File
... • The symbol for the positive element is written first, followed by the symbol of the negative element • Subscripts are used to indicate the numbers of ions needed to produce an electrically neutral compound. ...
... • The symbol for the positive element is written first, followed by the symbol of the negative element • Subscripts are used to indicate the numbers of ions needed to produce an electrically neutral compound. ...
Chem 1411 Chapt2
... Types of CompoundsIonic- Consists of metals and non-metals (Or in general cations and anions). NaCl, MgCl2, K2S, Na2SO4 Molecular (covalent)- Consists of non-metals only. HCl, N2O4, C3H6O, C6H12O6 Note- All compounds can be molecules; not all molecules can be compounds. Ions- Are chemical species th ...
... Types of CompoundsIonic- Consists of metals and non-metals (Or in general cations and anions). NaCl, MgCl2, K2S, Na2SO4 Molecular (covalent)- Consists of non-metals only. HCl, N2O4, C3H6O, C6H12O6 Note- All compounds can be molecules; not all molecules can be compounds. Ions- Are chemical species th ...
Classification – 3 main groups
... products, taste different, smell different, can it react with water or acid? Physical Properties-characteristic of matter you can observe without changing its identity; color, size, shape, odor, texture, hardness, malleable, ductile, melting pt, boiling pt, density, volume, mass, solid, liquid, gas, ...
... products, taste different, smell different, can it react with water or acid? Physical Properties-characteristic of matter you can observe without changing its identity; color, size, shape, odor, texture, hardness, malleable, ductile, melting pt, boiling pt, density, volume, mass, solid, liquid, gas, ...
Here
... A. Definition – bonding that results from electrical attraction between (+) ions (cations) and (-) ions (anions) 1. Cations – 1+, 2+, 3+ - P.T. Trends – show valence e- and dots 2. Anions – 3-, 2-, 1- - Same as above B. Difference in e-neg >1.7 ex:// Na=.9 and Cl=3.0 C. Typically the joining of a me ...
... A. Definition – bonding that results from electrical attraction between (+) ions (cations) and (-) ions (anions) 1. Cations – 1+, 2+, 3+ - P.T. Trends – show valence e- and dots 2. Anions – 3-, 2-, 1- - Same as above B. Difference in e-neg >1.7 ex:// Na=.9 and Cl=3.0 C. Typically the joining of a me ...
STUDY GUIDE for DIGESTION and NUTRITION
... Distinguish metals from non metals using properties Recognize elements in the alkali, alkaline earth, halogen, and noble gas families. Describe how hydrogen is a “family of one” Explain the difference between “families” and “periods” on a periodic table. Explain the difference between atom ...
... Distinguish metals from non metals using properties Recognize elements in the alkali, alkaline earth, halogen, and noble gas families. Describe how hydrogen is a “family of one” Explain the difference between “families” and “periods” on a periodic table. Explain the difference between atom ...
Document
... Now we actually will use the Debye-Huckel limiting law itself. There are three very important things about applying the Debye-Huckel theory. First, it only applies to ions. Molecules that are not charged have an activity coefficient of 1.0 according to this theory (in reality, that is not true, but ...
... Now we actually will use the Debye-Huckel limiting law itself. There are three very important things about applying the Debye-Huckel theory. First, it only applies to ions. Molecules that are not charged have an activity coefficient of 1.0 according to this theory (in reality, that is not true, but ...
Determination of electrochemical equivalent of copper and
... number of NA ions weights as much as is ion’s atomic weight. ...
... number of NA ions weights as much as is ion’s atomic weight. ...
FXM Rev 1 Key - Grande Cache Community High School
... the Planetary Atomic Model. hydrocarbons These are organic compounds that contain both carbon and hydrogen. Methane (CH4) is an example. Avogadro’s number This is a number that groups a very large amount of atoms or molecules to facilitate measurement and calculations in chemistry. It is the number ...
... the Planetary Atomic Model. hydrocarbons These are organic compounds that contain both carbon and hydrogen. Methane (CH4) is an example. Avogadro’s number This is a number that groups a very large amount of atoms or molecules to facilitate measurement and calculations in chemistry. It is the number ...
Honors Unit 5 Practice Test
... When a stable covalent bond forms, the potential energy of the atoms a. increases. c. remains constant. b. decreases. d. becomes zero. What group of elements satisfies the octet rule without forming compounds? a. halogen c. alkali metal b. noble gas d. alkaline-earth metal In drawing a Lewis structu ...
... When a stable covalent bond forms, the potential energy of the atoms a. increases. c. remains constant. b. decreases. d. becomes zero. What group of elements satisfies the octet rule without forming compounds? a. halogen c. alkali metal b. noble gas d. alkaline-earth metal In drawing a Lewis structu ...
Chemistry ~ Fall Final Review
... Measurement: significant figures, sci. notation, guess digits, density Properties of Matter: atoms/molecules, elements & compounds, chemical/physical changes History of the atom: models & scientists Wave calculations: properties of waves, energy, frequency, wavelength Electron configuration: orbital ...
... Measurement: significant figures, sci. notation, guess digits, density Properties of Matter: atoms/molecules, elements & compounds, chemical/physical changes History of the atom: models & scientists Wave calculations: properties of waves, energy, frequency, wavelength Electron configuration: orbital ...
PPT - gserianne.com
... • There are three major types of chemical bonds to know… – Ionic (electrovalent) bonds – attraction between oppositely charged ions – Covalent bonds – sharing of electrons – Hydrogen bonds – weak, electrostatic interaction between atoms ...
... • There are three major types of chemical bonds to know… – Ionic (electrovalent) bonds – attraction between oppositely charged ions – Covalent bonds – sharing of electrons – Hydrogen bonds – weak, electrostatic interaction between atoms ...
