ExamView - test.practice.questions.tst
... ____ 25. 4.4 - WWBAT convert between moles & grams What is the mass of 4.7 moles of Na3PO4 (molar mass= 164 grams/mole)? a. 164 g c. 781 g b. 34.9 g d. 542 g ____ 26. 4.4 - WWBAT convert between moles & grams How many moles of carbon-12 are contained in exactly 6 grams of carbon-12? a. 0.5 mole c. m ...
... ____ 25. 4.4 - WWBAT convert between moles & grams What is the mass of 4.7 moles of Na3PO4 (molar mass= 164 grams/mole)? a. 164 g c. 781 g b. 34.9 g d. 542 g ____ 26. 4.4 - WWBAT convert between moles & grams How many moles of carbon-12 are contained in exactly 6 grams of carbon-12? a. 0.5 mole c. m ...
6.7 – Ionic Compounds
... noble gas electron configuration. Therefore, atoms will lose or gain electrons to either have 0 or 8 valence electrons. Example: Magnesium is in Group 2A and therefore has 2 valence electrons. Magnesium will lose those 2 valence electrons in order to achieve the octet rule (have 0 valence electrons) ...
... noble gas electron configuration. Therefore, atoms will lose or gain electrons to either have 0 or 8 valence electrons. Example: Magnesium is in Group 2A and therefore has 2 valence electrons. Magnesium will lose those 2 valence electrons in order to achieve the octet rule (have 0 valence electrons) ...
Chemical Compounds
... S Take your ion and find someone you can bond with S Attempt to create the compound H2O, MgCl2..and so on S We will come together as a class and try to figure out if you ...
... S Take your ion and find someone you can bond with S Attempt to create the compound H2O, MgCl2..and so on S We will come together as a class and try to figure out if you ...
CHEMISTRY
... number of atoms of each element • H20 has 2 atoms of hydrogen & 1 atom of oxygen • Coefficients before a formula tell the number of molecules • 3O2 represents 3 molecules of oxygen or (3x2) or 6 atoms of oxygen ...
... number of atoms of each element • H20 has 2 atoms of hydrogen & 1 atom of oxygen • Coefficients before a formula tell the number of molecules • 3O2 represents 3 molecules of oxygen or (3x2) or 6 atoms of oxygen ...
File - Science With BLT
... c. number of covalent bonds each contains. d. mobile electrons that they contain. ____ 34. Compared with nonmetals, the number of valence electrons in metals is generally a. smaller. c. about the same. b. greater. d. almost triple that of nonmetals. ____ 35. In metallic bonds, the mobile electrons s ...
... c. number of covalent bonds each contains. d. mobile electrons that they contain. ____ 34. Compared with nonmetals, the number of valence electrons in metals is generally a. smaller. c. about the same. b. greater. d. almost triple that of nonmetals. ____ 35. In metallic bonds, the mobile electrons s ...
Ionic and Covalent Bonding
... and attract on another by electrostatic forces. Ionic Bonds bind oppositely charged ions. The total positive charges of cations =’s the total negative charges or the anions ... so, compounds are neutral. ...
... and attract on another by electrostatic forces. Ionic Bonds bind oppositely charged ions. The total positive charges of cations =’s the total negative charges or the anions ... so, compounds are neutral. ...
chemistry - cloudfront.net
... READ THE FOLLOWING PARAGRAPH BEFORE YOU START! This worksheet is meant to be a “practice test” to help you prepare for your final exam. Suggestions on how to prepare: I would first order my notes and homework by the dates on them. Then I would look at the topic statement below (the capital letter ph ...
... READ THE FOLLOWING PARAGRAPH BEFORE YOU START! This worksheet is meant to be a “practice test” to help you prepare for your final exam. Suggestions on how to prepare: I would first order my notes and homework by the dates on them. Then I would look at the topic statement below (the capital letter ph ...
stable structure - Rothschild Science
... 1. Color the cations one color and the anions another. 2. Build the neutral compounds. 3. Remember your + charges need to equal the - charges. 4. Name the compounds! ...
... 1. Color the cations one color and the anions another. 2. Build the neutral compounds. 3. Remember your + charges need to equal the - charges. 4. Name the compounds! ...
topic 1 sol review homework
... to gain electrons? a) P b) C c) Cl d) B 7. Which of the following has the least tendency to gain electrons? a) F b) I c) Br d) Cl 8. List two things that the elements listed in #7 have in common: all are diatomics, all have 7 valence electrons, all are halogens 9. The increase in atomic radius of ea ...
