TYPES OF REACTIONS
... Balance half-equations Atoms other than H and O O atoms (add H2O) H atoms (adding H+) Balance charge with electrons Combine half-reactions Add number of OH- ion equal to number of H+ ions on both sides of overall reaction and combine hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions to form water when they app ...
... Balance half-equations Atoms other than H and O O atoms (add H2O) H atoms (adding H+) Balance charge with electrons Combine half-reactions Add number of OH- ion equal to number of H+ ions on both sides of overall reaction and combine hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions to form water when they app ...
General Chemistry First Semester Review General
... 5. Sketch and label the location and charges of the subatomic particles in an atom of oxygen-15. 6. What physical properties distinguish metals from nonmetals? 7. Elemental oxygen forms diatomic molecules (O2). Draw a Lewis structure for an oxygen molecule (that’s showing the total valence electrons ...
... 5. Sketch and label the location and charges of the subatomic particles in an atom of oxygen-15. 6. What physical properties distinguish metals from nonmetals? 7. Elemental oxygen forms diatomic molecules (O2). Draw a Lewis structure for an oxygen molecule (that’s showing the total valence electrons ...
Chemistry Vocab for Quiz 12/21 or 12/22 Atom – The smallest
... Atom – The smallest particle of an element. Atomic number - The number of protons in the nucleus of an element Atomic mass – The average mass of one atom of an element Proton – A small positively particle in the nucleus Neutron – a small particle in the nucleus with no charge Electron – A tiny negat ...
... Atom – The smallest particle of an element. Atomic number - The number of protons in the nucleus of an element Atomic mass – The average mass of one atom of an element Proton – A small positively particle in the nucleus Neutron – a small particle in the nucleus with no charge Electron – A tiny negat ...
FORMAL CHARGE AND OXIDATION NUMBER - IDC
... a) For :C:::O: Carbon: 4 – 2 – 3 = –1; Oxygen: 6 – 2 – 3 = +1 Structures that do not obey the octet rule (for carbon): b) For :C:O::: Carbon: 4 – 2 – 1 = +1; Oxygen: 6 – 6 – 1 = –1 c) For :C::O:: Carbon: 4 – 2 –2 = 0; Oxygen: 6 – 4 – 2 = 0 Comment: All three structures are acceptable (because the fo ...
... a) For :C:::O: Carbon: 4 – 2 – 3 = –1; Oxygen: 6 – 2 – 3 = +1 Structures that do not obey the octet rule (for carbon): b) For :C:O::: Carbon: 4 – 2 – 1 = +1; Oxygen: 6 – 6 – 1 = –1 c) For :C::O:: Carbon: 4 – 2 –2 = 0; Oxygen: 6 – 4 – 2 = 0 Comment: All three structures are acceptable (because the fo ...
sch3u unit 1 test: matter
... 5. In the alkali metals group, as the atomic number increases a. the electronegativity increases b. the electronegativity decreases c. the atomic radius decreases d. the electron affinity increases 6. In a neutral atom a. the number of protons is always equal to the number of neutrons b. the number ...
... 5. In the alkali metals group, as the atomic number increases a. the electronegativity increases b. the electronegativity decreases c. the atomic radius decreases d. the electron affinity increases 6. In a neutral atom a. the number of protons is always equal to the number of neutrons b. the number ...
Resistance of constantan wire
... As you may know the current in a wire is due to the motion of free electrons within the wire. These electrons are not bound to any particular atom but are free to 'wander' through the body of the material. The more free electrons per unit volume the greater the current for a given voltage difference ...
... As you may know the current in a wire is due to the motion of free electrons within the wire. These electrons are not bound to any particular atom but are free to 'wander' through the body of the material. The more free electrons per unit volume the greater the current for a given voltage difference ...
NOMENCLATURE OF IONIC COMPOUNDS CHEMISTRY 1405
... The prefixes mono, di, tri, tetra etc are used only for binary covalent compounds. ...
... The prefixes mono, di, tri, tetra etc are used only for binary covalent compounds. ...
Unit 2: Biochem Notes
... Electrons (e-) – Particles found traveling at specific distances (orbitals/energy levels/shells) from the nucleus; has a negative charge and a mass so small that it is not factored into the mass of the atom. The first and closest energy level/orbital/shell can hold a maximum of 2 e-. The rest of the ...
... Electrons (e-) – Particles found traveling at specific distances (orbitals/energy levels/shells) from the nucleus; has a negative charge and a mass so small that it is not factored into the mass of the atom. The first and closest energy level/orbital/shell can hold a maximum of 2 e-. The rest of the ...
Chapter 1: Chemistry and You
... Isotopic Notation, Subatomic particles Valence Electrons and Ions 3. Describe the basic structure of the atom in the modern atomic theory (be able to label protons, neutrons, electrons, and the nucleus) (Ch. 3): ...
... Isotopic Notation, Subatomic particles Valence Electrons and Ions 3. Describe the basic structure of the atom in the modern atomic theory (be able to label protons, neutrons, electrons, and the nucleus) (Ch. 3): ...
Chemistry Part 1
... Molecule—two or more like atoms combined chemically Compound—two or more different atoms combined chemically ...
