04 Biochemistry
... • You can draw an atom by showing how electrons are arranged in each energy level. • Electrons move around the energy levels (aka “electron shells” or “electron orbitals”) outside the nucleus rapidly to form an electron cloud ...
... • You can draw an atom by showing how electrons are arranged in each energy level. • Electrons move around the energy levels (aka “electron shells” or “electron orbitals”) outside the nucleus rapidly to form an electron cloud ...
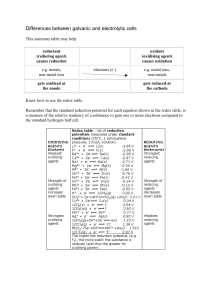
Differences between galvanic and electrolytic cells
... Think about what you expect might happen. The solutions will contain Na+ ions, Cl– ions and H2O molecules. You would not expect any significant number of hydrogen or hydroxide ions to be present as water is neutral (pH=7). So, reactions taking place at the electrodes might include: 2H2O(l) + 2e– Na+ ...
... Think about what you expect might happen. The solutions will contain Na+ ions, Cl– ions and H2O molecules. You would not expect any significant number of hydrogen or hydroxide ions to be present as water is neutral (pH=7). So, reactions taking place at the electrodes might include: 2H2O(l) + 2e– Na+ ...
Investigating Chemistry - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... Why? To gain a noble gas electron configuration (very stable). ...
... Why? To gain a noble gas electron configuration (very stable). ...
Fundamentals Fall Final Review
... 18. Know what happens to the size of atoms as you move across a period or down a group. Know which member of the following pairs of particles is larger: Pd, Rb; Mg, Ba; Cs, Lu; Se, O. 19. Which of the following atoms would we expect to have the largest radius? Li, B, O, or F 20. Know which is larger ...
... 18. Know what happens to the size of atoms as you move across a period or down a group. Know which member of the following pairs of particles is larger: Pd, Rb; Mg, Ba; Cs, Lu; Se, O. 19. Which of the following atoms would we expect to have the largest radius? Li, B, O, or F 20. Know which is larger ...
chemical bond
... Most of the rocks and minerals that make up the Earth’s crust consists of (+) and (-) ions held together by ionic bonding. An ionic compound transfers electron so that the compound becomes neutral. Metal + non-metal = ionic bonding (Overhead) ...
... Most of the rocks and minerals that make up the Earth’s crust consists of (+) and (-) ions held together by ionic bonding. An ionic compound transfers electron so that the compound becomes neutral. Metal + non-metal = ionic bonding (Overhead) ...
New quasiatomic nanoheterostructures: Superatoms and Excitonic
... dielectrics. Ionization energy superatomic take large values (about 3 eV), which is almost three orders of magnitude higher than the binding energy of excitons in semiconductors. Thus, the observed effect is a significant increase in the binding energy of the singlet ground state of the exciton quas ...
... dielectrics. Ionization energy superatomic take large values (about 3 eV), which is almost three orders of magnitude higher than the binding energy of excitons in semiconductors. Thus, the observed effect is a significant increase in the binding energy of the singlet ground state of the exciton quas ...
Chemistry Cram Sheet
... Shielding Which has the bigger atomic radius Na or Cl? Which has a larger first ionization energy Li or Cs? ...
... Shielding Which has the bigger atomic radius Na or Cl? Which has a larger first ionization energy Li or Cs? ...
Use the following to answer questions 1-14:
... ____ 2. Metallic elements form cations. ____ 3. Cations are negatively charged ions. ____ 4. Valence electrons are located in the outermost electron shell of the atom. ____ 5. Noble gases are very stable; other elements give up, gain, or share electrons to acquire a valence shell like those of noble ...
... ____ 2. Metallic elements form cations. ____ 3. Cations are negatively charged ions. ____ 4. Valence electrons are located in the outermost electron shell of the atom. ____ 5. Noble gases are very stable; other elements give up, gain, or share electrons to acquire a valence shell like those of noble ...
Exam 3 Review
... The symbol for the magnetic quantum number is m which defines the orbital. m = - , (- + 1), (- +2), .....0, ......., ( -2), ( -1), The last quantum number is the spin quantum number which has the symbol m s which characterizes the single electron. The spin quantum number only has two pos ...
... The symbol for the magnetic quantum number is m which defines the orbital. m = - , (- + 1), (- +2), .....0, ......., ( -2), ( -1), The last quantum number is the spin quantum number which has the symbol m s which characterizes the single electron. The spin quantum number only has two pos ...
What is matter made of?
... describes all of the physical substances around us: your table, your body, a pencil, water, air or all solids liquids & gasses. Anything that has mass and volume (takes up space) Made up of different kinds of atoms ...
... describes all of the physical substances around us: your table, your body, a pencil, water, air or all solids liquids & gasses. Anything that has mass and volume (takes up space) Made up of different kinds of atoms ...
Notes - Ms. Dawkins
... A neutron has about the ______________ ___________ as a proton. They are grouped together in the ______________________. Atoms are extremely ________________. The electron cloud is about _______________ times the size of the __________________. Electrons are much smaller than _____________________ ...
