Ionization methods - 2-CI - Florida International University
... – The amount of excess of energy imparted on an [M + H]+ ion on its formation depends on the relative affinities of the conjugate base of the reactant ion (CH 4, NH3 and so on) and the compound M. • Decrease in PA (proton affinity) of the conjugate base (or increase in acidity of the reactant gas io ...
... – The amount of excess of energy imparted on an [M + H]+ ion on its formation depends on the relative affinities of the conjugate base of the reactant ion (CH 4, NH3 and so on) and the compound M. • Decrease in PA (proton affinity) of the conjugate base (or increase in acidity of the reactant gas io ...
CHEMISTRY notes
... IN FRONT of a molecule to “balance” the # of atoms of REACTANT with Na Na Cl the # of atoms of PRODUCT, Cl Cl Law of Conservation representing the in a chemical equation Na Na Cl ...
... IN FRONT of a molecule to “balance” the # of atoms of REACTANT with Na Na Cl the # of atoms of PRODUCT, Cl Cl Law of Conservation representing the in a chemical equation Na Na Cl ...
CVB101 – Lecture 3 Chemical Bonding • Chemical bonding
... Ionic bonds are a result of electron transfer between atoms to form ions – electrostatic attraction of positive and negative ions This type of bonding occurs between ionic compounds Ionic bonds are present in compounds of metals and non-metals ...
... Ionic bonds are a result of electron transfer between atoms to form ions – electrostatic attraction of positive and negative ions This type of bonding occurs between ionic compounds Ionic bonds are present in compounds of metals and non-metals ...
Review for Exam 1
... Determine how many of each ion type is needed for an overall charge of zero. When the cation and anion have different charges, use the ion charges to determine the number of ions of each needed. ...
... Determine how many of each ion type is needed for an overall charge of zero. When the cation and anion have different charges, use the ion charges to determine the number of ions of each needed. ...
Formulas of Compounds
... Negative portion comes last. There are additional rules if the compound is binary, ternary or higher or takes the form of acids, bases or salts. Writing formulas 1. Now we can use names and formulas of cations and anions to write formulas of compounds. 2. In these formulas, the sum of the total cati ...
... Negative portion comes last. There are additional rules if the compound is binary, ternary or higher or takes the form of acids, bases or salts. Writing formulas 1. Now we can use names and formulas of cations and anions to write formulas of compounds. 2. In these formulas, the sum of the total cati ...
1) - Kurt Niedenzu
... 32) The increase in atomic radius of each successive element within a group is primarily due to an increase in the number of a) neutrons in the nucleus b) electrons in the outermost shell c) unpaired electrons d) occupied principal energy levels 33) Elements that have properties of both metals and n ...
... 32) The increase in atomic radius of each successive element within a group is primarily due to an increase in the number of a) neutrons in the nucleus b) electrons in the outermost shell c) unpaired electrons d) occupied principal energy levels 33) Elements that have properties of both metals and n ...
4. bonding - New Hartford Central Schools
... Elements with more than one positive oxidation number (Transition Metals) (This is called the Stock System) When the oxidation number varies we us a Roman numeral in parentheses to indicate the charge. Roman number is used for the positive element only!!! ...
... Elements with more than one positive oxidation number (Transition Metals) (This is called the Stock System) When the oxidation number varies we us a Roman numeral in parentheses to indicate the charge. Roman number is used for the positive element only!!! ...
Midterm Review Packet - Mrs. McKenzie`s Chemistry and ICP Classes
... 4. Charged particles that move around an atom's nucleus are called ________________________. 5. Chemical bonds are broken, atoms are rearranged, and new bonds are formed during ___________________________ ______________________________. 6. Atoms with filled outermost energy levels tend _____________ ...
... 4. Charged particles that move around an atom's nucleus are called ________________________. 5. Chemical bonds are broken, atoms are rearranged, and new bonds are formed during ___________________________ ______________________________. 6. Atoms with filled outermost energy levels tend _____________ ...
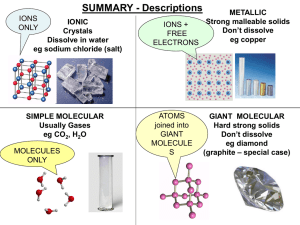
smart_materials_1 - Aldercar High School
... Regular structure, layers slide CONDUCT: YES (very well) Free electrons between ions ...
