Ionic Bonding
... with the largest principle quantum number A transition metal always loses electrons first from the higher 's' subshell, before losing from the underlying 'd' subshell. Iron will not have a noble gas core (iron salts will have color) Fe: [Ar]4s23d6 Fe2+ [Ar] 3d6 Fe: [Ar]4s23d6 Fe3+ [Ar] 3d5 ...
... with the largest principle quantum number A transition metal always loses electrons first from the higher 's' subshell, before losing from the underlying 'd' subshell. Iron will not have a noble gas core (iron salts will have color) Fe: [Ar]4s23d6 Fe2+ [Ar] 3d6 Fe: [Ar]4s23d6 Fe3+ [Ar] 3d5 ...
Instrumental Analysis
... Positive ions are accelerated into separation chamber The fast moving particles are subjected to a strong magnetic field in which they travel in a curved path The radius depends upon their velocity and mass as well as the field strength ...
... Positive ions are accelerated into separation chamber The fast moving particles are subjected to a strong magnetic field in which they travel in a curved path The radius depends upon their velocity and mass as well as the field strength ...
Basic Chemistry - Biology with Radjewski
... • Atoms with unfilled outer shells tend to undergo chemical reactions to fill their outer shells. • They can attain stability by sharing electrons with other atoms (covalent bond) or by losing or gaining electrons (ionic bond) • The atoms are then bonded together into molecules. • Octet rule—atoms ...
... • Atoms with unfilled outer shells tend to undergo chemical reactions to fill their outer shells. • They can attain stability by sharing electrons with other atoms (covalent bond) or by losing or gaining electrons (ionic bond) • The atoms are then bonded together into molecules. • Octet rule—atoms ...
Exam Review – Part 1
... Forming Stable Ions • To become stable some atoms will gain or lose electrons to form an ion • For an atom to become stable, it must look like a noble gas • That is, they must have a full outer (valence) shell of electrons (stable octet) ...
... Forming Stable Ions • To become stable some atoms will gain or lose electrons to form an ion • For an atom to become stable, it must look like a noble gas • That is, they must have a full outer (valence) shell of electrons (stable octet) ...
Ionic Bonding - Effingham County Schools
... about the charges on ions. •Ionic compounds are formed as a result of the formation of (+) and (-) ions. ...
... about the charges on ions. •Ionic compounds are formed as a result of the formation of (+) and (-) ions. ...
File
... In non-molecular substances there are only strong forces of attraction between the particles; these are known as primary bonds. (2) ...
... In non-molecular substances there are only strong forces of attraction between the particles; these are known as primary bonds. (2) ...
atoms, molecules, and matter (2)
... ELEMENTS – Greek theory of physical world. All earthly objects are a mixture of: 1. EARTH (bottom – center of universe) 2. WATER (water covers earth) 3. AIR (air over water) 4. FIRE (highest – at top) 5. Ether = QUINTESSENCE (Latin) – substance whose natural motion is that most symmetrical and etern ...
... ELEMENTS – Greek theory of physical world. All earthly objects are a mixture of: 1. EARTH (bottom – center of universe) 2. WATER (water covers earth) 3. AIR (air over water) 4. FIRE (highest – at top) 5. Ether = QUINTESSENCE (Latin) – substance whose natural motion is that most symmetrical and etern ...
Chemical Bond - Cobb Learning
... positive and negative oxidation numbers is zero. The Crisscross Method or Swap N’ Drop Method can also work. 4) All compounds are neutral so the oxidation numbers should combine in ratios that will add up to zero. The number of ions combining in the compound will be written as subscripts in the fina ...
... positive and negative oxidation numbers is zero. The Crisscross Method or Swap N’ Drop Method can also work. 4) All compounds are neutral so the oxidation numbers should combine in ratios that will add up to zero. The number of ions combining in the compound will be written as subscripts in the fina ...
1. I can define valence electron and use the periodic
... 6. Which elements react violently with water? 7. Which anions are most reactive? 8. Why are these atoms the most reactive ones? 9. If you were trying to explain to a fellow freshman how valence electrons relate to chemical reactivity, what would you say? #4. I can define ion and use the periodic tab ...
... 6. Which elements react violently with water? 7. Which anions are most reactive? 8. Why are these atoms the most reactive ones? 9. If you were trying to explain to a fellow freshman how valence electrons relate to chemical reactivity, what would you say? #4. I can define ion and use the periodic tab ...
document
... element is willing to gain, lose, or share to form compounds. 5. Ionic Bond E. States that all elements want either a full outer shell or eight 6. Subscript electrons in their outer electron shell. 7. Polyatomic Ion F. A multiplier. It is used to balance equations. 8. Synthesis Reaction G. A reactio ...
... element is willing to gain, lose, or share to form compounds. 5. Ionic Bond E. States that all elements want either a full outer shell or eight 6. Subscript electrons in their outer electron shell. 7. Polyatomic Ion F. A multiplier. It is used to balance equations. 8. Synthesis Reaction G. A reactio ...
Acid-Base Theories Arrhenius Acids and Bases • An acid is a
... between an electron-pair donor and an electron-pair acceptor. ...
... between an electron-pair donor and an electron-pair acceptor. ...
1305- practise exam 2
... B) Ternary ionic C) Binary molecular D) Binary acid -------12. What is the term for a single atom bearing a positive or a negative charge as the result of gaining or losing valence electrons? A) Anion B) Cation C) Monoatomic ion D) Polyatomic ion -------13. The compound Na2SO4 is classified as which ...
