* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Basic Electrical Quantities - Pojęcia
Electrical wiring wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
National Electrical Code wikipedia , lookup
Electromigration wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Static electricity wikipedia , lookup
Insulator (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
High voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
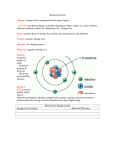
Basic Electrical Quantities - PojÄ™cia.doc (30 KB) Pobierz electron – basic particle of electrical charge.  atom – the smallest particle of an element that retains the characteristics of that element. Atoms have planetary type of structure, consisting of central nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons. Hydrogen is the simplest atom.  atomic number – the number of protons in the nucleus.  atomic weight – approximately the numbers of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.  copper – the most commonly used metal in electrical applications.  shells – the orbits in which the electrons are resolving.  free electron – if atom gains sufficient energy from the surrounding media, it can break away from the parrent atom.  conductor – material that allows current to flow easily, has a large number of free electrons.  semiconductors – materials are classed below conductors in their ability to carry current because they have fewer free electrons in their structure.  insulators – poor conductors of electric current. used to prevent current where it is not wanted.  electron – smallest particle that exhibits negative electrical charge. 1 electron has a charge of 11.6x10^-19 C  coulomb – the unit of electrical charge, one coulomb is the total charge possessed by 6.25x10^18 electrons. [C]  negative charge are created when atom acquire an extra electrons in the outer shell and becomes a negative ion  positive charge are created when valence electron is pulled away from atom, (more protons than electrons) becomes a positive ion.  the unit of voltage is volt, symbolized by V | V= W/Q   W-energy Q-unit charge  Sources of voltage:  the battery – one type of voltage source that convers chemical energy into electrical energy, the amountof voltage provided by a battery varied.  elecronic supply – convert the ac voltage from the wall outlet to a constant volatage(dc).  solar cell – based on photovoltaic action, which is the process – light energy is converted directly into electrical energy.  generator – convert mechanical energy into electrical energy using electromagnetic induction. Conductor is rotated through a magnetic field, and voltage is produced across the conductor. if voltage is placed across the conductive material movement of free electrons is directionaly.  electrical current – the movement of free electrons from the negative end of the material to the positive end.  ampere – this is the unit of curren, symbolized by capital A. One ampere is the amount of current flowing when a number of electrons having one coulomb of charge move past a given point in one second. I = Q/t Q – charge t –time A=C/s  electrical circuit can be represented by a schematic diagram using standard symbols for each element.  switches – are used for controlling the opening or closing of circuits by either mechanical or electronic means.  s-single d-double p-pole t-throw SPST – wylacznik 1 biegunowy, jednopolozeniowy SPDT – wylacznik 1 biegunowy, dwupolozeniowy DPST – wylacznik dwubiegunowy, jednopolozeniowy DPDT – wylacznik dwubiegunowy, dwupolozeniowy PB –push button – connection is made between two contacts when button is depressed. NCPB – normally closed push button – connection is broken whe button is depressed. SP Rotary – 1 biegunowy, rotacyjny – knob is turned to make connection.  resistance – property of a material that restrict the flow of electrons. Is the opposition current. Unit of resistance is Ohm. 1 ohm is resistance when 1A of current flows in a material with 1V applied.  Resistors - componnet specifically designed to have a certain amount of resistance. fixed, variable - value can be changed easily with a manual or an automatic adjustment.  Fuses – used to deliberately create an open circuit, when the current exceeds a specifed number of amperes, or other abnormal condition in a circuit.  multimeter – can measure voltage, current, resistance and other. voltmeter – parallel connection ammeter – series connection  Plik z chomika: kswidrak87 Inne pliki z tego folderu: angol.doc (28 KB) Basic Electrical Quantities - PojÄ™cia.doc (30 KB) Czasowniki nieregularne.doc (180 KB) Basic Electrical Quantities - SÅ‚owka.doc (101 KB) Elektryk - SÅ‚owka.doc (54 KB) Inne foldery tego chomika: Dokumenty Galeria KLC.Consulting.SMAC.Professional.v2.7.BETA.Incl.Keygen-Lz0 Prywatne SMAC Pro 2.7 B ZgÅ‚oÅ› jeÅ›li naruszono regulamin Strona główna AktualnoÅ›ci Kontakt Dla Mediów DziaÅ‚ Pomocy Opinie Program partnerski Regulamin serwisu Polityka prywatnoÅ›ci Ochrona praw autorskich Platforma wydawców Copyright © 2012 Chomikuj.pl