Exam 3 Answer Key
... A. In Bohr’s atomic theory, when an electron moves from one energy level to another energy level more distant from the nucleus, energy is emitted. B. The principal quantum number determines the size and the shape of the orbitals. C. Mendeleev assembled the periodic table according to the element’s e ...
... A. In Bohr’s atomic theory, when an electron moves from one energy level to another energy level more distant from the nucleus, energy is emitted. B. The principal quantum number determines the size and the shape of the orbitals. C. Mendeleev assembled the periodic table according to the element’s e ...
Notes on QA - Scarsdale Public Schools
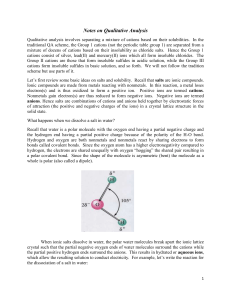
... cations consist of silver, lead(II) and mercury(II) ions which all form insoluble chlorides. The Group II cations are those that form insoluble sulfides in acidic solution, while the Group III cations form insoluble sulfides in basic solution, and so forth. We will not follow the tradition scheme bu ...
... cations consist of silver, lead(II) and mercury(II) ions which all form insoluble chlorides. The Group II cations are those that form insoluble sulfides in acidic solution, while the Group III cations form insoluble sulfides in basic solution, and so forth. We will not follow the tradition scheme bu ...
Elements PPT
... We have joined two elements together with an ionic bond to form the mineral Halite or more commonly salt. ...
... We have joined two elements together with an ionic bond to form the mineral Halite or more commonly salt. ...
Ch. 2 The Chemistry of Life
... - pH scale - _________________ system to indicate the _______________ of ____ ions in ______________, ranges from _______ - Acid – any ______________ that forms _____ ions in ____________ - __________ solutions have __________ concentration of ____ ions than pure _________ & have ____ values _______ ...
... - pH scale - _________________ system to indicate the _______________ of ____ ions in ______________, ranges from _______ - Acid – any ______________ that forms _____ ions in ____________ - __________ solutions have __________ concentration of ____ ions than pure _________ & have ____ values _______ ...
Ionic and Covalent bonding (WLC)
... • Electron Dot Structure-a notation that depicts valence electrons as dots around the atomic symbol of the element; represents inner electrons of the nucleus ...
... • Electron Dot Structure-a notation that depicts valence electrons as dots around the atomic symbol of the element; represents inner electrons of the nucleus ...
Notes on Atoms and Molecules
... Atom contains less than four electrons in its outermost shell; the valency of an atom is equal to the number of electrons present in the valence shell. Example: Sodium has one electron in its outermost shell, so the valency of sodium is 1. Calcium has two electrons in its outermost shell, so the val ...
... Atom contains less than four electrons in its outermost shell; the valency of an atom is equal to the number of electrons present in the valence shell. Example: Sodium has one electron in its outermost shell, so the valency of sodium is 1. Calcium has two electrons in its outermost shell, so the val ...
lecture slides of chap8
... the reduced electron repulsion resulting from removal of electrons make the electron clouds shrink. Anion is always larger than atom from which it is formed. This is because the nuclear charge remains the same but electron repulsion resulting from the additional electron enlarges the electron clouds ...
... the reduced electron repulsion resulting from removal of electrons make the electron clouds shrink. Anion is always larger than atom from which it is formed. This is because the nuclear charge remains the same but electron repulsion resulting from the additional electron enlarges the electron clouds ...
Coulomb’s Law
... • Electrostatics is the study of electrical charges that are not moving. Electro – charges, statics– not moving. • Review chemistry – Protons, positively charged, in nucleus – Neutrons, not charged, in nucleus – Electrons, negatively charged , outside of nucleus ...
... • Electrostatics is the study of electrical charges that are not moving. Electro – charges, statics– not moving. • Review chemistry – Protons, positively charged, in nucleus – Neutrons, not charged, in nucleus – Electrons, negatively charged , outside of nucleus ...