... Molecule—two or more like atoms combined chemically Compound—two or more different atoms combined chemically ...
Review Sheet for Benchmark Exam
... When we did the penny lab, why did we use three pennies even though we only put two in the NaOH solution? What is the third penny called? ...
... When we did the penny lab, why did we use three pennies even though we only put two in the NaOH solution? What is the third penny called? ...
CHEM_1305_Practice_Exam_2
... 1) What is the subatomic particle having a negligible mass and a negative charge? A) electron ...
... 1) What is the subatomic particle having a negligible mass and a negative charge? A) electron ...
Chapter 2 - Saint Joseph High School
... – All materials are made of matter (solid, liquid, gas) ...
... – All materials are made of matter (solid, liquid, gas) ...
Midterm Review 2017
... Table are considered in order from top to bottom, the ionization energy of each successive element decreases. This decrease is due to 1) decreasing radius and decreasing shielding effect 2) decreasing radius and increasing shielding effect 3) increasing radius and decreasing shielding effect 4) incr ...
... Table are considered in order from top to bottom, the ionization energy of each successive element decreases. This decrease is due to 1) decreasing radius and decreasing shielding effect 2) decreasing radius and increasing shielding effect 3) increasing radius and decreasing shielding effect 4) incr ...
Nuclear Tracks
... When heavy charged particles [proton upward] traverse a dielectric medium, they are able to leave long lived trials of damage that may be observed either directly by ...
... When heavy charged particles [proton upward] traverse a dielectric medium, they are able to leave long lived trials of damage that may be observed either directly by ...
Dr Davids Essential Chemistry Definitions Bk1
... A molecule that is non-superimposable on its mirror image; such a molecule is optically active (meaning that it will rotate the plane of plane polarised light to the right or to the left). Chiral molecules frequently contain one or more asymmetric carbon atoms. Conjugate acid-base pairs: These are f ...
... A molecule that is non-superimposable on its mirror image; such a molecule is optically active (meaning that it will rotate the plane of plane polarised light to the right or to the left). Chiral molecules frequently contain one or more asymmetric carbon atoms. Conjugate acid-base pairs: These are f ...
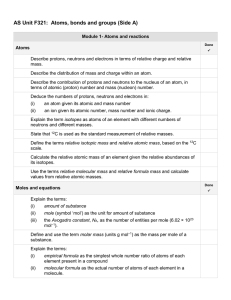
AS Unit F321 Unit 1 Side A check list
... State the formulae of the common acids: hydrochloric, 2ulphuric and nitric acids. State that common bases are metal oxides, metal hydroxides and ammonia. State that an alkali is a soluble base that releases OH– ions in aqueous solution. State the formulae of the common alkalis: sodium hydroxide, pot ...
... State the formulae of the common acids: hydrochloric, 2ulphuric and nitric acids. State that common bases are metal oxides, metal hydroxides and ammonia. State that an alkali is a soluble base that releases OH– ions in aqueous solution. State the formulae of the common alkalis: sodium hydroxide, pot ...
Note 1.1 Chemistry of Life
... the chemical and physical properties of the element. An atom is made up of three different sub atomic particles; neutrons (no charge), protons (positive charge), and electrons (negative charge). Atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of the atom. It determines the particular ato ...
... the chemical and physical properties of the element. An atom is made up of three different sub atomic particles; neutrons (no charge), protons (positive charge), and electrons (negative charge). Atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of the atom. It determines the particular ato ...
The Chemical Earth
... Valence energy level The outermost shell of an atom is referred to as the valence energy level. Similarly, the electrons that occupy the outermost shell are called valence electrons. In the periodic table elements with the same number of valence electrons occur in the same column or group. ...
... Valence energy level The outermost shell of an atom is referred to as the valence energy level. Similarly, the electrons that occupy the outermost shell are called valence electrons. In the periodic table elements with the same number of valence electrons occur in the same column or group. ...
Document
... a) an element which has 5 electrons in each atom b) an element which has 5 electrons in its outer energy level c) an element for which the second energy level is completely filled d) an element which forms ions by gaining only one electron e) how many elements are there in the sixth period? f) the e ...
... a) an element which has 5 electrons in each atom b) an element which has 5 electrons in its outer energy level c) an element for which the second energy level is completely filled d) an element which forms ions by gaining only one electron e) how many elements are there in the sixth period? f) the e ...
HW 10: Electron Configuration Practice -
... nucleus of the atom. An electron configuration provides information about the number of electrons in each orbital. The letters in the electron configuration correspond to the different orbitals present. The lowest orbital is labeled as an s, and it can hold up to two electrons. The p orbital can hol ...
... nucleus of the atom. An electron configuration provides information about the number of electrons in each orbital. The letters in the electron configuration correspond to the different orbitals present. The lowest orbital is labeled as an s, and it can hold up to two electrons. The p orbital can hol ...
Review 1st Qtr KEY
... Ultraviolet light causes a chemical reaction in your skin and darkens the pigments in your skin. If the wavelength of these photons is 200 nanometers, 2 x 10-7 meters ...
... Ultraviolet light causes a chemical reaction in your skin and darkens the pigments in your skin. If the wavelength of these photons is 200 nanometers, 2 x 10-7 meters ...