nature of Matter
... Depending on how the electrons interact, the type of bond is decided. The main types of chemical bonds are Ionic & Covalent. When electrons are transferred from one atom to another, an ionic bond is formed. An atom that loses electrons has a + charge. An atom that gains an electron has a – charge. T ...
... Depending on how the electrons interact, the type of bond is decided. The main types of chemical bonds are Ionic & Covalent. When electrons are transferred from one atom to another, an ionic bond is formed. An atom that loses electrons has a + charge. An atom that gains an electron has a – charge. T ...
Chap 11 Sect 1 Notes Atomic Theory
... are pure substances. They can’t be separated into elements by phase changes because the atoms of different elements are bonded to one another and are not easily ...
... are pure substances. They can’t be separated into elements by phase changes because the atoms of different elements are bonded to one another and are not easily ...
Glowing Tubes for Signs, Television Sets, and Computers
... a blue glow appears. The presence of krypton gives an intense white light. A television picture tube or computer monitor is also fundamentally a cathode ray tube. In this case the electrons are directed onto a screen containing chemical compounds that glow when struck by fast-moving electrons. The u ...
... a blue glow appears. The presence of krypton gives an intense white light. A television picture tube or computer monitor is also fundamentally a cathode ray tube. In this case the electrons are directed onto a screen containing chemical compounds that glow when struck by fast-moving electrons. The u ...
2008 Midterm Multiple Choice
... The characteristic bright-line spectrum of an element is produced when its electrons A) form an ionic bond B) return to a lower energy state C) move to a higher energy state D) form a covalent bond ...
... The characteristic bright-line spectrum of an element is produced when its electrons A) form an ionic bond B) return to a lower energy state C) move to a higher energy state D) form a covalent bond ...
Shiny, Happy Pretest - Alex LeMay – Science
... that Rutherford should let Marsden get some lab experience. __________________________ 15. Believed that the world was made of matter that could be divided infinitely. _____________ 16. Figured out that radiation can be divided into alpha particles, beta particles and gamma rays and that atoms were ...
... that Rutherford should let Marsden get some lab experience. __________________________ 15. Believed that the world was made of matter that could be divided infinitely. _____________ 16. Figured out that radiation can be divided into alpha particles, beta particles and gamma rays and that atoms were ...
Chapter 3 Make up Test 2004
... ______26. Which of the following statements explains why chemists do not count atoms and molecules directly? A. Atoms and molecules are extremely small B. All of the relationships in a chemical reaction can be expressed as mass ratios C. Matter is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction ...
... ______26. Which of the following statements explains why chemists do not count atoms and molecules directly? A. Atoms and molecules are extremely small B. All of the relationships in a chemical reaction can be expressed as mass ratios C. Matter is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction ...
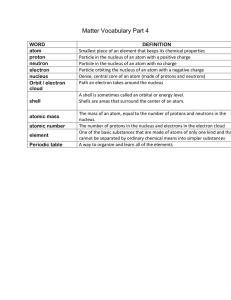
Matter Vocab Part 4
... Particle in the nucleus of an atom with a positive charge Particle in the nucleus of an atom with no charge Particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom with a negative charge Dense, central core of an atom (made of protons and neutrons) Path an electron takes around the nucleus A shell is sometimes cal ...
... Particle in the nucleus of an atom with a positive charge Particle in the nucleus of an atom with no charge Particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom with a negative charge Dense, central core of an atom (made of protons and neutrons) Path an electron takes around the nucleus A shell is sometimes cal ...
Properties of Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids
... Using the periodic table on page 10 of this study guide, answer the following questions: 1. Which element stands alone in its family? _______________ 2. Which element has a larger atomic radius O or Ca? _____________ 3. Which element has a larger atomic radius Ca or Ba? _____________ 4. Which elemen ...
... Using the periodic table on page 10 of this study guide, answer the following questions: 1. Which element stands alone in its family? _______________ 2. Which element has a larger atomic radius O or Ca? _____________ 3. Which element has a larger atomic radius Ca or Ba? _____________ 4. Which elemen ...
Polyatomic Ions (Memorize for Wednesday, January 31
... Oxidation Numbers (similar to valence electrons) Group 1 = +1 Group 2 = +2 Groups 13-18 = group # - 10 for most elements d-block elements must be looked up (groups 3-12 use roman numerals) oxidation numbers for ALL compounds MUST equal zero Metal-Non-metal (binary ionic compounds, only 2 elements) M ...
... Oxidation Numbers (similar to valence electrons) Group 1 = +1 Group 2 = +2 Groups 13-18 = group # - 10 for most elements d-block elements must be looked up (groups 3-12 use roman numerals) oxidation numbers for ALL compounds MUST equal zero Metal-Non-metal (binary ionic compounds, only 2 elements) M ...