Matter Quiz 2 With Answers
... a. Kinetic Atomic Theory b. Kinetic Molecular Theory c. Kinetic Theory d. Phasic Changing Hypothesis 6. In any physical or chemical change, matter is neither created nor destroyed. Matter can only be changed from one form to another. This scientific law is called _______________________. a. The seco ...
... a. Kinetic Atomic Theory b. Kinetic Molecular Theory c. Kinetic Theory d. Phasic Changing Hypothesis 6. In any physical or chemical change, matter is neither created nor destroyed. Matter can only be changed from one form to another. This scientific law is called _______________________. a. The seco ...
Ch 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... - An ion is a charged particle composed of one or more atoms. Ions are positive (cation) if e-1’s are lost and negative (anion) if e-1’s are gained. - An ionic compound is neutral (no overall charge) and is composed of cations and anions together. - Solid ionic compounds are crystals with a regular ...
... - An ion is a charged particle composed of one or more atoms. Ions are positive (cation) if e-1’s are lost and negative (anion) if e-1’s are gained. - An ionic compound is neutral (no overall charge) and is composed of cations and anions together. - Solid ionic compounds are crystals with a regular ...
Hints for Names and Formulas (Ch. 4 in Zumdahl Chemistry)
... (5) The positive ion (cation) is written first, and is usually a metallic ion and uses the name of the metal ● transition metals, tin and lead are known to have more than one ionic charge and must be shown in the name as a Roman numeral in parentheses ◘ examples: CuCl is copper(I) chloride and CuCl2 ...
... (5) The positive ion (cation) is written first, and is usually a metallic ion and uses the name of the metal ● transition metals, tin and lead are known to have more than one ionic charge and must be shown in the name as a Roman numeral in parentheses ◘ examples: CuCl is copper(I) chloride and CuCl2 ...
Test 4
... 1) Define, identify and/or give examples of: electron configuration, Aufbau Principle, Hund’s Rule, Pauli Exclusion Principle, ground state, excited state, degenerate orbital, shielding, effective nuclear charge, valence electrons, valence shell, s, p, d, & f block, atomic radius, periodic trends of ...
... 1) Define, identify and/or give examples of: electron configuration, Aufbau Principle, Hund’s Rule, Pauli Exclusion Principle, ground state, excited state, degenerate orbital, shielding, effective nuclear charge, valence electrons, valence shell, s, p, d, & f block, atomic radius, periodic trends of ...
Chapter 7, 8, and 9 Exam 2014 Name I. 50% of your grade will come
... Select the one lettered choice that best fits each statement and then fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. A choice may be used once, more than once, or not at all in each set. Questions 1–4 refer to the following types of energy. (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) ...
... Select the one lettered choice that best fits each statement and then fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. A choice may be used once, more than once, or not at all in each set. Questions 1–4 refer to the following types of energy. (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) ...
BASIC CHEMISTRY
... The atomic number for O is 8. How many protons in O? How many electrons in O? The atomic mass of O is 16. How many neutrons in O? Draw an Oxygen atom. Show the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and the electrons in the energy ...
... The atomic number for O is 8. How many protons in O? How many electrons in O? The atomic mass of O is 16. How many neutrons in O? Draw an Oxygen atom. Show the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and the electrons in the energy ...
Quiz 1 - sample quiz
... 5. When a water solution of potassium sulfate is added to a water solution of strontium nitrate, a precipitate of strontium sulfate forms. What is the correctly balanced net ionic equation for the reaction? a) K2SO4(aq) + Sr(NO3)2(aq) SrSO4(s) + 2KNO3(aq) b) 2K+(aq) + SO42–(aq) + Sr2+(aq) + 2NO3–( ...
... 5. When a water solution of potassium sulfate is added to a water solution of strontium nitrate, a precipitate of strontium sulfate forms. What is the correctly balanced net ionic equation for the reaction? a) K2SO4(aq) + Sr(NO3)2(aq) SrSO4(s) + 2KNO3(aq) b) 2K+(aq) + SO42–(aq) + Sr2+(aq) + 2NO3–( ...
