* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SP 212 Worksheet Lesson 18: Ch. 28.1, Magnetic Fields
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic stripe card wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Magnetometer wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
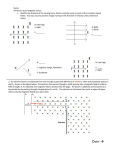
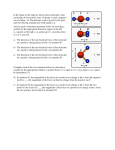
SP 212 Worksheet Lesson 18: Ch. 28.1, Magnetic Fields ~ = 1) An electron with velocity ~v = (2.9î + 3.8ĵ) × 106 m/s moves through a uniform magnetic field B (0.029î − 0.20ĵ) T. What is the magnitude of the magnetic force on the electron? 2) Mass spectrometer : An atomic ion has a net charge of magnitude e (it is either +e or −e, you decide). It is accelerated across a voltage V = 1000 V, then enters a region of uniform magnetic field of magnitude ~ The diameter of the ion’s circular trajectory is B = 8.00 × 10−2 T. It’s velocity is perpendicular to B. measured to be 1.6254 m. a) What is the ion’s kinetic energy after being accelerated? b) What is the mass of the ion?





![NAME: Quiz #5: Phys142 1. [4pts] Find the resulting current through](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006404813_1-90fcf53f79a7b619eafe061618bfacc1-150x150.png)