... Regular structure, layers slide CONDUCT: YES (very well) Free electrons between ions ...
4 - College of Arts and Sciences
... A sample of acetominophen (C8H9O2N) has 6.02 x 1023 atoms of Hydrogen. What is the mass in grams of the sample? How many atoms of H in one mole of C8H9O2N ? 9 x (6.02 x 1023) atoms of H Therefore have 1/9 of a mole of acetominophen What is the molecular weight of acetominophen ? ...
... A sample of acetominophen (C8H9O2N) has 6.02 x 1023 atoms of Hydrogen. What is the mass in grams of the sample? How many atoms of H in one mole of C8H9O2N ? 9 x (6.02 x 1023) atoms of H Therefore have 1/9 of a mole of acetominophen What is the molecular weight of acetominophen ? ...
Pure Substances and Mixtures
... • Pure substances contain only one kind of molecule. – Molecules are small groups of atoms that make up matter. Example: Water is a molecule of two hydrogen atoms, and one oxygen atom • Atoms are the smallest particles of elements ...
... • Pure substances contain only one kind of molecule. – Molecules are small groups of atoms that make up matter. Example: Water is a molecule of two hydrogen atoms, and one oxygen atom • Atoms are the smallest particles of elements ...
chemistry i
... 38. If an electron drops from n=6 to n=2, what type of electromagnetic radiation is emitted? A. Ultraviolet (UV) b. Visible c. Infrared (IR) d. Radiowaves 39. How many protons and electrons are in a 6429Cu2+ ion? A) 27 protons, 29 electrons C) 27 protons, 31 electrons B) 29 protons, 27 electrons D) ...
... 38. If an electron drops from n=6 to n=2, what type of electromagnetic radiation is emitted? A. Ultraviolet (UV) b. Visible c. Infrared (IR) d. Radiowaves 39. How many protons and electrons are in a 6429Cu2+ ion? A) 27 protons, 29 electrons C) 27 protons, 31 electrons B) 29 protons, 27 electrons D) ...
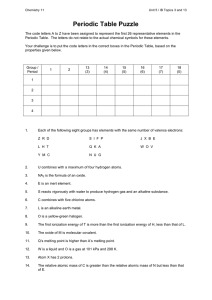
Periodic Table Puzzle
... The code letters A to Z have been assigned to represent the first 26 representative elements in the Periodic Table. The letters do not relate to the actual chemical symbols for these elements. Your challenge is to put the code letters in the correct boxes in the Periodic Table, based on the ...
... The code letters A to Z have been assigned to represent the first 26 representative elements in the Periodic Table. The letters do not relate to the actual chemical symbols for these elements. Your challenge is to put the code letters in the correct boxes in the Periodic Table, based on the ...
Chemistry: The Nature of Matter
... o 2nd shell has a little more energy and holds 8 electrons o 3rd shell has even more energy, etc. ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ Electron config ...
... o 2nd shell has a little more energy and holds 8 electrons o 3rd shell has even more energy, etc. ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ Electron config ...
effective nuclear charge
... 1st IE generally increases across the period ◦ effective nuclear charge increases ...
... 1st IE generally increases across the period ◦ effective nuclear charge increases ...
First Semester Final - Review Questions
... 42. What type of instrument is best for measuring mass, volume, and length? 43. How is the uncertainty of an instrument determined? 44. State the Atlantic-Pacific Rule for determining significant figures. 45. How many significant figures are in the following measurements? a. 0.000653 g c. 8.50x10-9 ...
... 42. What type of instrument is best for measuring mass, volume, and length? 43. How is the uncertainty of an instrument determined? 44. State the Atlantic-Pacific Rule for determining significant figures. 45. How many significant figures are in the following measurements? a. 0.000653 g c. 8.50x10-9 ...
Conservation of Mass
... If its ionic, determine the two ions involved and write cation then anion and you’re done. (Remember that if the cation is a transition/post-transition metal, the ion is named with the charge in roman numerals inside parentheses (usually). ...
