Periodic Trends
... The outermost orbital size increases down a group, making the atom larger. ...
... The outermost orbital size increases down a group, making the atom larger. ...
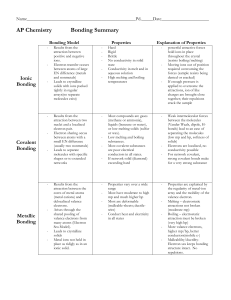
Types of Bonding Summary
... small EN difference (usually two nonmetals) Leads to separate molecules with specific shapes or to extended networks ...
... small EN difference (usually two nonmetals) Leads to separate molecules with specific shapes or to extended networks ...
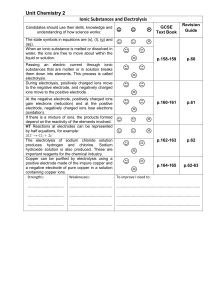
Unit_Chemistry_2_Ionic_Substances_and_Electrolysis
... The electrolysis of sodium chloride solution produces hydrogen and chlorine. Sodium hydroxide solution is also produced. These are important reagents for the chemical industry. Copper can be purified by electrolysis using a positive electrode made of the impure copper and a negative electrode of pur ...
... The electrolysis of sodium chloride solution produces hydrogen and chlorine. Sodium hydroxide solution is also produced. These are important reagents for the chemical industry. Copper can be purified by electrolysis using a positive electrode made of the impure copper and a negative electrode of pur ...
Unit 1 Inorganic Flashcards
... surrounding molecules or ions by dative covalent bonds (also known as coordinate bonds). ...
... surrounding molecules or ions by dative covalent bonds (also known as coordinate bonds). ...
Electromagnetic Spectrum Wavelength Wavenumber Frequency
... surrounding molecules or ions by dative covalent bonds (also known as coordinate bonds). ...
... surrounding molecules or ions by dative covalent bonds (also known as coordinate bonds). ...
Valence electrons and Lewis Dot Structures
... Usually, a compound formed by a metal and a nonmetal is _________, and a compound formed by two nonmetals is ____________. ...
... Usually, a compound formed by a metal and a nonmetal is _________, and a compound formed by two nonmetals is ____________. ...
Biol 1441
... Nonpolar covalent bond: the electrons of the bond are shared equally. Ex: N2 Polar covalent bond: the electrons of the bond are not shared equally. Ex: HCl Ionic Bonds: Two atoms are so unequal in their attraction for valence electrons that the more electronegative atom strips an electron completely ...
... Nonpolar covalent bond: the electrons of the bond are shared equally. Ex: N2 Polar covalent bond: the electrons of the bond are not shared equally. Ex: HCl Ionic Bonds: Two atoms are so unequal in their attraction for valence electrons that the more electronegative atom strips an electron completely ...
Chemistry Review
... 1. a. What is the difference between an atom, element, molecule, and compound? ...
... 1. a. What is the difference between an atom, element, molecule, and compound? ...
Ch. 2 - Ltcconline.net
... 2. subatomic particles make up the atom. 3. Differences in elements 4. isotopes - different numbers of neutrons so mass changes E. Electron arrangement determines chemical properties of atom 1. electrons determine how an atom behaves 2. electrons vary in energy 3. electrons occur at certain energy l ...
... 2. subatomic particles make up the atom. 3. Differences in elements 4. isotopes - different numbers of neutrons so mass changes E. Electron arrangement determines chemical properties of atom 1. electrons determine how an atom behaves 2. electrons vary in energy 3. electrons occur at certain energy l ...
Notes for powerpoint and worksheets PDF
... Polyatomic ions are ions made of many atoms and usually have parenthesis around them How are compound named? (Type I & II) all metals (cations) use the _______________________________________________________ all non metal ions (anions) use the ___________________________________________________ ...
... Polyatomic ions are ions made of many atoms and usually have parenthesis around them How are compound named? (Type I & II) all metals (cations) use the _______________________________________________________ all non metal ions (anions) use the ___________________________________________________ ...
topic-2.doc
... o First energy level: one s orbital, holds 2 electrons o Second energy level: one s and three p orbitals, holds 8 electrons Chemical properties of an atom depend on the number of valence electrons Valence electrons: electrons in outermost energy shell (valence shell) o Unfilled spaces determine numb ...
... o First energy level: one s orbital, holds 2 electrons o Second energy level: one s and three p orbitals, holds 8 electrons Chemical properties of an atom depend on the number of valence electrons Valence electrons: electrons in outermost energy shell (valence shell) o Unfilled spaces determine numb ...
Compounds Power point
... Using the Periodic Table, we can predict an element’s oxidation number. “Oxidation Number” means the charge of an ion (can be + or -), a particle which has gained or lost electrons. A (-) charge = gained electrons A (+) charge = lost electrons ...
... Using the Periodic Table, we can predict an element’s oxidation number. “Oxidation Number” means the charge of an ion (can be + or -), a particle which has gained or lost electrons. A (-) charge = gained electrons A (+) charge = lost electrons ...
