* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Polyatomic Ions (Memorize for Wednesday, January 31
Debye–Hückel equation wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Artificial photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Elastic recoil detection wikipedia , lookup
Flux (metallurgy) wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Alkaline earth metal wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Organosulfur compounds wikipedia , lookup
Stability constants of complexes wikipedia , lookup
Oxidation state wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Surface properties of transition metal oxides wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Coordination complex wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
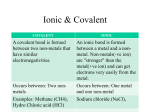
CHEMICAL NOMENCLATURE Oxidation Numbers (similar to valence electrons) Group 1 = +1 Group 2 = +2 Groups 13-18 = group # - 10 for most elements d-block elements must be looked up (groups 3-12 use roman numerals) oxidation numbers for ALL compounds MUST equal zero Metal-Non-metal (binary ionic compounds, only 2 elements) Metal (cation, +) named first, non-metal (anion, -) named second Metal name stays unchanged Non-metal ending changed to –ide EX – potassium + iodine potassium iodide calcium + oxygen calcium oxide Non-metal – non-metal (binary covalent compounds, only 2 elements) Name least electronegative element first (review periodic trends) Change ending of second element to –ide Use prefixes except mono on first element Crossing over charges = zero Mono 1 hexa 6 Di 2 hepta 7 Tri 3 octa 8 Tetra 4 nona 9 Penta 5 deca 10 EX – carbon C+4 + chlorine Cl-1x4 carbon tetrachloride Nitrogen N-3 + oxygen O-2 dinitrogen trioxide Polyatomic Ions Ammonium – Hydroxide – Acetate – Carbonate – Bicarbonate – Chlorate – Bromate – Nitrate – Sulfate – Chromate – Iodate – Phosphate – NH4+ OHCH3COO- or CH2COOHCO32HCO3ClO3BrO3NO3SO4-2 CrO4-2 IO3PO4-3 Arsenate Thiosulfate Silicate Oxalate Dichromate Thiocyanate Permanganate Selenate - AsO43S2O32SiO32C2O42Cr2O72CNSMnO4SeO42- Rules for polyatomic ions A = element besides oxygen O = oxygen Metal-polyatomic ion Name metal AOx = -ate ending of ion (most common form of ion) AOx+1 = add prefix per-, keep ending –ate AOx-1 = change –ate ending to –ite AOx-2 = add prefix hypo-, change –ate ending to –ite Oxyacids (hydrogen replaces the metal from above) Polyatomic ions ending in –ate form acids with an –ic ending EX – H2SO4: sulfate ion changes to sulfuric acid Polyatomic ions ending in –ite form acids with an –ous ending EX – HClO2: chlorite ion changes to chlorous acid The number of hydrogen atoms equals the charge on the polyatomic ion EX – H3PO4: H+1 x 3 = PO4-3 Transition Metal Compounds (Groups 3-12) Have multiple oxidation states Use roman numerals to indicate charge on metal (NOT the number of atoms) Older method Higher oxidation number ends with –ic EX – CuO cupric oxide ( copper has 2+) Lower oxidation number ends with –ous EX – Cu2O cuprous oxide (copper has 1+) Lead – plumbum Gold – aurum Mercury – hydrargyrum (little silver) Iron – ferrum Tin – stannum Antimony – stibium Silver – argentum Copper - cuprum