4.IonicCompounds - Gleneaglesunit1and2chemistry2012
... • Ionic bonds formed when metal atoms combined with non-metal atoms • Metallic bonds formed when metal atoms combined with metal atoms. • Covalent bonds formed when non-metal atoms combined with non-metal atoms. ...
... • Ionic bonds formed when metal atoms combined with non-metal atoms • Metallic bonds formed when metal atoms combined with metal atoms. • Covalent bonds formed when non-metal atoms combined with non-metal atoms. ...
Chemical Bonding Review
... according to arbitrary scales. • The definition of electronegativity is a common test question. Sometimes they do not use the word “electronegativity” in the question at all – you have to recognize that they are talking about it! • Electronegativity values for the elements are found in ...
... according to arbitrary scales. • The definition of electronegativity is a common test question. Sometimes they do not use the word “electronegativity” in the question at all – you have to recognize that they are talking about it! • Electronegativity values for the elements are found in ...
Unit 1 - Learning Objectives
... An ionic structure consists of a giant lattice of oppositely charged ions. The formula for an ionic compound gives the simplest ratio of positive ions to negative ions. A metallic structure consists of a giant lattice of positively charged ions and delocalised outer electrons. ...
... An ionic structure consists of a giant lattice of oppositely charged ions. The formula for an ionic compound gives the simplest ratio of positive ions to negative ions. A metallic structure consists of a giant lattice of positively charged ions and delocalised outer electrons. ...
Basic Electrical Quantities - Pojęcia
... semiconductors – materials are classed below conductors in their ability to carry current because they have fewer free electrons in their structure.  insulators – poor conductors of electric current. used to prevent current where it is not wanted.  electron – smallest particle that exhibits ...
... semiconductors – materials are classed below conductors in their ability to carry current because they have fewer free electrons in their structure.  insulators – poor conductors of electric current. used to prevent current where it is not wanted.  electron – smallest particle that exhibits ...
General Chemistry - Review for final exam: (Make sure you bring
... e. 2nd ionization energy 41. What are cations and anions? Which type of elements form each? 42. Write the ions formed by the following: State how many electrons were gained or lost. a. F b. Ca c. H d. S e. Al 43. What is the octet rule? 44. What are some basic properties of ionic compounds? 45. What ...
... e. 2nd ionization energy 41. What are cations and anions? Which type of elements form each? 42. Write the ions formed by the following: State how many electrons were gained or lost. a. F b. Ca c. H d. S e. Al 43. What is the octet rule? 44. What are some basic properties of ionic compounds? 45. What ...
2011 Chem Facts Key
... HCl(aq) NaCl(aq) CH3OH(aq) , NaOH(aq) 57. pH is the - log of the hydronium [H+] ion concentration. pH = -log[H+] 58. What is the pH of a 0.00001 molar HCl solution? 1, 9, 5, 4 59. Arrhenius model of acids and bases states: “Acids give off H+ to form H3O+ ions in aqueous solution as their only (+) io ...
... HCl(aq) NaCl(aq) CH3OH(aq) , NaOH(aq) 57. pH is the - log of the hydronium [H+] ion concentration. pH = -log[H+] 58. What is the pH of a 0.00001 molar HCl solution? 1, 9, 5, 4 59. Arrhenius model of acids and bases states: “Acids give off H+ to form H3O+ ions in aqueous solution as their only (+) io ...
Untitled - Washington County Schools
... neutrons? Electrons are the smallest of the three particles that make up atoms. Electrons are found in shells or orbitals that surround the nucleus of an atom. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus. They group together in the center of the atom. That's all you have to remember. Three easy pi ...
... neutrons? Electrons are the smallest of the three particles that make up atoms. Electrons are found in shells or orbitals that surround the nucleus of an atom. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus. They group together in the center of the atom. That's all you have to remember. Three easy pi ...
Chapter 9: Chemical Quantities
... - Emission and Absorption of Light by atoms and possible transitions of electrons ...
... - Emission and Absorption of Light by atoms and possible transitions of electrons ...