... to gain electrons? a) P b) C c) Cl d) B 7. Which of the following has the least tendency to gain electrons? a) F b) I c) Br d) Cl 8. List two things that the elements listed in #7 have in common: all are diatomics, all have 7 valence electrons, all are halogens 9. The increase in atomic radius of ea ...
Chemistry Nomenclature Notes
... Example 1: Sodium atoms tend to lose an electron to form the cation, Na1+. Chlorine atoms tend to gain electrons to form an anion, Cl1-. When these two elements are brought together under the proper conditions a chemical reaction takes place in which the sodium atom gives its electron to the chlorin ...
... Example 1: Sodium atoms tend to lose an electron to form the cation, Na1+. Chlorine atoms tend to gain electrons to form an anion, Cl1-. When these two elements are brought together under the proper conditions a chemical reaction takes place in which the sodium atom gives its electron to the chlorin ...
Chapter 8: Chemical Reactions and Physical Changes
... • Mass number: total protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus • Atomic mass: the average mass of a sample of atoms of that element found in nature • Periodic table: chart that arranges elements by atomic number into rows and columns according to similarities in their properties ...
... • Mass number: total protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus • Atomic mass: the average mass of a sample of atoms of that element found in nature • Periodic table: chart that arranges elements by atomic number into rows and columns according to similarities in their properties ...
worksheet 7b answers - Iowa State University
... 4) What atom has the SMALLEST atomic radius? Helium 5) Which of the following molecules would you expect to be Largest? a. Br2 Cl2 Br2 b. NaCl KCl KBr NaBr KBr 6) If the charge of an atom changes, does the radius of the atom change? Yes Cations are smaller, anions are larger 7) Which is larger? a. M ...
... 4) What atom has the SMALLEST atomic radius? Helium 5) Which of the following molecules would you expect to be Largest? a. Br2 Cl2 Br2 b. NaCl KCl KBr NaBr KBr 6) If the charge of an atom changes, does the radius of the atom change? Yes Cations are smaller, anions are larger 7) Which is larger? a. M ...
Unit 2: Atoms and Ions Homework Booklet
... their products in the form of a table. It’s quite surprising what chemists do! They make useful substances like soaps and bleach from raw materials such as sea water. Crude oil which is a sticky black mixture, can be manufactured into lubricating oils, plastics and ...
... their products in the form of a table. It’s quite surprising what chemists do! They make useful substances like soaps and bleach from raw materials such as sea water. Crude oil which is a sticky black mixture, can be manufactured into lubricating oils, plastics and ...
Activity Name: Polyatomic Ion Bingo
... Background Information: An ion is an atom or group of atoms that has a charge because of the loss or gain of electrons. A polyatomic ion is an ion that consists of at least two different elements. Polyatomic ions are common ingredients in many foods and household products. Phosphate, nitrate, sulfat ...
... Background Information: An ion is an atom or group of atoms that has a charge because of the loss or gain of electrons. A polyatomic ion is an ion that consists of at least two different elements. Polyatomic ions are common ingredients in many foods and household products. Phosphate, nitrate, sulfat ...
Ion Exchange
... (ionic) interactions. The stationary phase surface displays ionic functional groups (R-X) that interact with analyte ions of opposite charge. An ion-exchange resin or ion-exchange polymer is an insoluble matrix normally in the form of small (1–2 mm diameter) beads fabricated from an organic polymer ...
... (ionic) interactions. The stationary phase surface displays ionic functional groups (R-X) that interact with analyte ions of opposite charge. An ion-exchange resin or ion-exchange polymer is an insoluble matrix normally in the form of small (1–2 mm diameter) beads fabricated from an organic polymer ...
Atoms, Ions, and Molecules File
... The Mass of an Electron • The mass/charge ratio was measured by J.J. Thomson using a cathode ray tube. • The charge of an electron was measured in a famous experiment by Robert Millikan. • The mass of an electron was found to be about 2000 times less than the lightest atom ...
... The Mass of an Electron • The mass/charge ratio was measured by J.J. Thomson using a cathode ray tube. • The charge of an electron was measured in a famous experiment by Robert Millikan. • The mass of an electron was found to be about 2000 times less than the lightest atom ...
File
... Metal-like but does not contain all metal characteristics A positively charged particle A negatively charged particle Substance which produces hydrogen ions in aqueous solution, proton donor Not printed, Answer not present ...