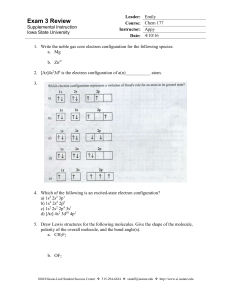
Exam 3 Review - Iowa State University
... 10. In terms of electronegativity, determine whether the following compounds contain nonpolar covalent, polar covalent, or ionic bonds. a. I—I b. NaI c. Cl—I d. H—I ...
... 10. In terms of electronegativity, determine whether the following compounds contain nonpolar covalent, polar covalent, or ionic bonds. a. I—I b. NaI c. Cl—I d. H—I ...
Ch. 2-2 Properties of Water
... oxygen and hydrogen atoms. • With 8 protons in its nucleus, an oxygen atom has a much stronger attraction for electrons than does the hydrogen atom with a single proton in its nucleus. ...
... oxygen and hydrogen atoms. • With 8 protons in its nucleus, an oxygen atom has a much stronger attraction for electrons than does the hydrogen atom with a single proton in its nucleus. ...
Matter
... Dissolving – The process in which particles of substances separate and spread evenly amongst each other. • Solute – substance that is dissolved. A solute is soluble, or able to dissolve. • A substance that is insoluble is unable to dissolve, forms a mixture that is not homogeneous, and therefore NOT ...
... Dissolving – The process in which particles of substances separate and spread evenly amongst each other. • Solute – substance that is dissolved. A solute is soluble, or able to dissolve. • A substance that is insoluble is unable to dissolve, forms a mixture that is not homogeneous, and therefore NOT ...
AQA Core Science Final Test - Atoms and Chemical equations
... When elements react, their atoms join with other atoms to form compounds. There are two types of bonds formed in a chemical reaction ...
... When elements react, their atoms join with other atoms to form compounds. There are two types of bonds formed in a chemical reaction ...
Covalent Bonds
... The central atom is often the 1st atom in the formula. c. Carbon is ALWAYS central. d. Hydrogen/halogens are always terminal (on end). ...
... The central atom is often the 1st atom in the formula. c. Carbon is ALWAYS central. d. Hydrogen/halogens are always terminal (on end). ...
Topic 3.1: Chemical Elements and Water
... molecule to develop a positive end (where the electrons spend less time) and a negative end (where the electrons spend more time). This has to do with the electronegativity of the atom. The more electronegative the atom the more it will hold on to the electrons. Oxygen is very electronegative (elect ...
... molecule to develop a positive end (where the electrons spend less time) and a negative end (where the electrons spend more time). This has to do with the electronegativity of the atom. The more electronegative the atom the more it will hold on to the electrons. Oxygen is very electronegative (elect ...
Semester 1 Exam Review Part 1
... atomic number is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus A = Atomic Number These are all equal to each P = Proton Number other E = Electron Number ...
... atomic number is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus A = Atomic Number These are all equal to each P = Proton Number other E = Electron Number ...
Quantum Numbers and Atomic Structure Honors
... Quantum Numbers and Atomic Structure Honors Chemistry Please do not write on this exam 1. In an atom of argon-40, the number of protons A) B) C) D) ...
... Quantum Numbers and Atomic Structure Honors Chemistry Please do not write on this exam 1. In an atom of argon-40, the number of protons A) B) C) D) ...
File - Mr. Walsh`s AP Chemistry
... Molecular (Non-metal) Nomenclature: Molecular compounds (made of all non-metals) are named by describing the molecular formula, using prefixes for the numbers. o You will need to memorize the number prefixes for the numbers 1–10. o E.g., P2O5 is diphosphorus pentoxide. **Note that the prefix “mono— ...
... Molecular (Non-metal) Nomenclature: Molecular compounds (made of all non-metals) are named by describing the molecular formula, using prefixes for the numbers. o You will need to memorize the number prefixes for the numbers 1–10. o E.g., P2O5 is diphosphorus pentoxide. **Note that the prefix “mono— ...
Revision topic 1-3
... Positive ions are smaller than their parent atoms (because of loss of the outer shell). Negative ions are larger than their parent atoms (because of increased electron repulsion by addition of electrons). The ionic radii decrease as a period is crossed from the left to the right (because of increase ...
... Positive ions are smaller than their parent atoms (because of loss of the outer shell). Negative ions are larger than their parent atoms (because of increased electron repulsion by addition of electrons). The ionic radii decrease as a period is crossed from the left to the right (because of increase ...
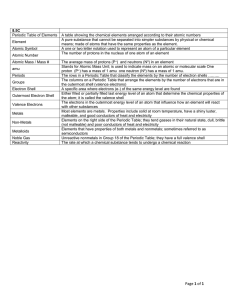
Atomic Structure Study Guide
... (2) Atoms of a given element are ___________ in all ways. (3) Atoms of different elements have different physical and chemical __________. (4) Atoms of different elements combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form _________. (5) In chemical reactions, atoms are rearranged, but are never ________ ...
... (2) Atoms of a given element are ___________ in all ways. (3) Atoms of different elements have different physical and chemical __________. (4) Atoms of different elements combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form _________. (5) In chemical reactions, atoms are rearranged, but are never ________ ...