Module 8 - Brookville Local Schools
... Part of the Chemistry For Dummies Cheat Sheet In bonding, atoms lose, gain, or share electrons in order to have the same number of electrons as the noble gas that's nearest on the periodic table. Ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds are formed by combinations of metals and nonmetals. Metal + nonmet ...
... Part of the Chemistry For Dummies Cheat Sheet In bonding, atoms lose, gain, or share electrons in order to have the same number of electrons as the noble gas that's nearest on the periodic table. Ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds are formed by combinations of metals and nonmetals. Metal + nonmet ...
2.4 Revision 1: There were two atoms. One got hit by an extremely
... c. Conducts electricity when solid and melted? d. Conducts electricity when dissolved or melted but not as a solid? e. Forces that hold non-polar molecular solids together. f. Can conduct heat and electrical charge. g. Which of the following solids have hydrogen bonds between molecules; hydrogen chl ...
... c. Conducts electricity when solid and melted? d. Conducts electricity when dissolved or melted but not as a solid? e. Forces that hold non-polar molecular solids together. f. Can conduct heat and electrical charge. g. Which of the following solids have hydrogen bonds between molecules; hydrogen chl ...
Basic Chemistry Notes II
... 3. The atomic number is the number of protons B. Neutrons 1. Found in nucleus 2. No charge 3. Can be found by subtracting the atomic number from the atomic weight C. Electrons 1. Found outside of nucleus in “shells” 2. Have a negative charge 3. Valence electrons – outermost electron shell. Most impo ...
... 3. The atomic number is the number of protons B. Neutrons 1. Found in nucleus 2. No charge 3. Can be found by subtracting the atomic number from the atomic weight C. Electrons 1. Found outside of nucleus in “shells” 2. Have a negative charge 3. Valence electrons – outermost electron shell. Most impo ...
Chemical Bonds
... • Forces holding atoms or ions together • Bonds form as a result of lowering of the total energy (energy of separated species is higher than that of bonded species) • Bond formation is accompanied by rearrangement of valence electrons – complete transfer of electrons – formation of ions ...
... • Forces holding atoms or ions together • Bonds form as a result of lowering of the total energy (energy of separated species is higher than that of bonded species) • Bond formation is accompanied by rearrangement of valence electrons – complete transfer of electrons – formation of ions ...
Periodic Trends
... • Far right side of periodic table • Properties – Brittle: break when hammered – Lack luster – Poor conductors – Solid or gas at room temperature (except Br) ...
... • Far right side of periodic table • Properties – Brittle: break when hammered – Lack luster – Poor conductors – Solid or gas at room temperature (except Br) ...
Atomic structure and bonding I can name group 1, 7 and 0 of the
... I can name group 1, 7 and 0 of the periodic table. I can state the names of the seven diatomic elements. I can label a diagram of an atom. I can state the mass, charge and position of a proton, neutron and electron within an atom. I can state the definition of an isotope. I can state the meaning of ...
... I can name group 1, 7 and 0 of the periodic table. I can state the names of the seven diatomic elements. I can label a diagram of an atom. I can state the mass, charge and position of a proton, neutron and electron within an atom. I can state the definition of an isotope. I can state the meaning of ...
SCIENCE 10: Chemical Reactions – Atomic Structure
... Metals & non-metals combine to form ionic compounds. Metals ions lose electrons to form positive ions. Non-metals gain electrons to form negative ions. The resulting compound must be electrically neutral: the positive charges must equal the negative charges. Example: magnesium combines with chlorine ...
... Metals & non-metals combine to form ionic compounds. Metals ions lose electrons to form positive ions. Non-metals gain electrons to form negative ions. The resulting compound must be electrically neutral: the positive charges must equal the negative charges. Example: magnesium combines with chlorine ...
Chemistry I Unit Review: The Atom Text Chapters 2 and 7 1. The
... How many protons are in the nucleus of each of the following elements? (also known as the atomic number) a. uranium c. helium b. selenium d. bohrium Give the number of neutrons in each of the following isotopes. (what is an isotope?) a. titanium-46 c. 3416S b. nitrogen-15 d. 6529Cu Fill in the blank ...
... How many protons are in the nucleus of each of the following elements? (also known as the atomic number) a. uranium c. helium b. selenium d. bohrium Give the number of neutrons in each of the following isotopes. (what is an isotope?) a. titanium-46 c. 3416S b. nitrogen-15 d. 6529Cu Fill in the blank ...
namimg compounds
... • Transition metals have a variety of ionic charges, but most form ions with a +2 charge. • If a metal has more than one common ion, the charge it takes is shown with Roman numerals. For example, copper(I) = Cu+, copper(II) = Cu2+, iron(II) =FeZ+, iron(III) = Fe3+. • The metals in Groups V and VI al ...
... • Transition metals have a variety of ionic charges, but most form ions with a +2 charge. • If a metal has more than one common ion, the charge it takes is shown with Roman numerals. For example, copper(I) = Cu+, copper(II) = Cu2+, iron(II) =FeZ+, iron(III) = Fe3+. • The metals in Groups V and VI al ...