... A neutron has about the ______________ ___________ as a proton. They are grouped together in the ______________________. Atoms are extremely ________________. The electron cloud is about _______________ times the size of the __________________. Electrons are much smaller than _____________________ ...
Properties of Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids
... Alkali metals, Alkaline Earth metals, Halogens, Noble Gases ...
... Alkali metals, Alkaline Earth metals, Halogens, Noble Gases ...
Properties of Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids
... Alkali metals, Alkaline Earth metals, Halogens, Noble Gases ...
... Alkali metals, Alkaline Earth metals, Halogens, Noble Gases ...
History of the Atom
... In 1909, performed the Gold Foil Experiment and suggested the following characteristics of the atom: o It consists of a small core, or nucleus, that contains most of the mass of the atom o This nucleus is made up of particles called protons, which have a positive charge o The protons are surrounde ...
... In 1909, performed the Gold Foil Experiment and suggested the following characteristics of the atom: o It consists of a small core, or nucleus, that contains most of the mass of the atom o This nucleus is made up of particles called protons, which have a positive charge o The protons are surrounde ...
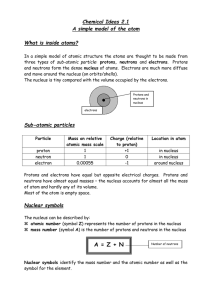
atomic number
... - atoms of different elements are different - every carbon atom is identical to every other carbon atom because they have the same chemical and physical properties - but carbon atoms are different from sulfur atoms because they have different chemical and physical properties. Atoms combine in simple ...
... - atoms of different elements are different - every carbon atom is identical to every other carbon atom because they have the same chemical and physical properties - but carbon atoms are different from sulfur atoms because they have different chemical and physical properties. Atoms combine in simple ...
Unit 13 - Electrochemistry
... Electrochemistry: The branch of chemistry that is the study of the relationship between electric forces and chemical reactions. Voltage: The potential difference or electromotive force, measured in volts; it represents the amount of work that moving an electric charge between two points would take. ...
... Electrochemistry: The branch of chemistry that is the study of the relationship between electric forces and chemical reactions. Voltage: The potential difference or electromotive force, measured in volts; it represents the amount of work that moving an electric charge between two points would take. ...
Eighth Grade Review - PAMS-Doyle
... Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. All matter is made up of small particles called atoms. ...
... Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. All matter is made up of small particles called atoms. ...
C2 Knowledge PowerPoint
... Ionic bonding – transferring electrons Chemical bonding: involves either transferring or sharing electrons in the highest occupied energy level (outer shell) of atoms to achieve the electronic structure of a noble gas (full outer shell) Compounds are usually very different from the elements that hav ...
... Ionic bonding – transferring electrons Chemical bonding: involves either transferring or sharing electrons in the highest occupied energy level (outer shell) of atoms to achieve the electronic structure of a noble gas (full outer shell) Compounds are usually very different from the elements that hav ...
Document
... Chemical bonding: involves either transferring or sharing electrons in the highest occupied energy level (outer shell) of atoms to achieve the electronic structure of a noble gas (full outer shell) Compounds are usually very different from the elements that have combined together to make them, for e ...
... Chemical bonding: involves either transferring or sharing electrons in the highest occupied energy level (outer shell) of atoms to achieve the electronic structure of a noble gas (full outer shell) Compounds are usually very different from the elements that have combined together to make them, for e ...
Semester Exam Review Guide
... 24. Plasmas include all of the following except: a. ionized gases b. lava c. lightning d. stars 26. If the mass of a steel bolt is 4.0 grams and its volume is 2 milliliters, what is the bolt’s density? a. 2 ml / g b. 2 g / ml c. .5 g / ml d. 8 ml / g 27. How many Hydrogen atoms are in the following ...
... 24. Plasmas include all of the following except: a. ionized gases b. lava c. lightning d. stars 26. If the mass of a steel bolt is 4.0 grams and its volume is 2 milliliters, what is the bolt’s density? a. 2 ml / g b. 2 g / ml c. .5 g / ml d. 8 ml / g 27. How many Hydrogen atoms are in the following ...
Chemistry Test Study Guide
... 21. A mixture is created when two pure substances are combined so that each of the pure substances retains its own properties. 22. Where is the majority of the mass of an atom located? In the nucleus.(Protons and Neutrons) 23. If an atom loses electron’s, will it have a positive or negative charge? ...
... 21. A mixture is created when two pure substances are combined so that each of the pure substances retains its own properties. 22. Where is the majority of the mass of an atom located? In the nucleus.(Protons and Neutrons) 23. If an atom loses electron’s, will it have a positive or negative charge? ...
Objective 1: Summarize the development of atomic theory
... Objective 1: Summarize the development of atomic theory. Identify the correct scientist to the clues as related to atomic theory history. 1. Modern atomic theory that describes the electronic structure of the atom as the probability of finding electrons within certain regions of space. 2. The atom ...
... Objective 1: Summarize the development of atomic theory. Identify the correct scientist to the clues as related to atomic theory history. 1. Modern atomic theory that describes the electronic structure of the atom as the probability of finding electrons within certain regions of space. 2. The atom ...