Trends in the periodic table - Brigham Young University
... • What happens to Zeff as we go from left to right along the table? • How does this affect the radius? ...
... • What happens to Zeff as we go from left to right along the table? • How does this affect the radius? ...
Chemistry of Life - juan-roldan
... and are called Valence Electrons Valence electrons occupy the valence shell (outermost shell) Changes in electron energy levels are important in energy conversions in organisms ...
... and are called Valence Electrons Valence electrons occupy the valence shell (outermost shell) Changes in electron energy levels are important in energy conversions in organisms ...
Chapter 8 Notes
... Lattice energy increases with decreasing ionic radii. This makes sense if you think about it. After-all the smaller the ion, the closer the positive nucleus is to the valence electrons responsible for bonding. So Magnesium compounds will have higher (negative) lattice energies than Calcium compounds ...
... Lattice energy increases with decreasing ionic radii. This makes sense if you think about it. After-all the smaller the ion, the closer the positive nucleus is to the valence electrons responsible for bonding. So Magnesium compounds will have higher (negative) lattice energies than Calcium compounds ...
transition metals
... number of the metal ion in complex ion: be sure to label the inner sphere (ligands bonded covalently to the metal) and outer sphere ligands (counter ions) in the complex! ...
... number of the metal ion in complex ion: be sure to label the inner sphere (ligands bonded covalently to the metal) and outer sphere ligands (counter ions) in the complex! ...
PS7aChemistryReviewRevised
... 1. How many electrons does the neutral atom contain? 2. The first 1 or 2 are placed into Energy Level #1 3. Energy Level 2 holds up to 8 electrons. 4. Energy Level 3 holds up to 8 electrons. 5. Energy Level 4 hold up to 8 electrons…etc. ...
... 1. How many electrons does the neutral atom contain? 2. The first 1 or 2 are placed into Energy Level #1 3. Energy Level 2 holds up to 8 electrons. 4. Energy Level 3 holds up to 8 electrons. 5. Energy Level 4 hold up to 8 electrons…etc. ...
•What makes up an atom? Draw an atom
... • Isotope: different number of neutrons changes the mass, but NOT the element • EX. C12 vs C14 • Carbon 14 is heavier since it has two more neutrons ...
... • Isotope: different number of neutrons changes the mass, but NOT the element • EX. C12 vs C14 • Carbon 14 is heavier since it has two more neutrons ...
Learning Goals - Issaquah Connect
... Go to the list of Phet HTML5 Chemistry simulations. Click on the Build an Atom simulation and start the sim. Once the simulation opens, click on “Atom”. a. Click on the X’s behind the Net Charge and Mass Number titles to display the graphics. Add protons, neutrons & electrons to the model until you ...
... Go to the list of Phet HTML5 Chemistry simulations. Click on the Build an Atom simulation and start the sim. Once the simulation opens, click on “Atom”. a. Click on the X’s behind the Net Charge and Mass Number titles to display the graphics. Add protons, neutrons & electrons to the model until you ...
Summer Assignment 2015
... 6. Naturally occurring chlorine is 75.78% 35Cl, which has an atomic mass of 34.969 amu, and 24.22% 37Cl, which has an atomic mass of 36.966 amu. Calculate the average atomic mass (that is, the atomic weight) of chlorine. 7. Write the empirical formulas for the following molecules: (a) glucose, a sub ...
... 6. Naturally occurring chlorine is 75.78% 35Cl, which has an atomic mass of 34.969 amu, and 24.22% 37Cl, which has an atomic mass of 36.966 amu. Calculate the average atomic mass (that is, the atomic weight) of chlorine. 7. Write the empirical formulas for the following molecules: (a) glucose, a sub ...
WS on obj. 1-11
... 14. _____ (T/F) Calcium will need to lose two electrons to get the electron configuration of argon. 15. _____ (T/F) All the alkaline earth elements (Group 2A) will need to lose two electrons to obtain a noble gas electron configuration. 16. _____ (T/F) All the elements of the oxygen group (Group 6A ...
... 14. _____ (T/F) Calcium will need to lose two electrons to get the electron configuration of argon. 15. _____ (T/F) All the alkaline earth elements (Group 2A) will need to lose two electrons to obtain a noble gas electron configuration. 16. _____ (T/F) All the elements of the oxygen group (Group 6A ...
FE Review Chemistry - UTSA College of Engineering
... • Element: a substance only composed of one type of atom • Isotope: element with the same number of protons but different atomic masses ...
... • Element: a substance only composed of one type of atom • Isotope: element with the same number of protons but different atomic masses ...
Unit 5 – Test Study Guide
... another energy level and many more inner core electrons the atoms is much bigger. This means the valence electrons are further away from the nucleus and they are less attracted to the nucleus due to all the inner core electrons. This makes the removal of an electron much easier resulting in a lower ...
