* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 2: Atoms and Ions Homework Booklet
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Ionic liquid wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Equilibrium chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Degenerate matter wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Acid dissociation constant wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer physics wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
Stability constants of complexes wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Ionic compound wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
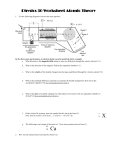
Knox Academy S3 Chemistry Unit 2: Atoms and Ions Homework Booklet DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET 1 Home ework 2.1 Lesso ons 1 & 2 1. In the Ruth herford sscatterin ng exper riment a tthin piec ce of gold foil wa as hit by a stream m of positive partticles. He e me surpriising results:notticed som a. Mo ost of the particles went straightt through h the foiil and b. A few f were e strongly deflected with h a smalle er num mber bouuncing sttraight back. Explain the ese 3 obsservation ns. (3)) 2. 3. Above e is a Ruttherford picture of a neutral atom m. a) Na ame the element.. b) What W is its s atomic number? ? c) Why W do we e say thaat this attom is ele ectricallyy neutral? (3)) Copy and complete the following g table:- me of Parrticle Nam Proton Ch harge Where W itss Found In the t nucleeus -1 (6)) 2 Oxyg gen has 8 neutronns. a. Draw w a label led Ruth herford diagram d oof one attom of oxyg gen. b. Labe el the nucleus and d the ele ectrons. c. Wha at is betw ween the e nucleus s and thee electron ns? (5)) 4. 5. a. b. c. e the elem ment whiich has an a atomicc numberr of 35. Name Name e the elem ment whiich has atoms a conntaining 20 protons. m elecctrons does each h atom in b) have? ? How many (3)) Home ework 2.2 Lesso ons 3 & 4 1. Use nuclide e notatio n to draw w the sym mbols foor a) nittrogen with 7 neuutrons. b) Bro omine witth 44 ne eutrons c) Tin n with 68 8 neutronns (3)) 2. e The followiing questtions refer to the iso otope sho own. ura anium a) Wh hat is its s mass nuumber? b) Ho ow many neutrons n s are in each e atom m? c) Wh hy is the atomic m mass of Uranium 238.028 89 and no ot exa actly 238 8 amu? (3)) 3. Cop py and co omplete the follo owing tab ble. Use a periodic tab ble to he elp you. 3 Symbol 37 Name of Element Number of Number of Number of Protons Electrons Neutrons Cl 17 11 12 Tin 69 (5) 4. Draw a diagram showing the electron energy levels of Potassium. Mark on the diagram the highest energy level and the lowest energy level. (3) 5. Draw diagrams to show the electron arrangement in:a) Helium b) Chlorine c) Magnesium (3) 6. What is the mass of:a) a proton b) a neutron c) an electron (3) Homework 2.3 Lessons 5 & 6 1. Draw the outer electron diagram for:a) Helium b) oxygen c) sodium d) Sulphur e) potassium (5) 2. a. b. How many outer electrons do the elements in group 7 have? What effect does this have on the chemical properties of these elements? (2) 4 3. a. b. c. What are the 2 types of bonding in compounds called? How can we tell which type of bonding a compound has? State whether the following compounds are ionic or covalent. i) sulphur dioxide ii) sodium fluoride (6) 4. Describe electrical conduction. (1) 5. What is the rule to tell which a) ionic compounds conduct and b) which covalent compounds conduct? (2) 6. British coins are Alloys. A20p coin contains copper (84%) and nickel (16%), a 50p coin contains copper (75%) and nickel (25%) and a £1 coin contains copper (70%), nickel (5.5%) and zinc (24.5%). Present this information in the form of a table. (4) Homework 2.4 Lessons 7 & 8 1. 2. a. Draw the target picture showing the electron energy levels for magnesium and oxygen. b. Draw the target pictures showing the electron energy levels for a magnesium ion and an oxide ion. (4) Which noble gas has the same electron arrangement as:a) The sulphide ion 5 b) The iodide ion c) The calcium ion d) The aluminium ion? (4) 3. What charge do a) metal ions have and b) non metal ions have? (2) 4. Draw a sectional diagram of how you would test a solution to see if it conducted electricity or not. (2) 5. Which type of solution does conduct electricity? (1) 6. Describe the conductivity of water as an ionic solution is gradually added to the water. (1) 7. Covalent bonds hold the atoms in methane together. a. b. c. What is a covalent bond? (1) Draw a diagram of the bonding in hydrogen sulphide. (3) How can you tell if the bonding in a substance is covalent? (2) Homework 2.5 Lessons 9 & 10 1. What elements has: a. Atomic number twenty-one b. Seven protons c. Eighteen electrons in one neutral atom d. Two elements which have the same electronarrangement as argon in their ions? (only 2 examples necessary) (5) 2. a. What is electrolysis? (1) 6 b. When zinc iodide is electrolysed what do you observe? (4) c. Name the products. (1) d. What ion is being oxidised and what ion is being reduced? (2) e. Why can ionic solutions be electrolysed and covalent solutions not be electrolysed? (2) 3. Read the following passage and list the raw materials and their products in the form of a table. It’s quite surprising what chemists do! They make useful substances like soaps and bleach from raw materials such as sea water. Crude oil which is a sticky black mixture, can be manufactured into lubricating oils, plastics and even petrol. Another fuel ,coal, can be changed into coke which, when mixed with iron ore and heated results in the production of iron and steel. Even seemingly useless materials such as sand can be changed by these amazing chemists into clear coloured or colourless glass! It’s surprising what these chemists can do. (5) Homework 2.6 Lessons 10 & 11 1. Calcium oxide is made by burning calcium in air. a. What type of solution is formed when it is dissolved in water? (1) b. What colour would Universal indicator turn when added to this solution? (1) c. What pH does this indicate? (1) 7 d. What other oxide would turn Universal indicator this colour? (1) 2. Yellow sulphur burns to form a gas. a. What is this gas called? (1) b. When the gas is shaken with water does the gas dissolve and if so what is the pH of the resulting solution? (2) c. When coal is burned a gas is given off that is weakly soluble in water. What is the gas and what is formed when it dissolves in water? (2) 3. a. Acids are used in Chemistry laboratories every day. It is important to know their formulae. Name 3 acids you have used in Chemistry and write the correct formula for each. (3) b. Are these acids ionic or covalent? (1) c. What property could you use to distinguish between ionic and covalent solutions? (1) 4. a. What ion is present in all acidic solutions? (1) b. Why does sulphuric acid have more ions than hydrochloric acid when they are both the same concentration? (1) 5. Why does burning coal lead to acid rain? (2) 6. Why is it necessary for some countries to add calcium oxide to their lakes? (2) 8 Homework 2.7 Lesson 12 1. Draw a diagram showing the electron arrangement of the ions in hydrochloric acid. (2) 2. a. b. What ion is present in all acids? Write its symbol showing state symbols. 3. a. b. What is electrolysis? (1) When acids are electrolysed the same element is always formed at one of the electrodes. What is this element and which electrode is it collected at? (2) 4. a. When hydrochloric acid is electrolysed what is formed at the positive electrode? (1) Is this an oxidation or a reduction? (1) b. (1) (1) 5. Draw a sectional diagram showing the electrolysis of Hydrochloric Acid. Include labels, word equations and ion equations to show what is happening at each electrode. (6) 9 Infformatio on taken for f SQA A data bo ooklet for Standaard Grade and Inttermedia ate 2 Che emistry – 2007 edition. 10 Info ormation tak ken for SQA A data book let for Stan ndard Grade e and Interm mediate 2 Ch hemistry – 20 007 edition. 11