THAT Corporation Design Note 100
... Q1 and Q2 form logarithmically adjustable current sources, and Q3 sets their full-scale currents. The rest of the design is relatively straightforward. The current through Q3 is the program current, and it sets up a voltage across Q3’s base-emitter junction. When VR4 and VR5 are adjusted to put this ...
... Q1 and Q2 form logarithmically adjustable current sources, and Q3 sets their full-scale currents. The rest of the design is relatively straightforward. The current through Q3 is the program current, and it sets up a voltage across Q3’s base-emitter junction. When VR4 and VR5 are adjusted to put this ...
A 26.8 dB Gain 19.7 dBm CMOS Power Amplifier Using 4
... coupling combiner applied in an mm-wave CMOS power amplifier (PA) design with wideband, large output power and high gain. Basing on the principle of both series and parallel combination concurrently working in a concentric distributed active transformer, the size of a 4-way power combiner can be dra ...
... coupling combiner applied in an mm-wave CMOS power amplifier (PA) design with wideband, large output power and high gain. Basing on the principle of both series and parallel combination concurrently working in a concentric distributed active transformer, the size of a 4-way power combiner can be dra ...
21.6 - A 60GHz Direct-Conversion CMOS Receiver
... The 7GHz unlicensed band around 60GHz provides the possibility of gigabit-per-second wireless communications. In addition to satisfying speed-intensive applications, such high data rates can also reduce the energy dissipated per bit because the power consumption of RF transceivers has historically i ...
... The 7GHz unlicensed band around 60GHz provides the possibility of gigabit-per-second wireless communications. In addition to satisfying speed-intensive applications, such high data rates can also reduce the energy dissipated per bit because the power consumption of RF transceivers has historically i ...
V OL (max)
... combined input capacitances of any loads being driven and the device’s own output capacitance. These narrow spikes of current are supplied by Vdd, which can be of 5mA. As the switching frequency increases, there will be more of these current spikes and the average current drawn from Vdd will increas ...
... combined input capacitances of any loads being driven and the device’s own output capacitance. These narrow spikes of current are supplied by Vdd, which can be of 5mA. As the switching frequency increases, there will be more of these current spikes and the average current drawn from Vdd will increas ...
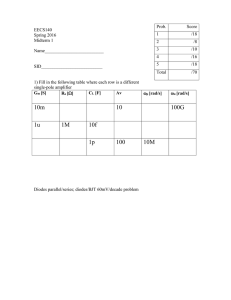
16spMid1b
... Estimate the transconductance, output resistance, and intrinsic gain of the transistor (give numerical answers). What is the gain if the transistor is used with a resistive load of 1M? transconductance output resistance Av, intrinsic Av, resistive load 4) You have biased the amplifier below with a ...
... Estimate the transconductance, output resistance, and intrinsic gain of the transistor (give numerical answers). What is the gain if the transistor is used with a resistive load of 1M? transconductance output resistance Av, intrinsic Av, resistive load 4) You have biased the amplifier below with a ...
Operational Transconductance Amplifier in 350nm CMOS technology
... discussed with emphasis on individual sub-blocks namely: Core, Common-Mode Feedback and Bias. Design procedure of each sub-block is given, as well. For this purpose a set of useful curves is extracted using SPICE giving the insight into MOS device behavior in target technology process. Important des ...
... discussed with emphasis on individual sub-blocks namely: Core, Common-Mode Feedback and Bias. Design procedure of each sub-block is given, as well. For this purpose a set of useful curves is extracted using SPICE giving the insight into MOS device behavior in target technology process. Important des ...
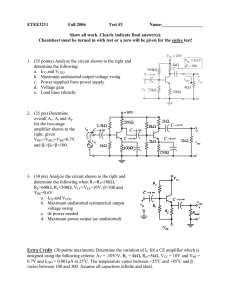
ETEE3211 Fall 2007
... 3. (20 points) For the circuit shown to the right, determine the output voltage, vout, when VBE=0.7V, β = 200 and vin=0. 4. (30 points) For the circuit of problem 1, use VCC=5V, VBE=0.7V, β=180, RC=RL=1kΩ, RE=100Ω, and all capacitors infinite and ideal. a. Select R1 and R2 for maximum output voltage ...