... If its ionic, determine the two ions involved and write cation then anion and you’re done. (Remember that if the cation is a transition/post-transition metal, the ion is named with the charge in roman numerals inside parentheses (usually). ...
Ch. 2-1 Nature of Matter
... Atoms Can Bond Together • Chemical compound—substance made of 2 or more different elements • Emergent properties—new properties present at one level that are not seen in the previous level ...
... Atoms Can Bond Together • Chemical compound—substance made of 2 or more different elements • Emergent properties—new properties present at one level that are not seen in the previous level ...
Electronic Spectroscopy of Transition Metal Ions
... • there are many different arrangements of electrons in d orbitals so this gives rise to many possible states (RussellSaunders ‘terms’) that represent different energies for the system as a whole eg. d2 ion 1st electron: any of the 5 d-orbitals and spin up or down gives rise to 10 possibilities 2nd ...
... • there are many different arrangements of electrons in d orbitals so this gives rise to many possible states (RussellSaunders ‘terms’) that represent different energies for the system as a whole eg. d2 ion 1st electron: any of the 5 d-orbitals and spin up or down gives rise to 10 possibilities 2nd ...
2nd Semester Review
... 4. Circle the correct atomic particle for each of the following: Defines an atom Protons Neutrons Electrons Isotopes: same type of atom with different number of Protons Neutrons Determines how atoms combine Protons Neutrons Electrons Ions: same type of atom with different number of Protons Neutrons ...
... 4. Circle the correct atomic particle for each of the following: Defines an atom Protons Neutrons Electrons Isotopes: same type of atom with different number of Protons Neutrons Determines how atoms combine Protons Neutrons Electrons Ions: same type of atom with different number of Protons Neutrons ...
File - Mr. Gittermann
... with no charge and is located in the nucleus of the atom • Electrons: Subatomic particle with a negative charge found in a certain region of space around the nucleus called the electron cloud; kept close to the atom due to the attraction between the opposite charges of the electron and proton ...
... with no charge and is located in the nucleus of the atom • Electrons: Subatomic particle with a negative charge found in a certain region of space around the nucleus called the electron cloud; kept close to the atom due to the attraction between the opposite charges of the electron and proton ...
Valence Electrons and Chemical Bonding
... eight electrons in their outer energy level or, in the case of elements 1-5, two in their outer shell level. ...
... eight electrons in their outer energy level or, in the case of elements 1-5, two in their outer shell level. ...
Atom (A) or Ion (I)
... 20. This substance is an isotope of carbon-12 (12C) 21. The Atomic Theory was first stated in the late 1700s. Which of the following is NOT part of this Atomic Theory? A) All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. B) Atoms are made of smaller particles of positive, neutral ...
... 20. This substance is an isotope of carbon-12 (12C) 21. The Atomic Theory was first stated in the late 1700s. Which of the following is NOT part of this Atomic Theory? A) All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. B) Atoms are made of smaller particles of positive, neutral ...
Topic 3 Structure of Metals and Ionic Compounds Bonding and
... • High melting point: typically several hundred or thousand Kelvin However: Salts that are liquid at room temperature have been prepared using organic cations • Very low electrical conductivity, but conduct electricity quite well when molten • Most dissolve in high polarity solvents to form conducti ...
... • High melting point: typically several hundred or thousand Kelvin However: Salts that are liquid at room temperature have been prepared using organic cations • Very low electrical conductivity, but conduct electricity quite well when molten • Most dissolve in high polarity solvents to form conducti ...
ATOMS
... • Most matter is in the form of COMPOUNDS or mixtures of compounds. For example: salt (NaCl), water (H20), carbon dioxide (CO2) • Compounds have properties UNLIKE those of their elements. For example: Salt—Sodium (Na) is a shiny, soft, gray, explosive metal with water & Chlorine (Cl) is a yellowish- ...
... • Most matter is in the form of COMPOUNDS or mixtures of compounds. For example: salt (NaCl), water (H20), carbon dioxide (CO2) • Compounds have properties UNLIKE those of their elements. For example: Salt—Sodium (Na) is a shiny, soft, gray, explosive metal with water & Chlorine (Cl) is a yellowish- ...