. 12. B. Three 13. B. None 14. C. Lithium i ...
Solution - ZOMUedu
... ■ Water is a good solvent because the molecules are polar ■ The oxygen atoms have a partial negative charge ■ The hydrogen atoms have a partial positive charge ○ Hydration ■ Process of breaking bonds ■ H+ ions attracts negative ions ■ O- attracts positive ions Solubility and Electrolytes ○ Solubilit ...
... ■ Water is a good solvent because the molecules are polar ■ The oxygen atoms have a partial negative charge ■ The hydrogen atoms have a partial positive charge ○ Hydration ■ Process of breaking bonds ■ H+ ions attracts negative ions ■ O- attracts positive ions Solubility and Electrolytes ○ Solubilit ...
Biochemistry Introduction day 1
... Isotopes: Atoms of an element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. Ex: Oxygen usually has 8 neutrons but 9 and 10 neutrons can be found in some oxygen atoms. Some isotopes are unstable in the nucleus which makes it more likely to decay and release energy. This i ...
... Isotopes: Atoms of an element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. Ex: Oxygen usually has 8 neutrons but 9 and 10 neutrons can be found in some oxygen atoms. Some isotopes are unstable in the nucleus which makes it more likely to decay and release energy. This i ...
chapter02_part1_lecture - bloodhounds Incorporated
... • Molecules form when two or more atoms bond together (example: O2) • Compounds form when two or more different elements bond together (H2O) • When a chemical reaction occurs, energy may be given off or absorbed. ...
... • Molecules form when two or more atoms bond together (example: O2) • Compounds form when two or more different elements bond together (H2O) • When a chemical reaction occurs, energy may be given off or absorbed. ...
Chapter 2 part 1
... • Molecules form when two or more atoms bond together (example: O2) • Compounds form when two or more different elements bond together (H2O) • When a chemical reaction occurs, energy may be given off or absorbed. ...
... • Molecules form when two or more atoms bond together (example: O2) • Compounds form when two or more different elements bond together (H2O) • When a chemical reaction occurs, energy may be given off or absorbed. ...
1.1 Safety in the Science Classroom
... compounds are made up of a metal and a non-metal. In ionic compounds, atoms gain or lose electrons to form ions. Example: NaCl ...
... compounds are made up of a metal and a non-metal. In ionic compounds, atoms gain or lose electrons to form ions. Example: NaCl ...
MatterPP4
... Dissolving – The process in which particles of substances separate and spread evenly amongst each other. • Solute – substance that is dissolved. A solute is soluble, or able to dissolve. • A substance that is insoluble is unable to dissolve, forms a mixture that is not homogeneous, and therefore NOT ...
... Dissolving – The process in which particles of substances separate and spread evenly amongst each other. • Solute – substance that is dissolved. A solute is soluble, or able to dissolve. • A substance that is insoluble is unable to dissolve, forms a mixture that is not homogeneous, and therefore NOT ...
Science Olympiad
... (B) atomic radius decreases due to an increase in effective nuclear charge. (C) electronegativity decreases due to an increase in atomic radius. (D) electron affinity decreases due to an increase in effective nuclear charge. (E) ionization energy increases due to an increase in atomic radius. ______ ...
... (B) atomic radius decreases due to an increase in effective nuclear charge. (C) electronegativity decreases due to an increase in atomic radius. (D) electron affinity decreases due to an increase in effective nuclear charge. (E) ionization energy increases due to an increase in atomic radius. ______ ...
Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reactions
... Step 1: Break the unbalanced equation into half-reactions. Step 2: Balance each half-reaction by following a-d. a. Balance all elements except O and H by adjusting coefficients. b. Balance O by adding H2O to the appropriate side. c. Balance H by adding the appropriate number of H+ ions to the side t ...
... Step 1: Break the unbalanced equation into half-reactions. Step 2: Balance each half-reaction by following a-d. a. Balance all elements except O and H by adjusting coefficients. b. Balance O by adding H2O to the appropriate side. c. Balance H by adding the appropriate number of H+ ions to the side t ...