... another energy level and many more inner core electrons the atoms is much bigger. This means the valence electrons are further away from the nucleus and they are less attracted to the nucleus due to all the inner core electrons. This makes the removal of an electron much easier resulting in a lower ...
S90 Notes U2 Topic 6 Chemical Compounds
... S90 Notes U2 Topic 6 Chemical Compounds Chemical compounds are formed by 2 or more elements. There are 2 types of compounds – ionic compounds and molecular compounds ...
... S90 Notes U2 Topic 6 Chemical Compounds Chemical compounds are formed by 2 or more elements. There are 2 types of compounds – ionic compounds and molecular compounds ...
Ch 6 Jeopardy Review
... In these bonds valence electrons are able to freely move between a cation lattice. ...
... In these bonds valence electrons are able to freely move between a cation lattice. ...
Biology Fall Semester Test 1 Study Guide
... In the metric system, the basic unit of length is the How many centimeters are in 2.4 km? The basic unit of mass in SI is the The three particles that make up atoms are ...
... In the metric system, the basic unit of length is the How many centimeters are in 2.4 km? The basic unit of mass in SI is the The three particles that make up atoms are ...
Chap 1-3 Review
... Bohr - Electrons are located in shells. Electrons are negatively charged particles located in shells surrounding a small dense positively charged nucleus. ...
... Bohr - Electrons are located in shells. Electrons are negatively charged particles located in shells surrounding a small dense positively charged nucleus. ...
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions C Kapler ` , , I 27 O//#W SELF
... 3. Describe zinc as a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid; main group, transition or posttransition element. Describe its place in the periodic table (group and period). ...
... 3. Describe zinc as a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid; main group, transition or posttransition element. Describe its place in the periodic table (group and period). ...
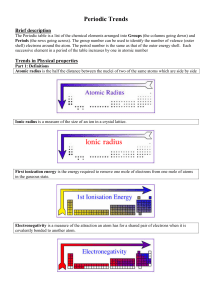
Topic 3 Periodicity notes SL - Chemical Minds
... Going down a group, the atomic radius and ionic radius increase due to an increase in the number of electron shells surrounding the nucleus. The ionisation energy and electronegativity decrease because i) there is a decrease in the electrostatic attraction between the positive protons in the nucleus ...
... Going down a group, the atomic radius and ionic radius increase due to an increase in the number of electron shells surrounding the nucleus. The ionisation energy and electronegativity decrease because i) there is a decrease in the electrostatic attraction between the positive protons in the nucleus ...
ChemicalBondingTestAnswers
... In beaker (A) - London forces--- Assume two molecules having no net dipole moment. Both have symmetrical charge distributions. But if by chance the electronic cloud of one molecule becomes asymmetrical and hence induces an instantaneous dipole in another molecule. Now this molecule induces a dipole ...
... In beaker (A) - London forces--- Assume two molecules having no net dipole moment. Both have symmetrical charge distributions. But if by chance the electronic cloud of one molecule becomes asymmetrical and hence induces an instantaneous dipole in another molecule. Now this molecule induces a dipole ...
Learning Standards vocab chemical basis and molecules of life 09
... Given the number of protons, identify the element using a Periodic Table. Explain the arrangement of the elements on the Periodic Table, including the significant relationships among elements in a given column or row. Explain how ions and ionic bonds are formed (e.g., sodium atoms lose an elec ...
... Given the number of protons, identify the element using a Periodic Table. Explain the arrangement of the elements on the Periodic Table, including the significant relationships among elements in a given column or row. Explain how ions and ionic bonds are formed (e.g., sodium atoms lose an elec ...
Science 9
... due to the loss or gain of electrons. 3. ___________________ is the attraction between positive and negative ions. 4. ___________________ is any of the group 2 elements beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and radium; all are reactive soft, low density metals. 5. ___________________ are ...
... due to the loss or gain of electrons. 3. ___________________ is the attraction between positive and negative ions. 4. ___________________ is any of the group 2 elements beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and radium; all are reactive soft, low density metals. 5. ___________________ are ...
Review Notes - Biochemistry
... 1. Ionic Bonding: When _1_ or more electrons are _TRANSFERRED_ from one atom to another. Ion: an atom with a_CHARGE_. When an electron is gained it will be _NEGATIVE_charged and when an electron is lost it will be _POSITIVE_ charged. ...
... 1. Ionic Bonding: When _1_ or more electrons are _TRANSFERRED_ from one atom to another. Ion: an atom with a_CHARGE_. When an electron is gained it will be _NEGATIVE_charged and when an electron is lost it will be _POSITIVE_ charged. ...