... B) Ternary ionic C) Binary molecular D) Binary acid -------12. What is the term for a single atom bearing a positive or a negative charge as the result of gaining or losing valence electrons? A) Anion B) Cation C) Monoatomic ion D) Polyatomic ion -------13. The compound Na2SO4 is classified as which ...
chapter2 - AlvarezHChem
... • Compounds formed from the electrostatic attraction of oppositely charged particles • Sodium chloride (NaCl): Sodium cations and chloride anions associate into a continuous network ...
... • Compounds formed from the electrostatic attraction of oppositely charged particles • Sodium chloride (NaCl): Sodium cations and chloride anions associate into a continuous network ...
Midterm Review
... • Which sequence of Group 18 elements demonstrates a gradual decrease in the strength of the Van der Waals forces? All the choices are elements in the liquid state choices are elements in the liquid state. ...
... • Which sequence of Group 18 elements demonstrates a gradual decrease in the strength of the Van der Waals forces? All the choices are elements in the liquid state choices are elements in the liquid state. ...
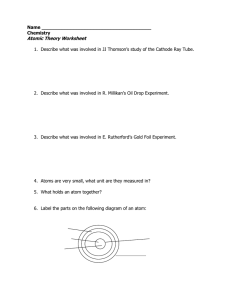
Atomic Theory Worksheet
... 4. Atoms are very small, what unit are they measured in? 5. What holds an atom together? 6. Label the parts on the following diagram of an atom: ...
... 4. Atoms are very small, what unit are they measured in? 5. What holds an atom together? 6. Label the parts on the following diagram of an atom: ...
Chemical Bonding
... of only one type of atom. • Isotopes are elements with different numbers of neutrons. • Because isotopes have the same number electrons, all isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties. ...
... of only one type of atom. • Isotopes are elements with different numbers of neutrons. • Because isotopes have the same number electrons, all isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties. ...
Chemical Formulas
... single atom Na+ or S2- usually tell by column on periodic table, some elements have more than one oxidation number or charge Binary compounds- only 2 elements in the compound Na2S Polyatomic ions - ions formed from more than one type of atom covalently bonded together OHPO43- NH4+ ...
... single atom Na+ or S2- usually tell by column on periodic table, some elements have more than one oxidation number or charge Binary compounds- only 2 elements in the compound Na2S Polyatomic ions - ions formed from more than one type of atom covalently bonded together OHPO43- NH4+ ...
The Nature of Molecules
... • There are discrete energy levels surrounding the nucleus of an atom; one level contains only 1 orbit of electrons, others contain 4 different orbits of electrons (each orbit is filled with 2 e-’s) • The filling of orbitals and energy levels relates to the chemical behavior of atoms • The number of ...
... • There are discrete energy levels surrounding the nucleus of an atom; one level contains only 1 orbit of electrons, others contain 4 different orbits of electrons (each orbit is filled with 2 e-’s) • The filling of orbitals and energy levels relates to the chemical behavior of atoms • The number of ...
Chapter 4 Notes - Atomic Theory
... Remember: positive charges must = negative charges Ex.1: What is the formula for magnesium phosphide? Magnesium is Mg2+ Phosphorous is P3– Lowest common multiple of 2 and 3 is 6 3 Mg2+ ions & 2 P3– ions (6 +ve’s & 6 –ve’s) ...
... Remember: positive charges must = negative charges Ex.1: What is the formula for magnesium phosphide? Magnesium is Mg2+ Phosphorous is P3– Lowest common multiple of 2 and 3 is 6 3 Mg2+ ions & 2 P3– ions (6 +ve’s & 6 –ve’s) ...
Introduction_to_Geochemistry_Pre-Lecture_Quiz
... (a) The diameter of an atom is less than the diameter of its nucleus. (b) The relative atomic mass of an atom is the mass of an atom relative to an atom of 12C. (c) p-orbitals can contain a maximum of 10 electrons. (d) The first ionisation energy of an element is the energy input (in kg mol-1) requi ...
... (a) The diameter of an atom is less than the diameter of its nucleus. (b) The relative atomic mass of an atom is the mass of an atom relative to an atom of 12C. (c) p-orbitals can contain a maximum of 10 electrons. (d) The first ionisation energy of an element is the energy input (in kg mol-1) requi ...
AP Chemistry Study Guide – Chapter 7, Atomic Structure
... 6) Account for each of the following in terms of principles of atomic structure, including the number, properties, and arrangements of subatomic particles. (a) The second ionization energy of sodium is about three times greater than the second ionization energy of magnesium. (b) The difference betwe ...
... 6) Account for each of the following in terms of principles of atomic structure, including the number, properties, and arrangements of subatomic particles. (a) The second ionization energy of sodium is about three times greater than the second ionization energy of magnesium. (b) The difference betwe ...
AP Chemistry Exam #2
... Write the formulas to show reactants and products. Assume that solutions are aqueous unless otherwise noted. Represent substances in solutions as ions if the substances are soluble or ionized in water. Omit formulas for any ions or molecules that are unchanged by the reactions. (Write net ionic equa ...
... Write the formulas to show reactants and products. Assume that solutions are aqueous unless otherwise noted. Represent substances in solutions as ions if the substances are soluble or ionized in water. Omit formulas for any ions or molecules that are unchanged by the reactions. (Write net ionic equa ...