Basics of Chemistry
... Elements & their valence shells Moving from left to right, each element has a sequential addition of electrons (and protons) ...
... Elements & their valence shells Moving from left to right, each element has a sequential addition of electrons (and protons) ...
Chapter 2
... Atoms or groups of atoms with a charge. Cations- positive ions - get by losing electrons(s). Anions- negative ions - get by gaining electron(s). Ionic bonding- held together by the opposite ...
... Atoms or groups of atoms with a charge. Cations- positive ions - get by losing electrons(s). Anions- negative ions - get by gaining electron(s). Ionic bonding- held together by the opposite ...
Chem 1a Midterm Review
... Ions: all transition metals when they ionize the first two electrons that are lost are from the ns shell not the (n-1)d shell. Filling orbitals 1. Pauli Principle: Every electron must have a unique set of 4 quantum numbers 2. Aufbau principle: Fill lowest energy orbitals first 3. Hund's Rule: In a d ...
... Ions: all transition metals when they ionize the first two electrons that are lost are from the ns shell not the (n-1)d shell. Filling orbitals 1. Pauli Principle: Every electron must have a unique set of 4 quantum numbers 2. Aufbau principle: Fill lowest energy orbitals first 3. Hund's Rule: In a d ...
AP Unit 1 Test Review
... (D) Iodine liberates free bromine from a solution of bromide ion. (E) Fluorine is the most electronegative of the halogens. 8. Question 8-11 refer to atoms for which the occupied atomic orbitals shown below. 8. Represents an atom that is chemically unreactive 9. Represents an atom in an excited stat ...
... (D) Iodine liberates free bromine from a solution of bromide ion. (E) Fluorine is the most electronegative of the halogens. 8. Question 8-11 refer to atoms for which the occupied atomic orbitals shown below. 8. Represents an atom that is chemically unreactive 9. Represents an atom in an excited stat ...
Bohr Model Notes - Northwest ISD Moodle
... 2 electrons can fit in the first energy level. 8 electrons can fit in the second energy level. 18 electrons can fit in the third energy level. Valence Electrons – electrons found in the outermost energy levels. Magnesium has 2 valence electrons. Rule of Eight – Elements that have the maximum n ...
... 2 electrons can fit in the first energy level. 8 electrons can fit in the second energy level. 18 electrons can fit in the third energy level. Valence Electrons – electrons found in the outermost energy levels. Magnesium has 2 valence electrons. Rule of Eight – Elements that have the maximum n ...
3. atomic structure
... There are two methods of identifying isotopes. 1. Write mass number with a hyphen after the name of the element, ex: Helium-3 or Helium-4, and 2. using the composition of the nucleus as the isotopes nuclear symbol, ex. 3He or 4He (the number of the bottom left would represent the atomic number which ...
... There are two methods of identifying isotopes. 1. Write mass number with a hyphen after the name of the element, ex: Helium-3 or Helium-4, and 2. using the composition of the nucleus as the isotopes nuclear symbol, ex. 3He or 4He (the number of the bottom left would represent the atomic number which ...
A = 27
... atom. If three e- were lost 10, are remaining. ANS-4 #33 The excited state must have the same # of electrons as the neutral atom, however one or more must be at a higher energy level (outermost shell) that the ground state of the periodic table ( for Al it is 2-8-3), 13 electrons.The ans is 1) 2-7-4 ...
... atom. If three e- were lost 10, are remaining. ANS-4 #33 The excited state must have the same # of electrons as the neutral atom, however one or more must be at a higher energy level (outermost shell) that the ground state of the periodic table ( for Al it is 2-8-3), 13 electrons.The ans is 1) 2-7-4 ...
Chapter 8: Chemical Bonding
... noble gas configuration Noble gases: all (except He) have s2p6 valence shells (8 e-) ...
... noble gas configuration Noble gases: all (except He) have s2p6 valence shells (8 e-) ...
Chapter 18 Resource: Matter
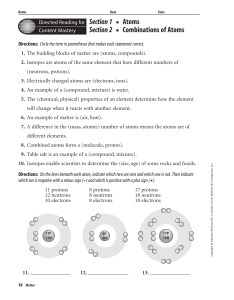
... 4. An example of a (compound, mixture) is water. 5. The (chemical, physical) properties of an element determine how the element will change when it reacts with another element. 6. An example of matter is (air, heat). 7. A difference in the (mass, atomic) number of atoms means the atoms are of differ ...
... 4. An example of a (compound, mixture) is water. 5. The (chemical, physical) properties of an element determine how the element will change when it reacts with another element. 6. An example of matter is (air, heat). 7. A difference in the (mass, atomic) number of atoms means the atoms are of differ ...
Atoms in Combination: The Chemical Bond
... In pictorial form, an oxidation reaction involves the transfer of electrons to oxygen atoms. When natural gas (CH4) burns, it combines with two oxygen molecules (O2) to form a molecule of carbon dioxide (CO2) and two molecules of water (H2O). ...
... In pictorial form, an oxidation reaction involves the transfer of electrons to oxygen atoms. When natural gas (CH4) burns, it combines with two oxygen molecules (O2) to form a molecule of carbon dioxide (CO2) and two molecules of water (H2O). ...
Topic Book periodicity
... d-d transition: The excitation of an e─ from the lower of two energy level groups to the upper. As the ligand approaches the metal, the five d orbitals split. The difference in energy between the two levels corresponds to the wavelength of visible light, as incoming light causes energy of a particul ...
... d-d transition: The excitation of an e─ from the lower of two energy level groups to the upper. As the ligand approaches the metal, the five d orbitals split. The difference in energy between the two levels corresponds to the wavelength of visible light, as incoming light causes energy of a particul ...