* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Topic 3.1: Chemical Elements and Water
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
State of matter wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
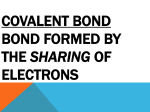
Topic 3: The Chemistry of Life SL and HL Topic 3.1: Chemical Elements and Water A. Basic Atomic Structure Matter: anything that takes up space and has mass Element: (atoms) a substance that cannot be broken down by ordinary means. The material making up matter. There are 92 naturally occurring elements, of these 25 are essential to life. 4 of these make up 96% of living matter ( Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen,and Nitrogen). The rest are called trace elements. These are required in minute amounts( Zinc, Cobalt, Iron, Magnesium). Molecules: Two or more different atoms combined. Atomic Number: The total number of protons or electrons in an atom. Atomic Mass: The total number of neutrons and protons in an atom. Neutral atoms: electron # = proton # Ions: # of electrons & protons differ Cation: positive charge, electron(s) lost Anion: negative charge, electron(s) gained B. Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonding: Atoms will interact with each other depending on their incomplete valence shell. There are several types of chemical bonds: Covalent Bond: These bonds are the strongest of the bonds. They are formed by the sharing of electrons. There are several subsets of covalent bonding: a). Nonpolar: Here the electrons are shared equally, thus eliminating a positive and negative end on the molecule. 1). double nonpolar: O2 2). triple nonpolar: N3 b). Polar covalent bond: Here the electrons are shared unequally, causing the molecule to develop a positive end (where the electrons spend less time) and a negative end (where the electrons spend more time). This has to do with the electronegativity of the atom. The more electronegative the atom the more it will hold on to the electrons. Oxygen is very electronegative (electronegative - the power of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself). Hydrogen is not. Ionic Bond: These bonds are formed by the taking of electrons. Anion: negative ion, Cl- and (OH-) Cation: positive ion, Na+ and (NH4)+. Molecules formed form ionic bonds are called ionic molecules Molecules formed from covalent bonds are called covalent molecules Non-Polar Covalent Bond Polar Covalent Bond C. The importance of some elements for life Hydrogen, Oxygen, Carbon are the most common molecules in living cells a. Carbon -Can make four covalent bonds with other atoms -This allows carbon to form complex molecules with other elements. -This molecule forms the basis of life. Without carbon life would not exist! -Forms 4 bonds with other molecules. b. Oxygen - Forms two covalent bonds with other molecules. -Oxygen allows organisms to get more energy from food. -It is also important in holding complex molecules together. c. Hydrogen -Forms one covalent with other molecules. -Most common element in the universe. -Also helps to stabilize and hold molecules together. d. Nitrogen -needed for proteins in plants and animals -promotes growth of leaves and stems in plants e. Sulfur -needed for proteins in plants and animals f. Phosphorus -needed for nucleic acids in plants and animals -also needed in plants for converting sugars to other molecules g. Iron -needed by haemoglobin (which carries oxygen in red blood cells) -required for the synthesis of chlorophyll h. Sodium and Potassium -needed for transmitting nervous impulses in neurons and for cell respiration in animals -Potassium – needed for photosynthesis and cell respiration in plants D. The importance of water for life -Water is made up of hydrogen and oxygen -Water has slightly negative and slightly positive areas -This gives water it’s unique properties which make life possible. Properties of water Thermal Properties Cohesive Properties Solvent Properties