... 3. (20 points) For the circuit shown to the right, determine the output voltage, vout, when VBE=0.7V, β = 200 and vin=0. 4. (30 points) For the circuit of problem 1, use VCC=5V, VBE=0.7V, β=180, RC=RL=1kΩ, RE=100Ω, and all capacitors infinite and ideal. a. Select R1 and R2 for maximum output voltage ...
The FEE board requires 4 channels of DAC for the voltage regulator
... expected that a simple 2 or 3 transistor amplifier will give adequate performance at a lower power level than would be achieved with a design based on an op-amp. A common-base input stage will be used to handle the SiPM capacitance; an input transistor per SiPM might be considered. The response of a ...
... expected that a simple 2 or 3 transistor amplifier will give adequate performance at a lower power level than would be achieved with a design based on an op-amp. A common-base input stage will be used to handle the SiPM capacitance; an input transistor per SiPM might be considered. The response of a ...
DESIGN EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT HIGH
... • By replacing high-pass filter LC with RC: resulted voltage output and current output are the same. • Using C1 = C2 = C3 = C4 = 1 uF and R1 = R2 = R3 = 4.3 ohm, with NMOS and PMOS to Ln = Lp = 0.35 μm, Wn = 0.69 μm, Wp = 2.97 μm • Inverter 2 should be equal to 4 times of inverter 1. (Other combinat ...
... • By replacing high-pass filter LC with RC: resulted voltage output and current output are the same. • Using C1 = C2 = C3 = C4 = 1 uF and R1 = R2 = R3 = 4.3 ohm, with NMOS and PMOS to Ln = Lp = 0.35 μm, Wn = 0.69 μm, Wp = 2.97 μm • Inverter 2 should be equal to 4 times of inverter 1. (Other combinat ...
Implementing Logic Using Electronic circuits
... ovens, washing machines and dishwashers, are including embedded systems to provide flexibility, efficiency and features. Advanced HVAC systems use networked thermostats to more accurately and efficiently control temperature that can change by time of day and season. Home automation uses wired- a ...
... ovens, washing machines and dishwashers, are including embedded systems to provide flexibility, efficiency and features. Advanced HVAC systems use networked thermostats to more accurately and efficiently control temperature that can change by time of day and season. Home automation uses wired- a ...
ELEC 5970-001/6970-001 Special Topics in Electrical Engineering
... change to 1, necessary and sufficient condition is that both inputs have completed their 0 to 1 transitions. Thus, the first output transition is caused by two input transitions, one on each input. This subtracts 1 from the above upper bound. Next, consider the last transition at the output. The las ...
... change to 1, necessary and sufficient condition is that both inputs have completed their 0 to 1 transitions. Thus, the first output transition is caused by two input transitions, one on each input. This subtracts 1 from the above upper bound. Next, consider the last transition at the output. The las ...
MATLAB Array Operations
... Today's Learning Objectives After today's class, students will be able to: • Recognize and assemble series and parallel circuits. • Construct electric circuits using a breadboard. • Demonstrate how voltage, current and resistance are measured. • Identify and use Ohm’s Law, Power Law, Kirchhoff’s ...
... Today's Learning Objectives After today's class, students will be able to: • Recognize and assemble series and parallel circuits. • Construct electric circuits using a breadboard. • Demonstrate how voltage, current and resistance are measured. • Identify and use Ohm’s Law, Power Law, Kirchhoff’s ...
Take an example of CMOS transistor
... OUTPUT will be high floating first, then the output will take a value depending on the time that the output stays unconnected. During this period the voltage value will decrease. Will it be a ‘1’ or ‘0’? That depends on the Vh definition. ...
... OUTPUT will be high floating first, then the output will take a value depending on the time that the output stays unconnected. During this period the voltage value will decrease. Will it be a ‘1’ or ‘0’? That depends on the Vh definition. ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.