... Metal-like but does not contain all metal characteristics A positively charged particle A negatively charged particle Substance which produces hydrogen ions in aqueous solution, proton donor Not printed, Answer not present ...
ap chemistry review – multiple choice
... Questions 15-18 refer to the following (a) Heisenbery uncertainty principle (b) Pauli exclusion principle (c) Hund’s rule (principle of maximum multiplicity) (d) Shielding effect (e) Wave nature of matter 15. Can be used to predict that a gaseous carbon atom in it ground state is paramagnetic 16. E ...
... Questions 15-18 refer to the following (a) Heisenbery uncertainty principle (b) Pauli exclusion principle (c) Hund’s rule (principle of maximum multiplicity) (d) Shielding effect (e) Wave nature of matter 15. Can be used to predict that a gaseous carbon atom in it ground state is paramagnetic 16. E ...
Chemistry primer Atom = the smallest unit of an element Element
... Ion: in an ion the number of e- is not equal to the number of P+ Charge = number of P+ minus number of eAtomic weight is equal to the number of protons plus the number of neutrons Atomic number si equal to the number protons Atomic number determines the identity of the atom or ion. In other words at ...
... Ion: in an ion the number of e- is not equal to the number of P+ Charge = number of P+ minus number of eAtomic weight is equal to the number of protons plus the number of neutrons Atomic number si equal to the number protons Atomic number determines the identity of the atom or ion. In other words at ...
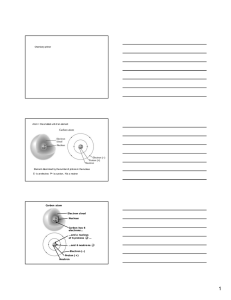
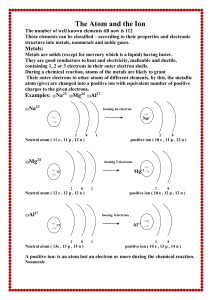
The Atom and the Ion
... The number of well known elements till now is 112 Those elements can be classified – according to their properties and electronic structure into metals, nonmetals and noble gases. ...
... The number of well known elements till now is 112 Those elements can be classified – according to their properties and electronic structure into metals, nonmetals and noble gases. ...
Additional Chemistry
... Knowing the periodic table will help you first work out what bonding is taking place (ionic, covalent or metallic). ...
... Knowing the periodic table will help you first work out what bonding is taking place (ionic, covalent or metallic). ...
LIST OF TOPICS COVERED DURING THIS COURSE
... The following should serve as a checklist for your notebook. The topics below include all topics that have been covered this semester and are testable on your final exam. These topics should be studied from a variety of source including inclass notes, homework questions, lab questions, assignments, ...
... The following should serve as a checklist for your notebook. The topics below include all topics that have been covered this semester and are testable on your final exam. These topics should be studied from a variety of source including inclass notes, homework questions, lab questions, assignments, ...
The topic that fascinated me the most in my Science lessons this
... chlorine atom because its valence electron is nearer to the positively charged nucleus. Therefore, Beryllium forms covalent bonds where it shares the electron with chlorine. An atom is happiest when its shell is fully filled and these atoms form the noble gases group. Every atom aspires to become it ...
... chlorine atom because its valence electron is nearer to the positively charged nucleus. Therefore, Beryllium forms covalent bonds where it shares the electron with chlorine. An atom is happiest when its shell is fully filled and these atoms form the noble gases group. Every atom aspires to become it ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... decomposition: one reactant disintegrates (decomposes) to form two or more products: AB+C single replacement (sometimes called single displacement): atoms of one element replace atoms of another in a compound: A + BC AC + B Most often, AC and BC are ionic compounds, which means A and B are metals ...
... decomposition: one reactant disintegrates (decomposes) to form two or more products: AB+C single replacement (sometimes called single displacement): atoms of one element replace atoms of another in a compound: A + BC AC + B Most often, AC and BC are ionic compounds, which means A and B are metals ...
The Nature of Matter
... • # of protons= #of electrons • Balances out protons positive charge • In constant motion • Valence electrons are in outermost shell • Valence electrons determine the chemical nature of an atom • Smallest subatomic particle ...
... • # of protons= #of electrons • Balances out protons positive charge • In constant motion • Valence electrons are in outermost shell • Valence electrons determine the chemical nature of an atom • Smallest subatomic particle ...