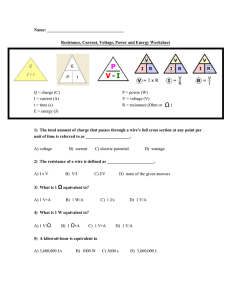
CMOS CIRCUIT TECHNOLOGY
... where k is the number of inputs and C is the equivalent capacitance at the output of the gate ...
... where k is the number of inputs and C is the equivalent capacitance at the output of the gate ...
Low Power Design of Integrated Systems Assoc. Prof. Dimitrios
... Dynamic Power Consumption (2) • For technologies up to 0.35 m, the dynamic consumption is about 80% of the total consumption • Goal ===> reduce dynamic power consumption ...
... Dynamic Power Consumption (2) • For technologies up to 0.35 m, the dynamic consumption is about 80% of the total consumption • Goal ===> reduce dynamic power consumption ...
Electric Current - Wissahickon School District
... Voltage difference- push that causes charges to move- measured in volts (V) For charges to flow, the wire must always be connected in a closed path, or circuit http://www.school-for-champions.com/science/dc.htm ...
... Voltage difference- push that causes charges to move- measured in volts (V) For charges to flow, the wire must always be connected in a closed path, or circuit http://www.school-for-champions.com/science/dc.htm ...
Lecture 14 - Transitors, Gates, and Logic Circuits
... • Discrete states on and off map to voltage levels +5V and 0V on an analog device • Connect these devices to perform logical ...
... • Discrete states on and off map to voltage levels +5V and 0V on an analog device • Connect these devices to perform logical ...
Circuits1 – VIR
... • Air is conductive…if you have enough voltage to push the electrons through it (i.e. – lightening) • 10,000 volts might not hut you…but if it pushes just 1 amp of current through your heart it can be fatal • If the circuit has no resistance, it’s called a short circuit and infinite current will flo ...
... • Air is conductive…if you have enough voltage to push the electrons through it (i.e. – lightening) • 10,000 volts might not hut you…but if it pushes just 1 amp of current through your heart it can be fatal • If the circuit has no resistance, it’s called a short circuit and infinite current will flo ...
Document
... Unlike a multiplexer that selects one individual data input line and then sends that data to a single output line or switch, a Digital Encoder more commonly called a Binary Encoder takes ALL its data inputs one at a time and then converts them into a single encoded output. ...
... Unlike a multiplexer that selects one individual data input line and then sends that data to a single output line or switch, a Digital Encoder more commonly called a Binary Encoder takes ALL its data inputs one at a time and then converts them into a single encoded output. ...
Bias Current Effect on Gain of a CMOS OTA
... In the recent years, efforts have been made to reduce supply voltage of integrated circuits. Research efforts also have been made in reducing total power consumption of VLSI systems [1]. The realization of low voltage, high gain and low power amplifiers requires efficient circuit design techniques [ ...
... In the recent years, efforts have been made to reduce supply voltage of integrated circuits. Research efforts also have been made in reducing total power consumption of VLSI systems [1]. The realization of low voltage, high gain and low power amplifiers requires efficient circuit design techniques [ ...
6.2.6 Transistors
... Transistors Parts of the Transistor The First Transistor Transistors as Amplifiers Transistors as Switches Night Light Circuit ...
... Transistors Parts of the Transistor The First Transistor Transistors as Amplifiers Transistors as Switches Night Light Circuit ...
Transistors - Eisenhower
... Transistors Parts of the Transistor The First Transistor Transistors as Amplifiers Transistors as Switches Night Light Circuit ...
... Transistors Parts of the Transistor The First Transistor Transistors as Amplifiers Transistors as Switches Night Light Circuit ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.